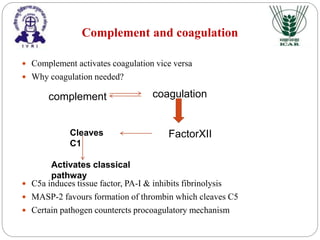
The document discusses the crosstalk between the complement system and other immune systems. It outlines how the complement system interacts and regulates toll-like receptors, B cell and T cell immunity, tissue factor production, and lipid metabolism. Some key points are that complement pathways regulate TLR-induced cytokine production in macrophages and dendritic cells. Complement components like C3a and C5a are also essential for optimal CD4+ T cell and antibody responses. The complement system also activates coagulation and promotes processes like bone remodeling, tissue repair, and adipocyte lipid clearance through receptors on various cell types.