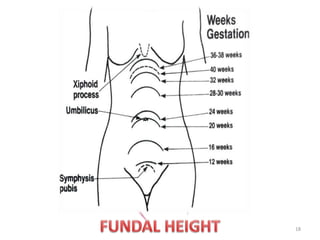
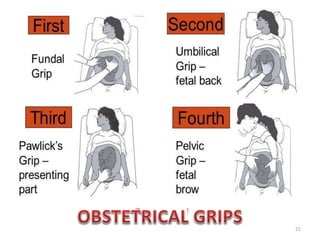
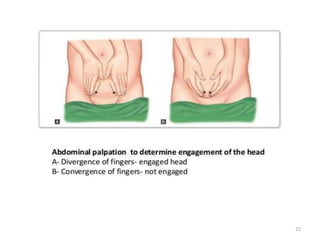
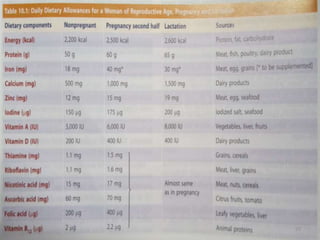
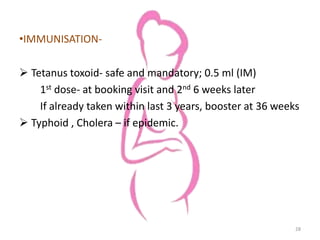
This document provides information about antenatal care. It discusses the objectives, process, and components of antenatal visits including history taking, examinations, investigations, diet and lifestyle advice, immunizations, common complaints and their management, and some key homeopathic medicines. The goals of antenatal care are to ensure a healthy pregnancy, mother, and baby and to address any risks or complications at the earliest opportunity through regular monitoring and education.