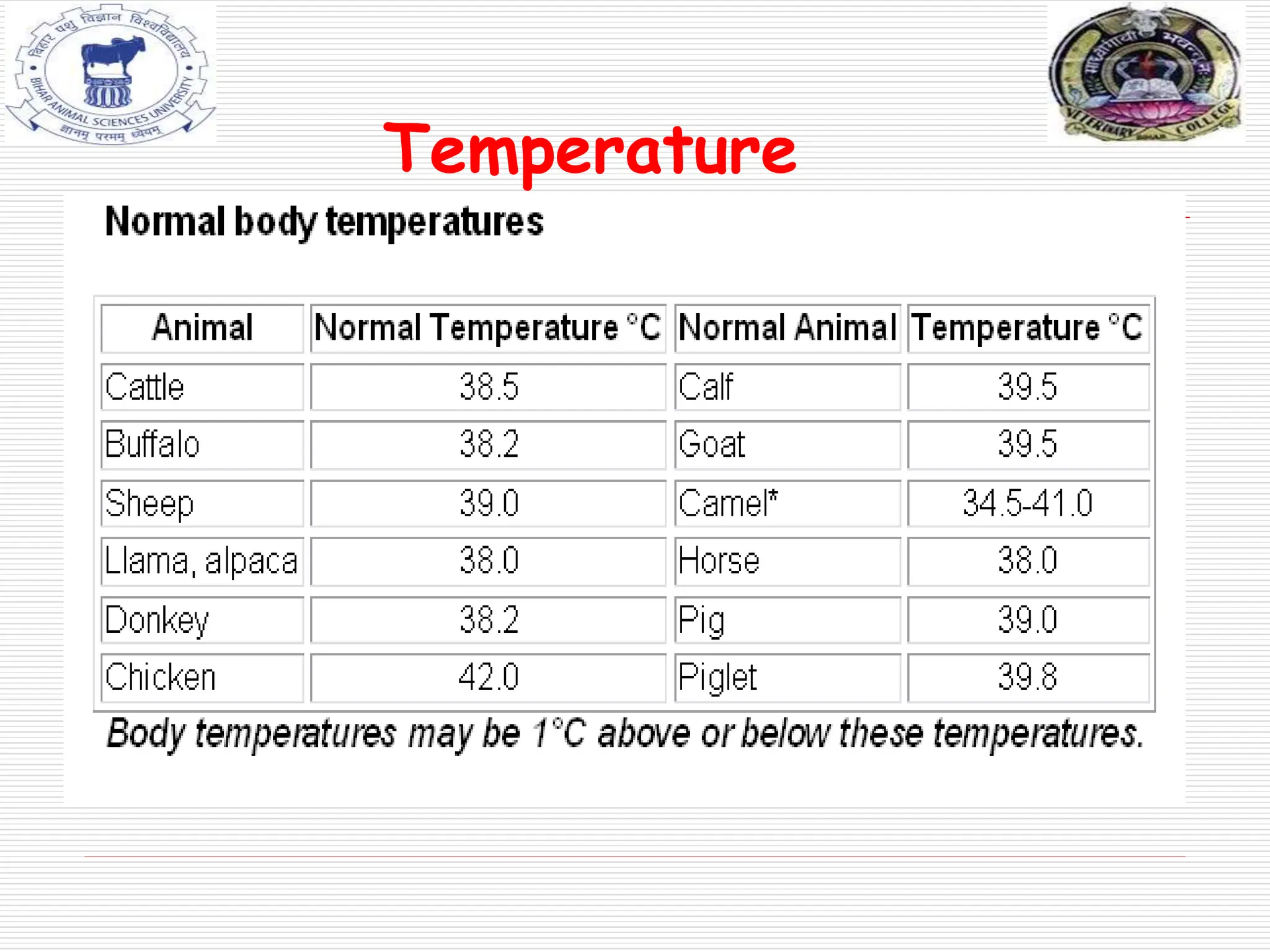
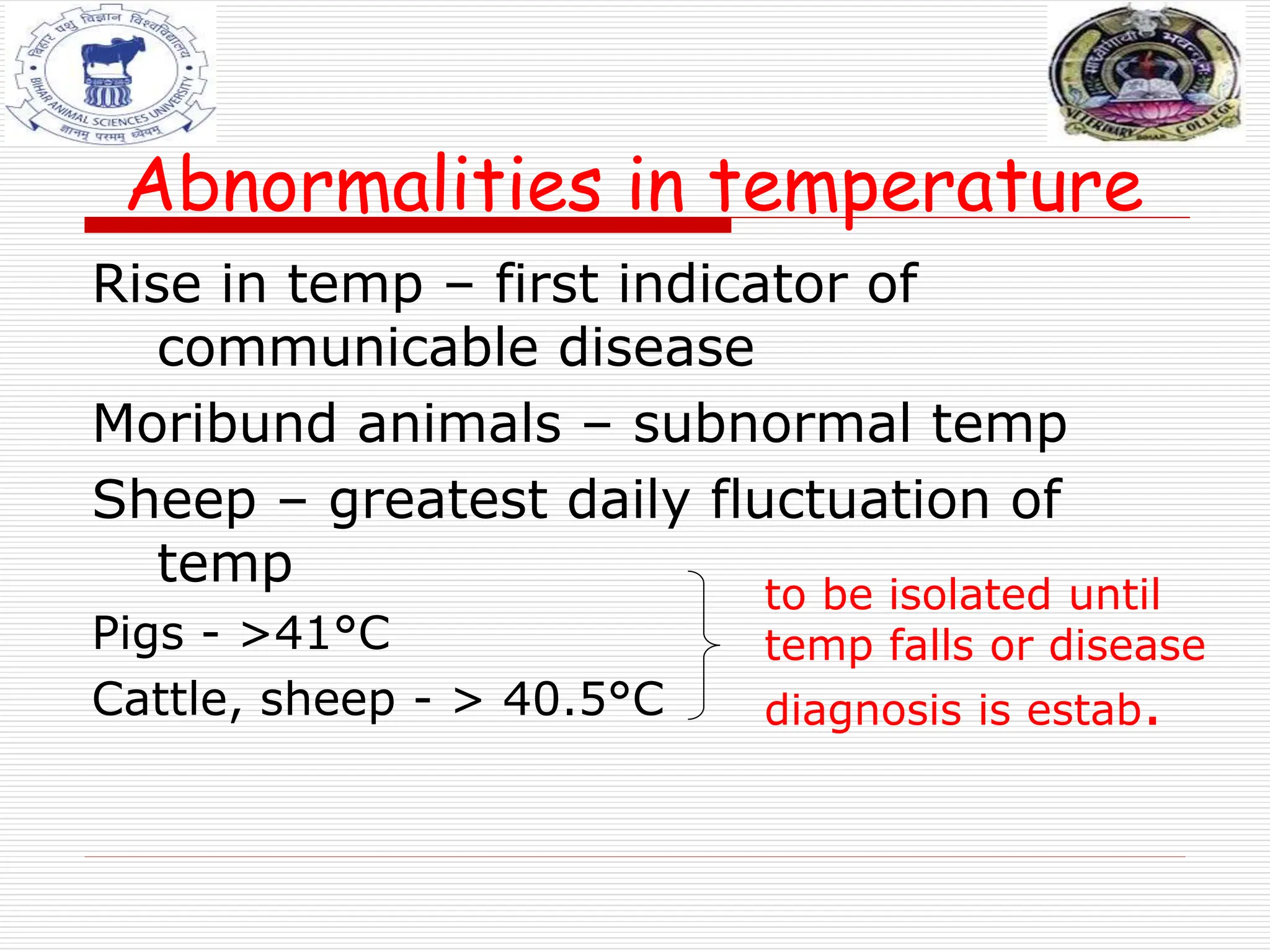
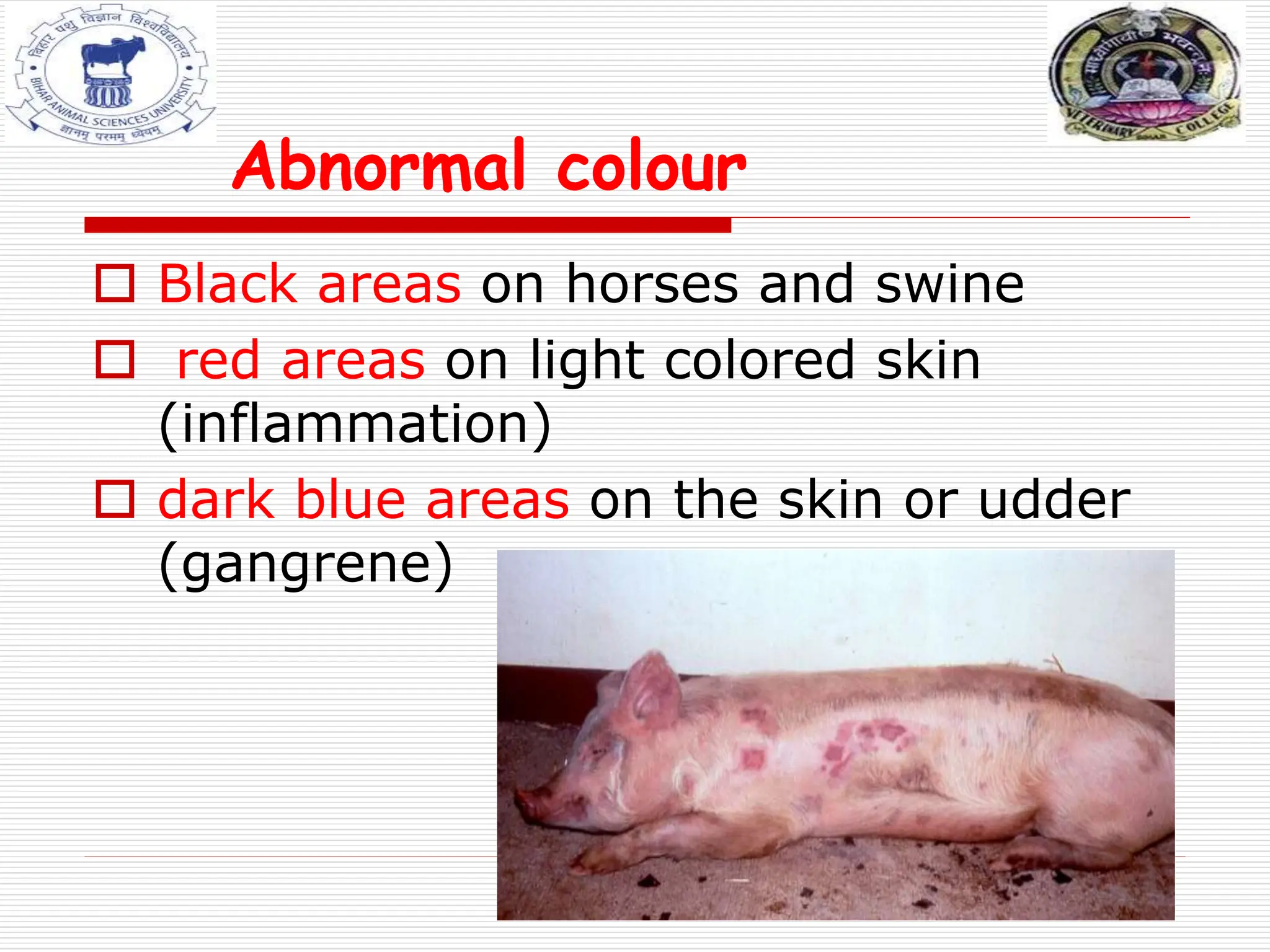
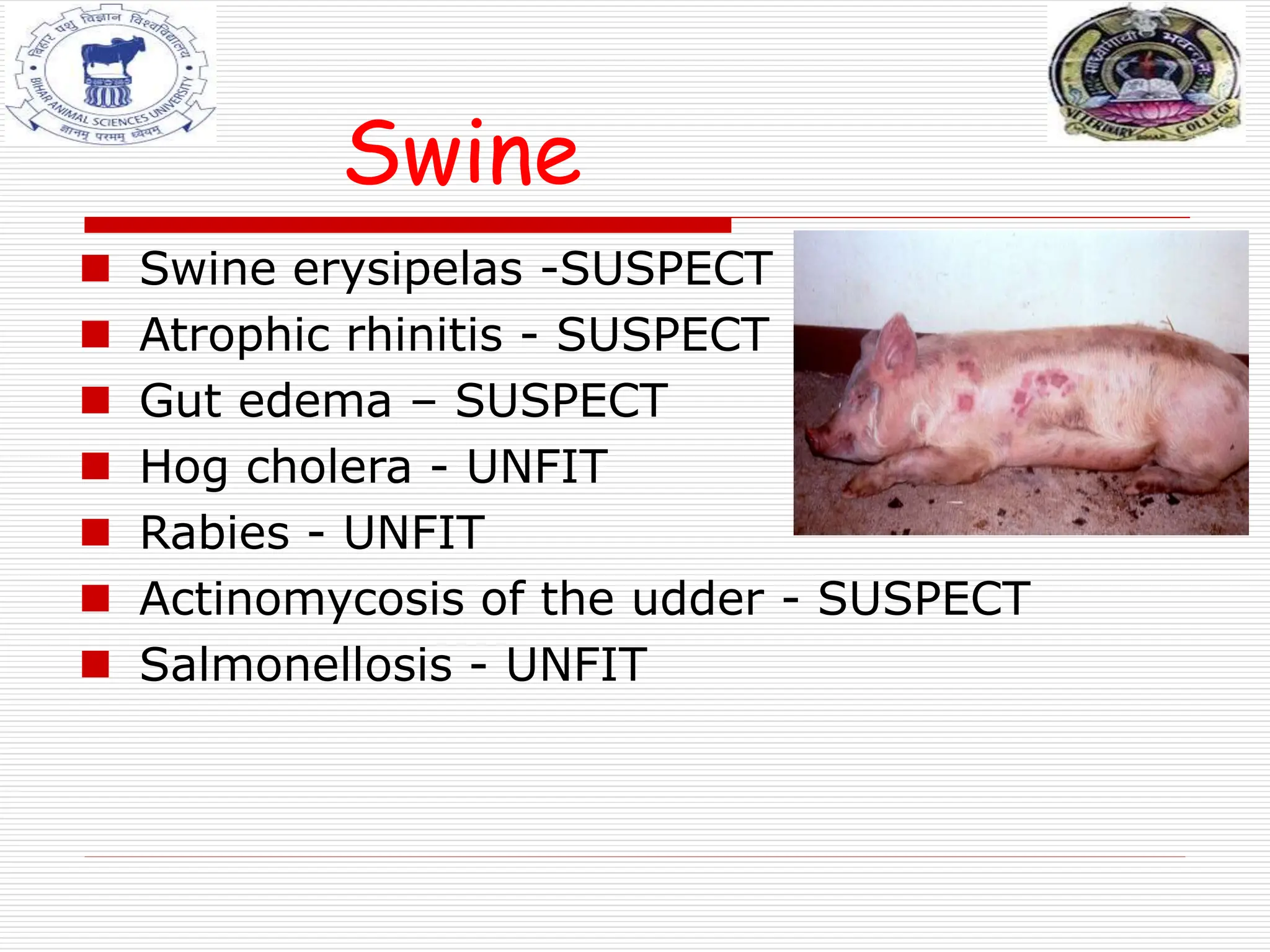
The document discusses ante-mortem inspection, which involves examining live animals before slaughter to screen for disease. A veterinarian examines each animal within 24 hours of slaughter, checking for abnormalities in behavior, appearance, temperature, and other signs. Animals found with diseases are either detained for further examination, designated for casualty slaughter if suffering chronic issues, or deemed unfit for slaughter and condemned. The inspection aims to ensure meat is safe for human consumption and prevent spread of disease.