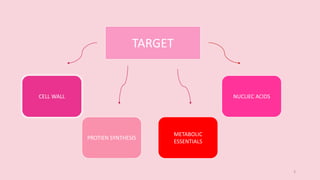
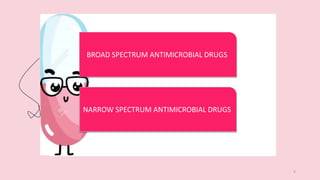
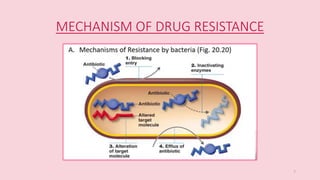
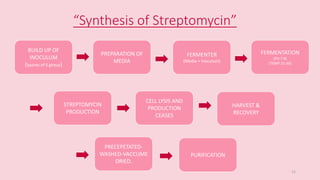
This document discusses antimicrobials and their uses. It defines antimicrobials as substances that reduce microbes like bacteria and molds. Antimicrobial drugs are classified based on the microorganisms they target or their function. Broad spectrum antimicrobials affect many types of microbes while narrow spectrum drugs target specific microbes. The document also discusses antimicrobial resistance and how microbes develop resistance. It provides streptomycin as an example antimicrobial drug, describing its discovery, mode of action in inhibiting protein synthesis, and production process. Streptomycin is derived from bacteria and was an early antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis. The document concludes that while antimicrobials are useful, their overuse can lead to increased antimicrobial resistance in micro