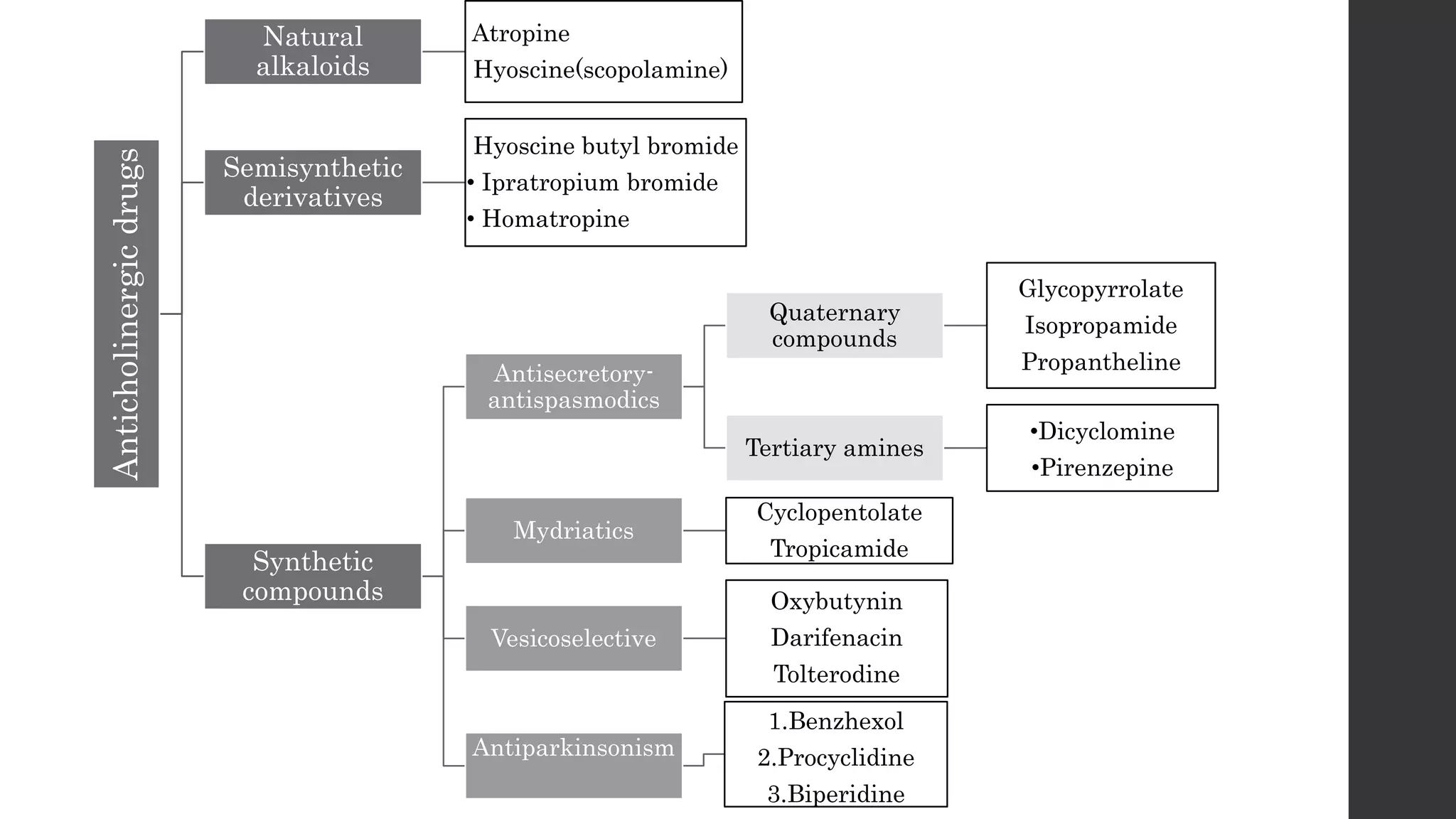
Anticholinergic drugs work by competitively blocking acetylcholine receptors. They are classified as natural alkaloids like atropine, semisynthetic derivatives, and synthetic compounds. They have various therapeutic uses such as treating peptic ulcers, intestinal cramps, urinary incontinence, and respiratory disorders like asthma. Common side effects include dry mouth, blurred vision, flushed skin, excitement, and delirium. Neuromuscular blockers and ganglion blockers are also anticholinergic drugs that work by blocking nicotinic receptors at neuromuscular junctions or autonomic ganglia respectively.