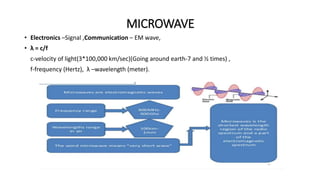
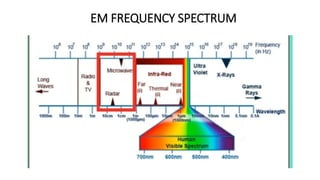
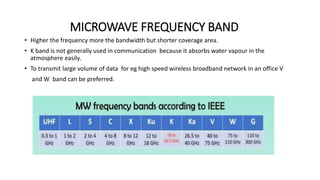
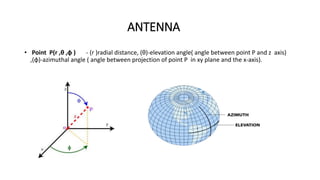
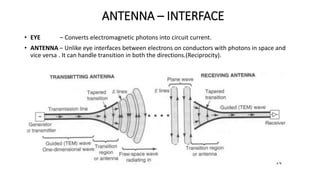
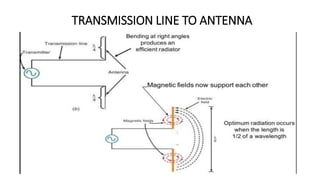
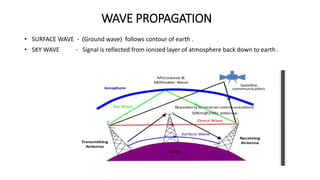
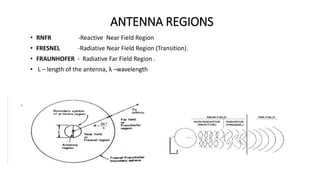
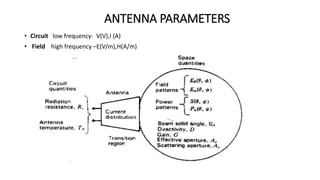
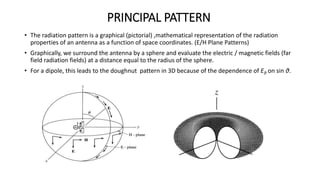
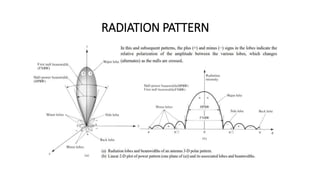
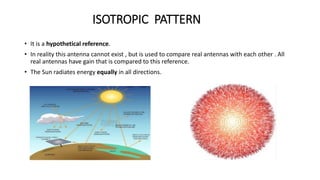
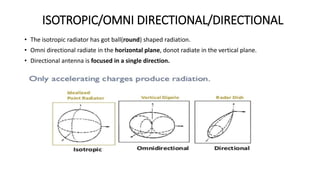
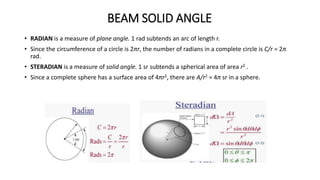
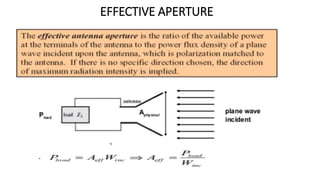
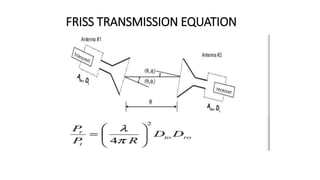
The document outlines an upcoming virtual faculty development programme on antennas and microwave engineering from June 22-26, 2020. It will consist of 5 units covering topics such as introduction to microwave systems and antennas, radiation mechanisms, antenna arrays and applications, passive and active microwave devices, and microwave design principles. Each unit will be presented by a different professor. The agenda includes introductions to key concepts like engineering, microwaves, frequency bands, applications, antennas, and parameters. [/SUMMARY]