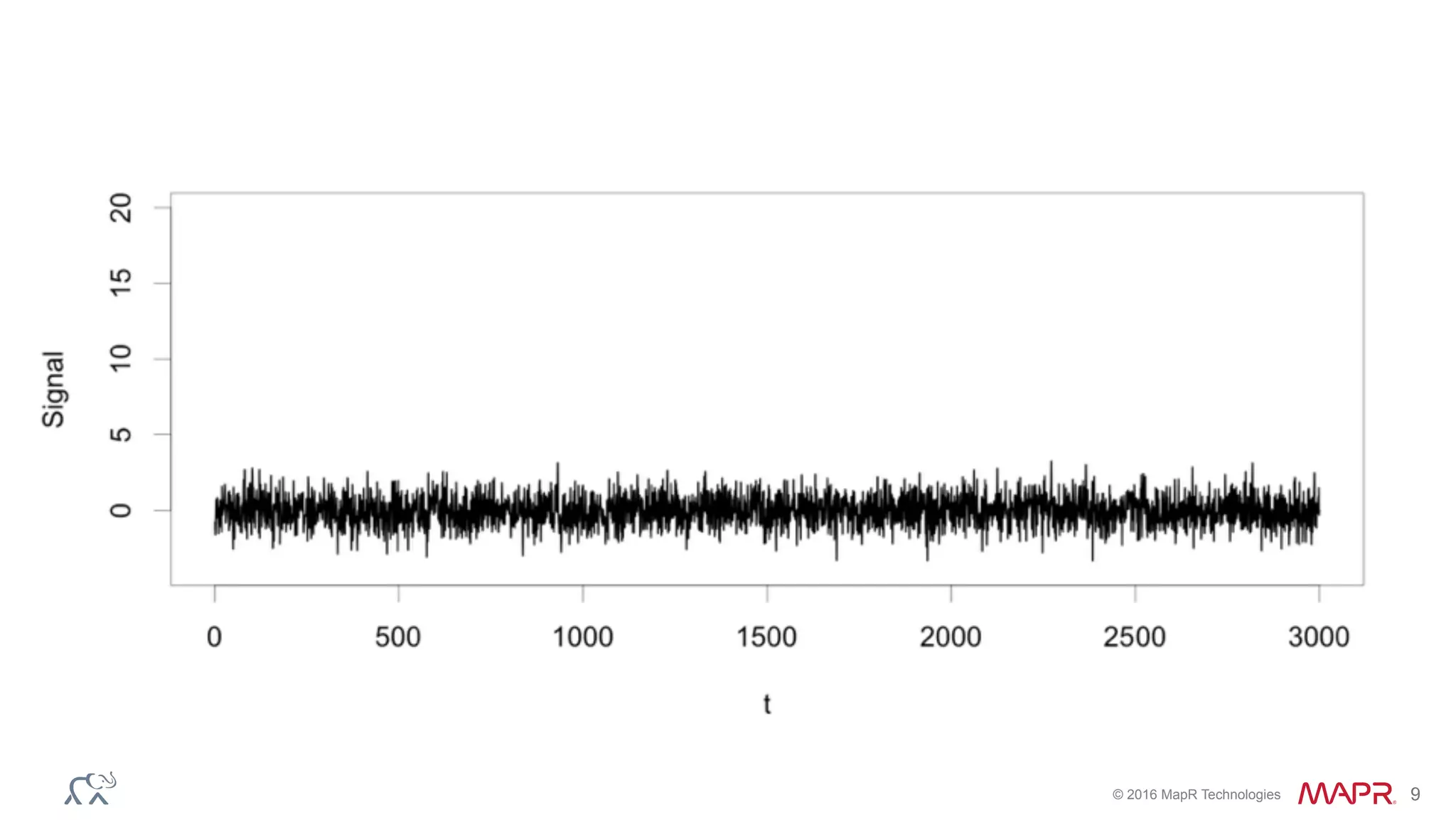
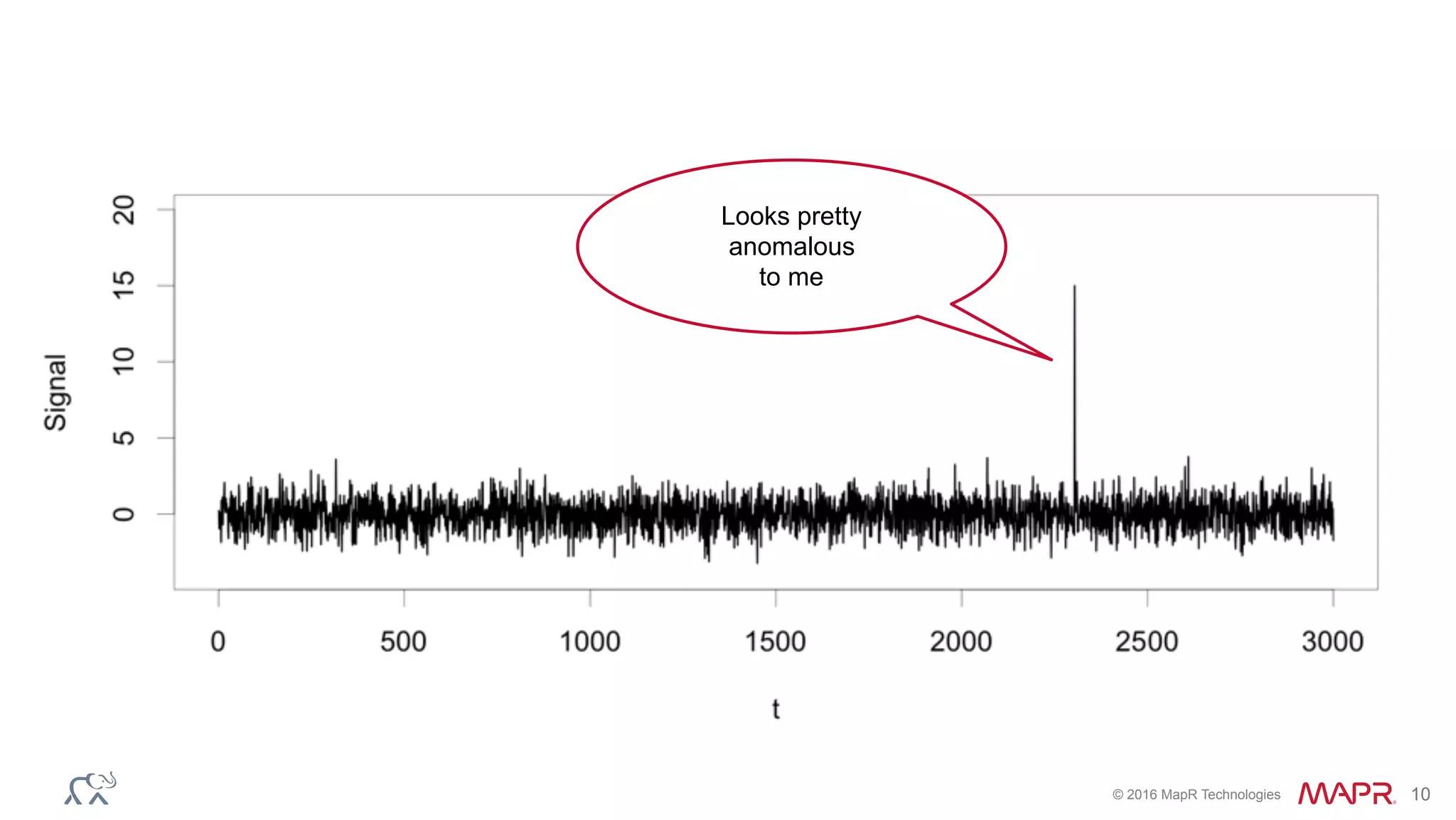
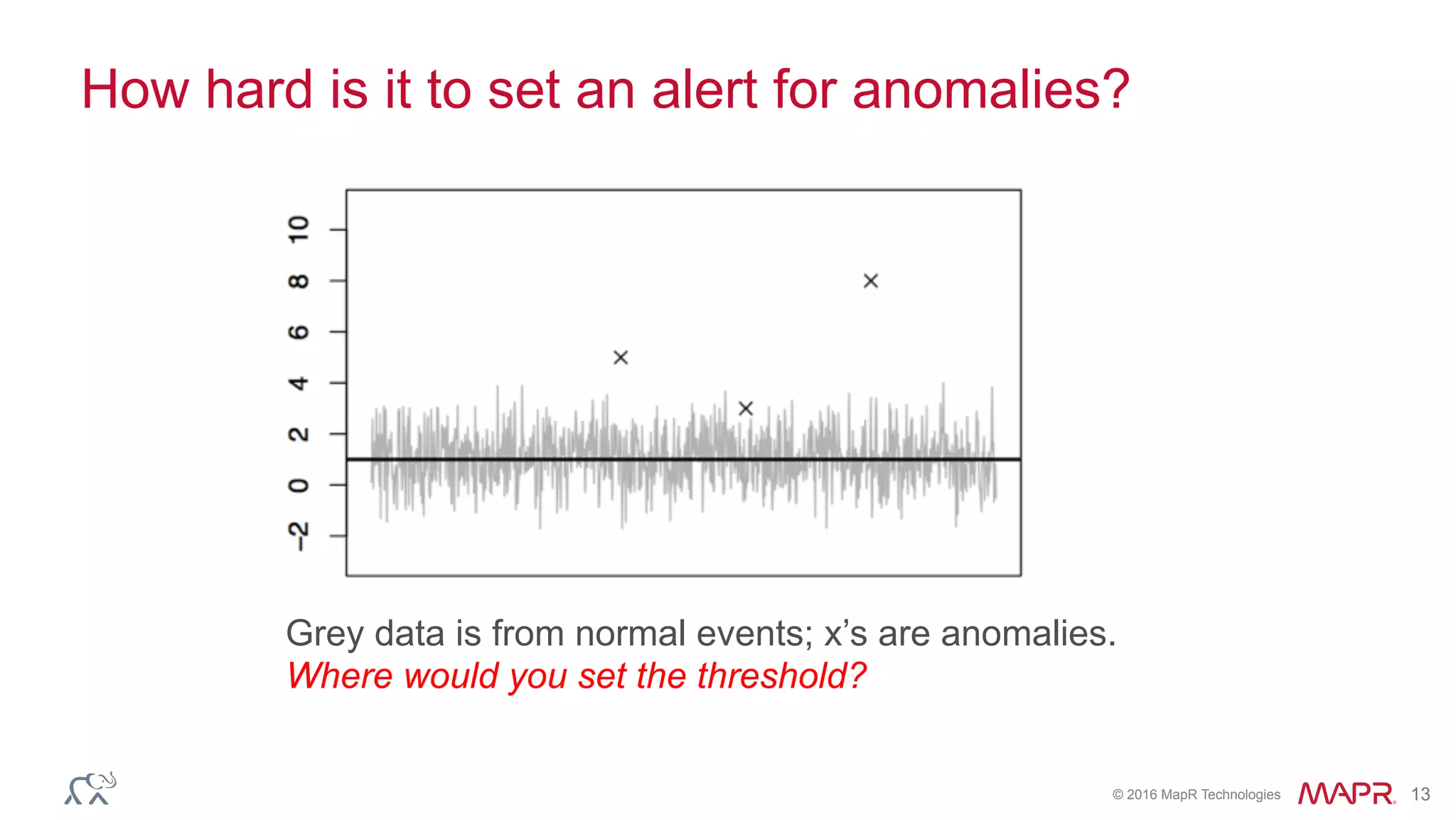
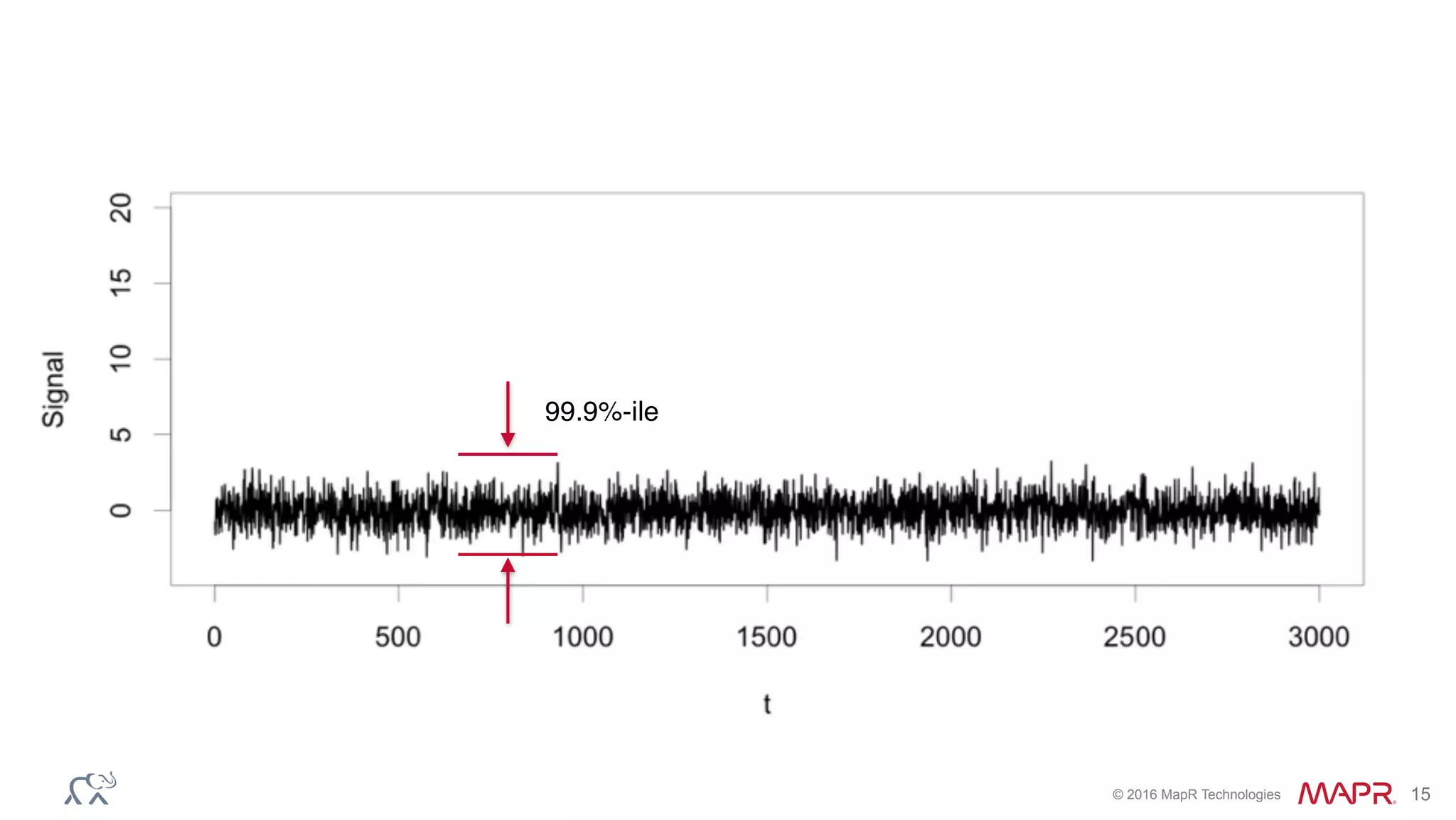
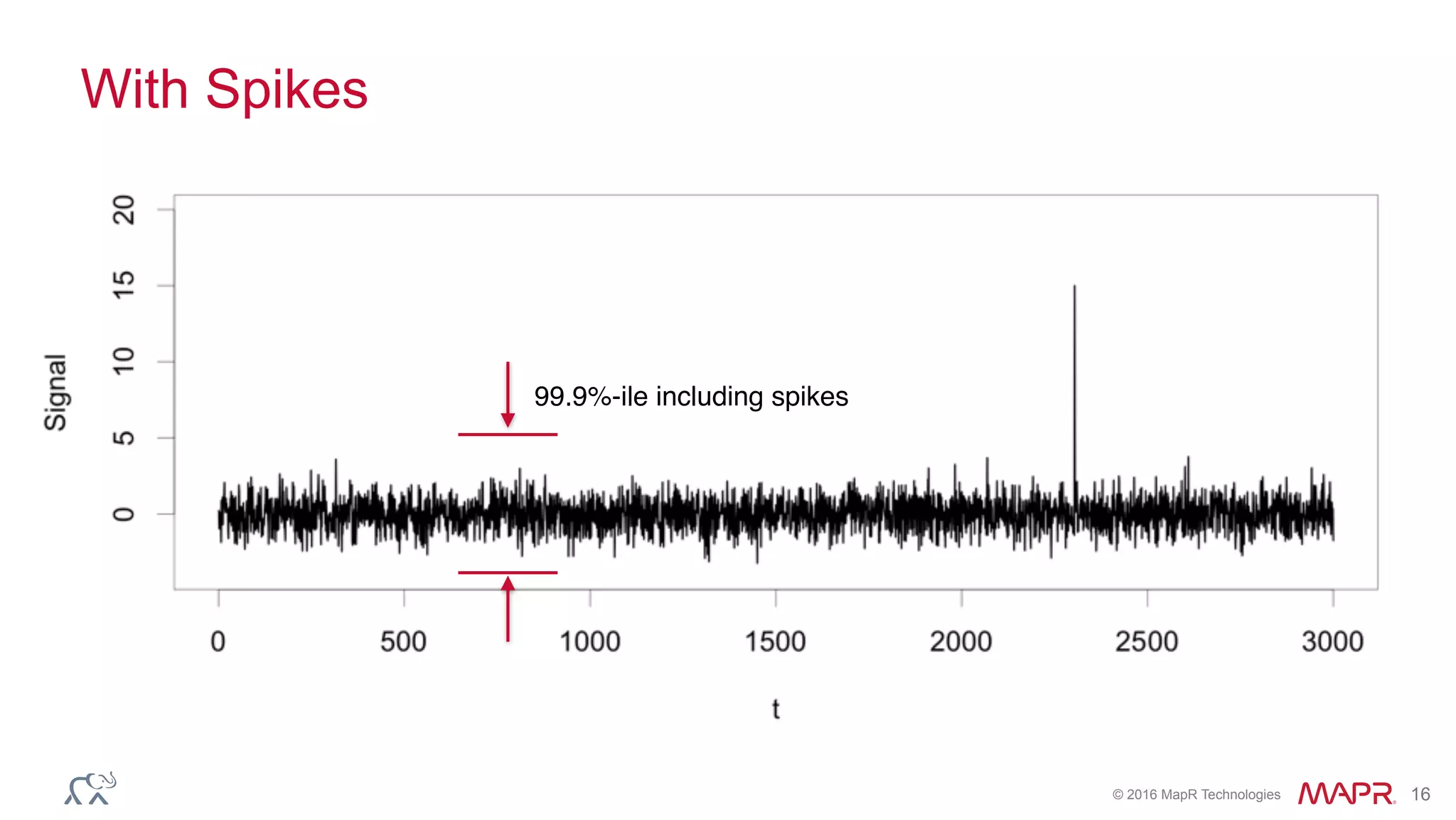
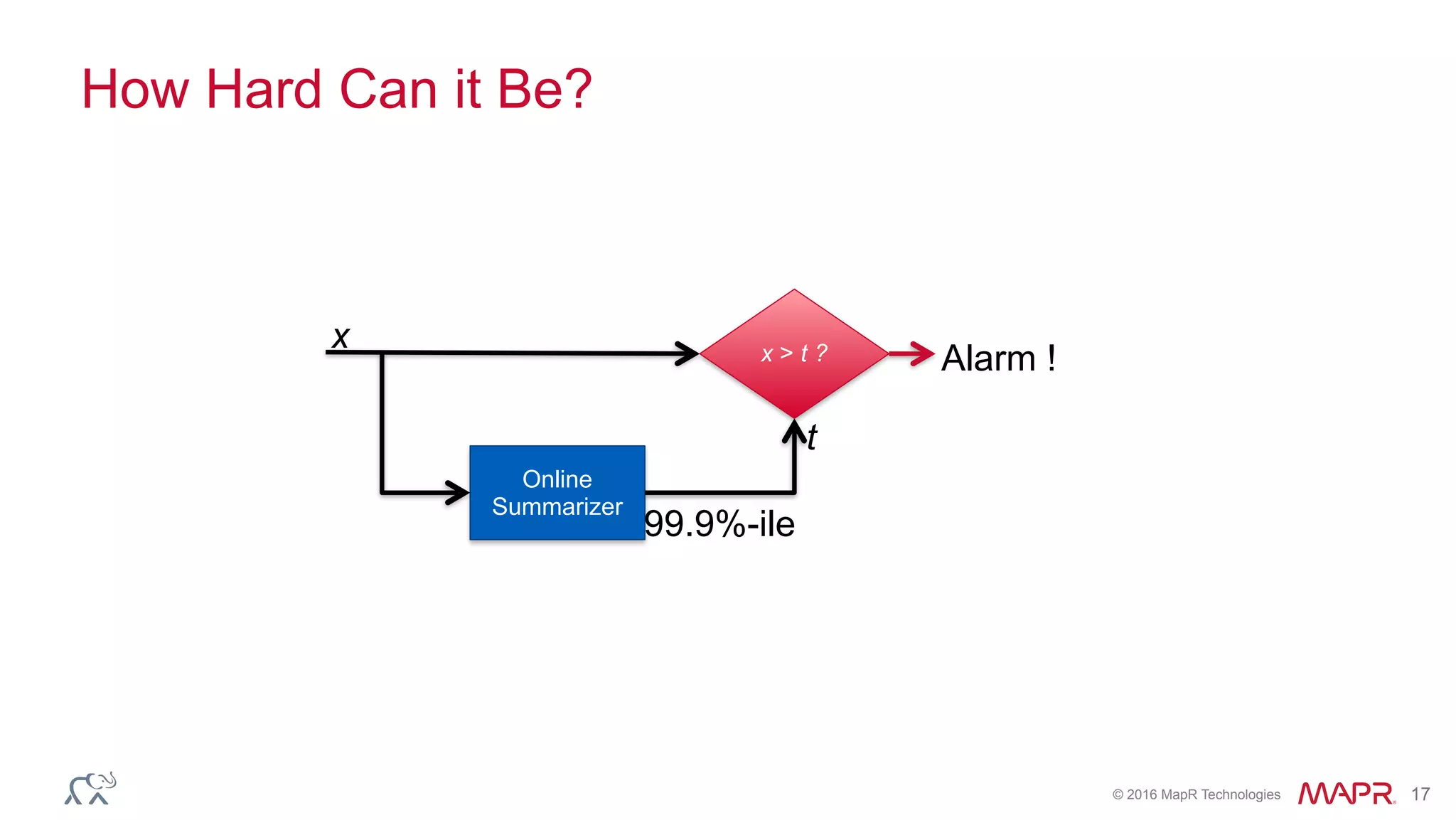
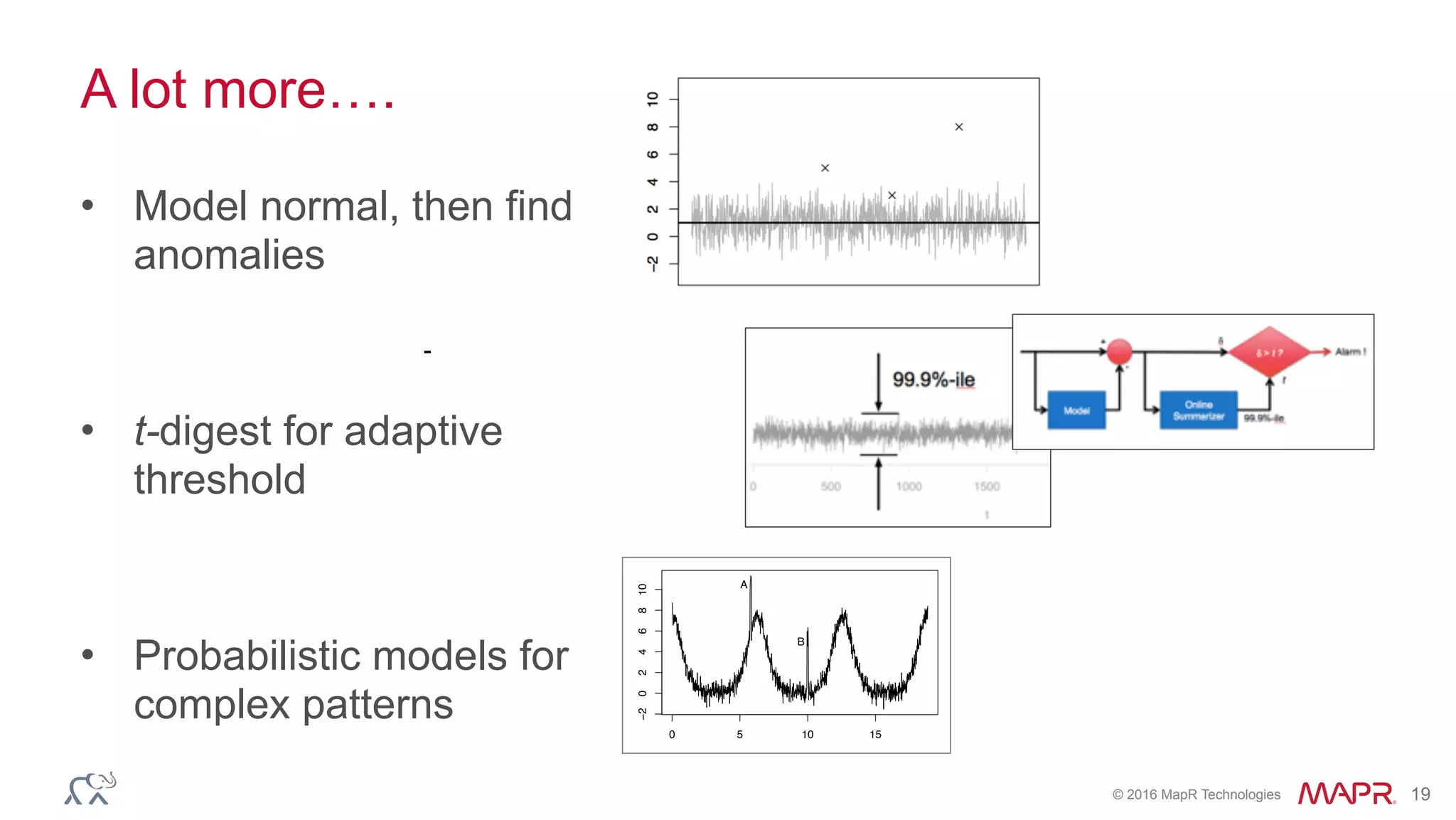
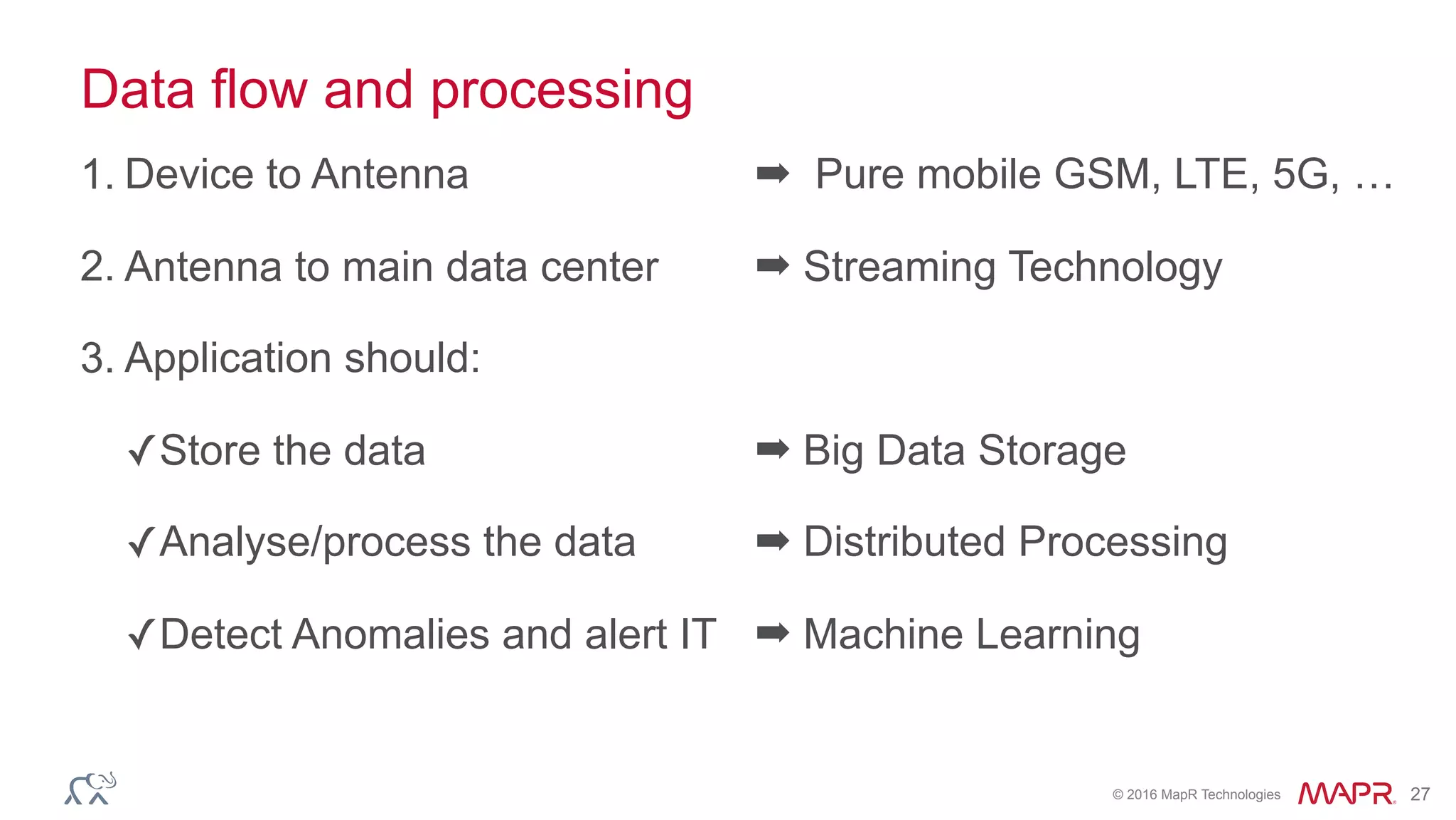
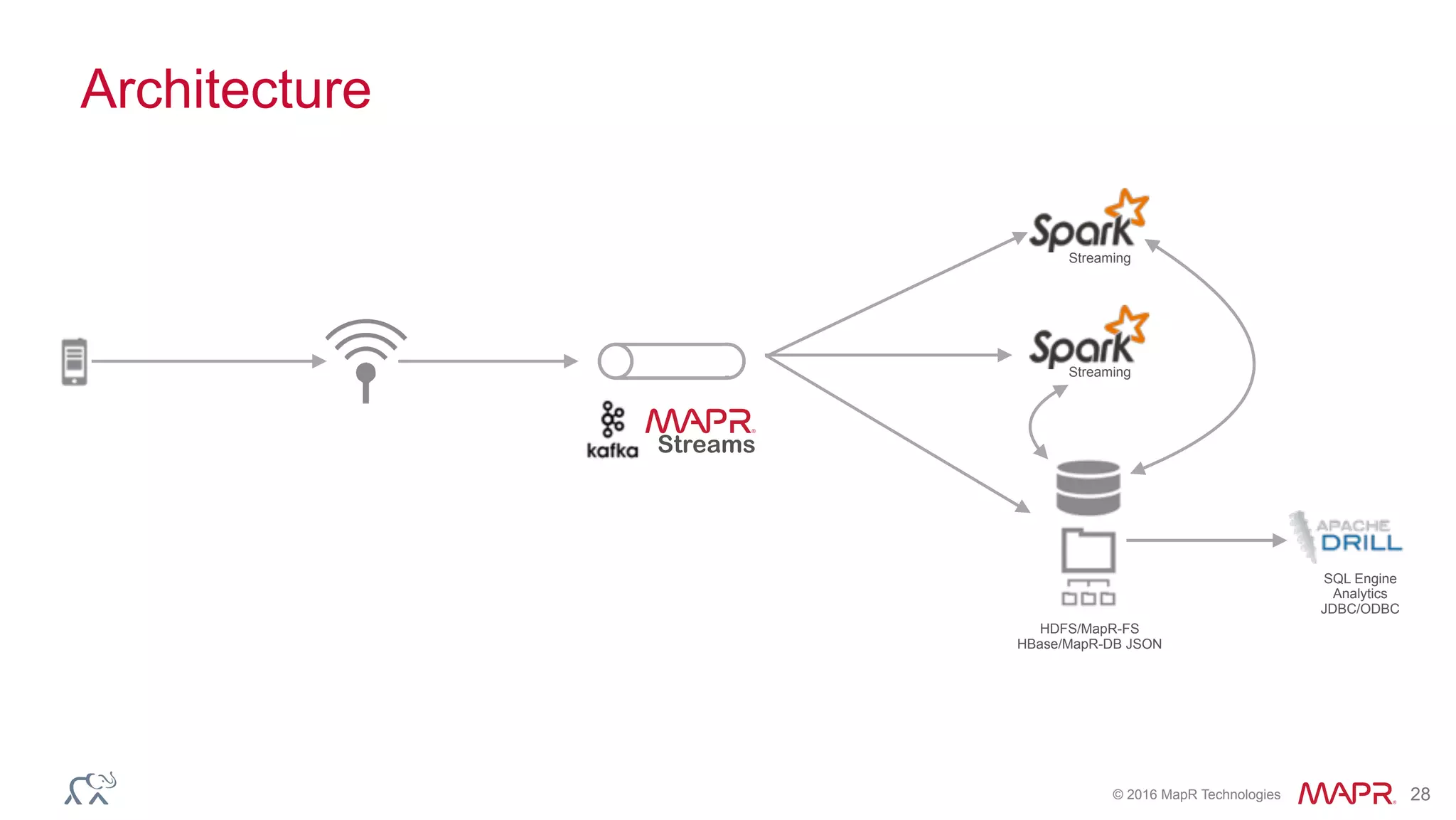
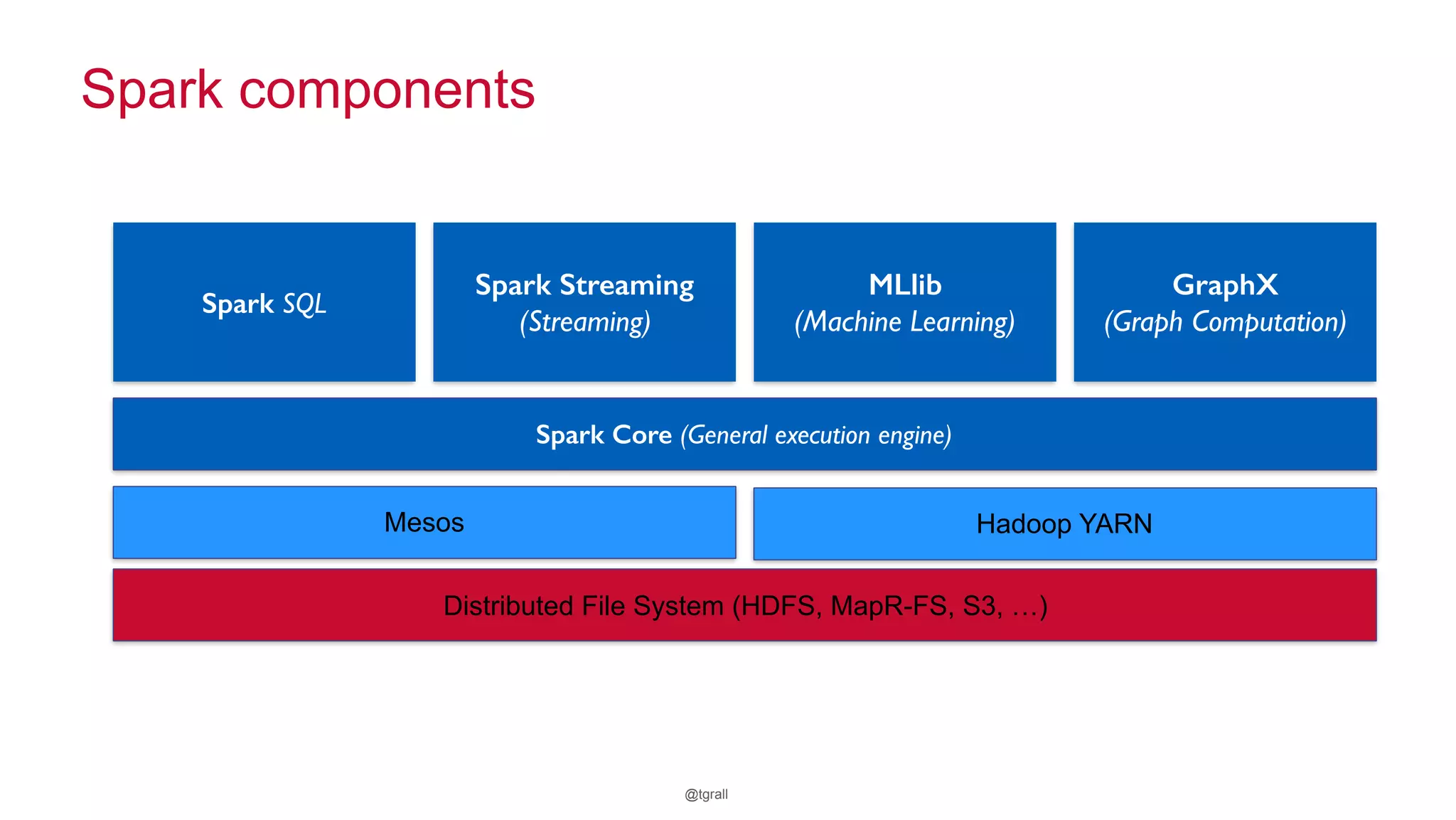
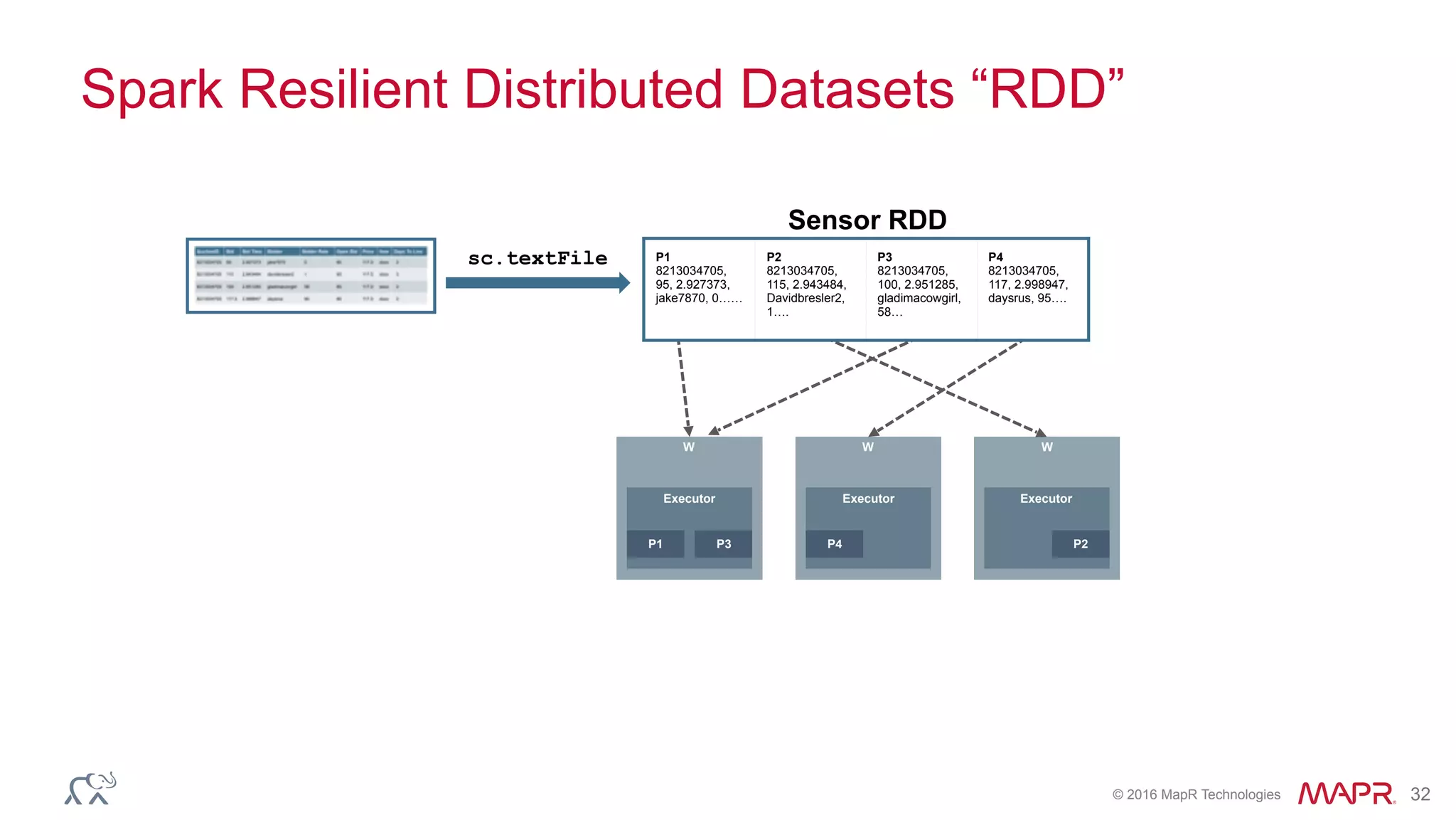
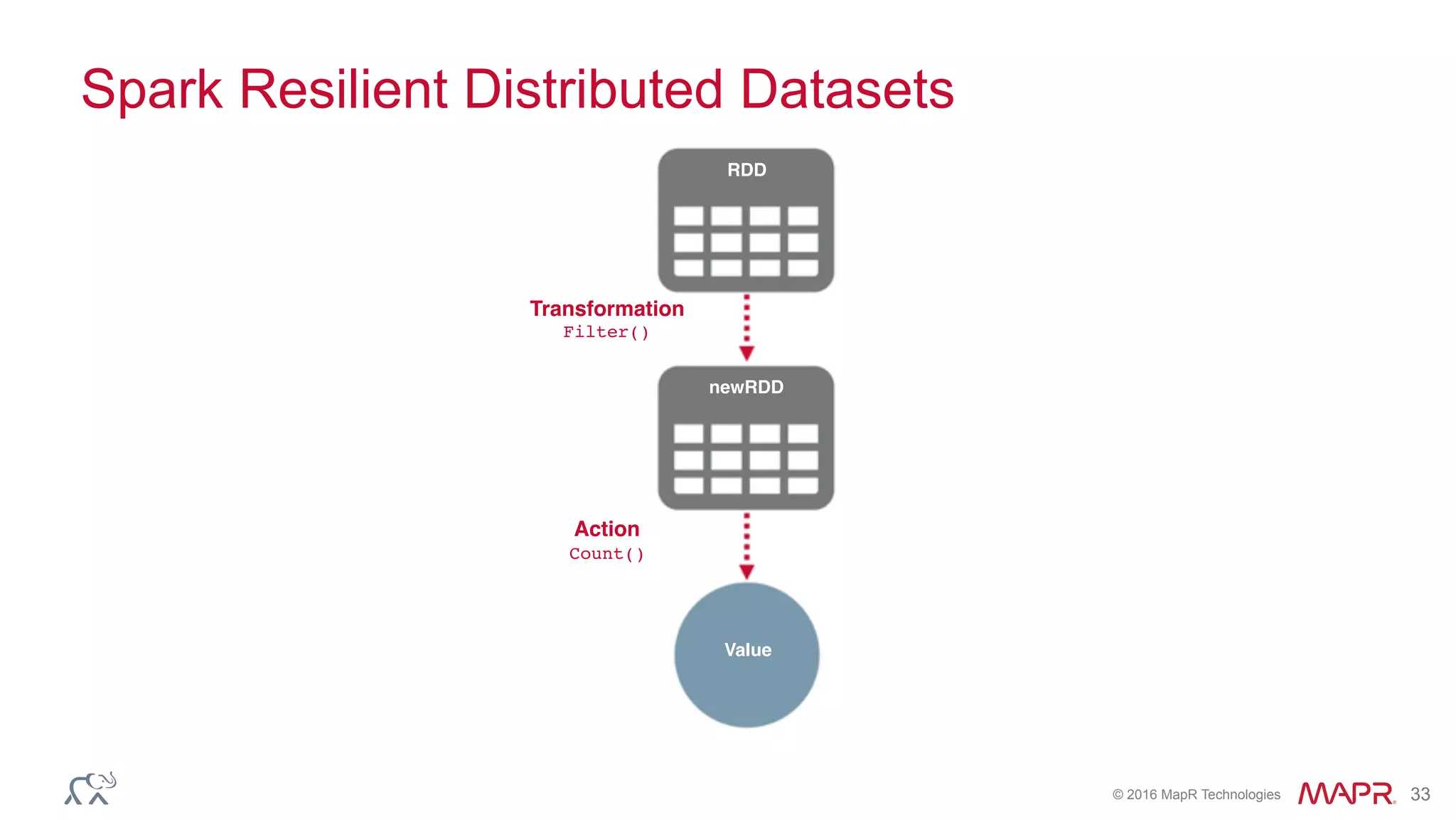
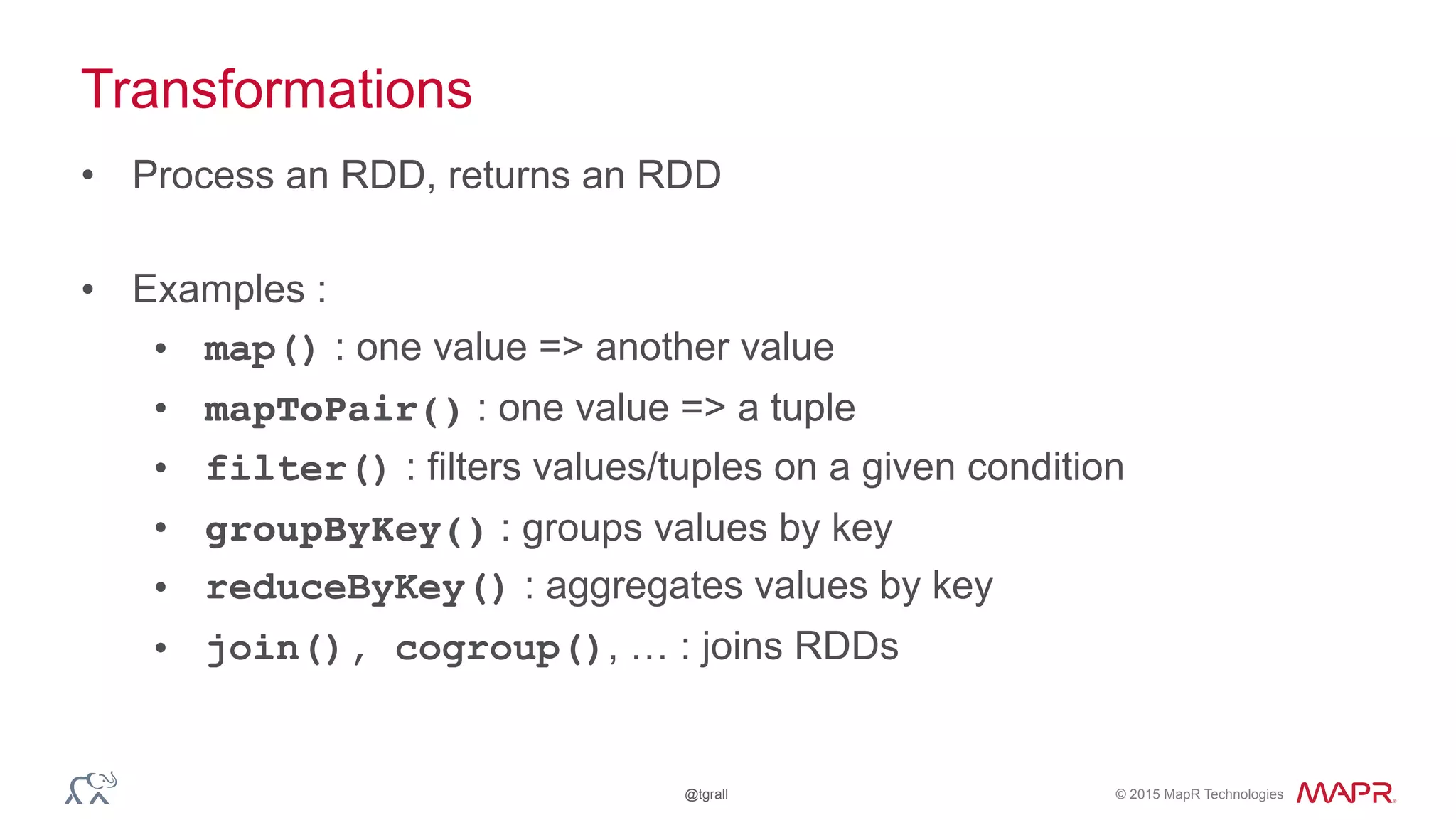
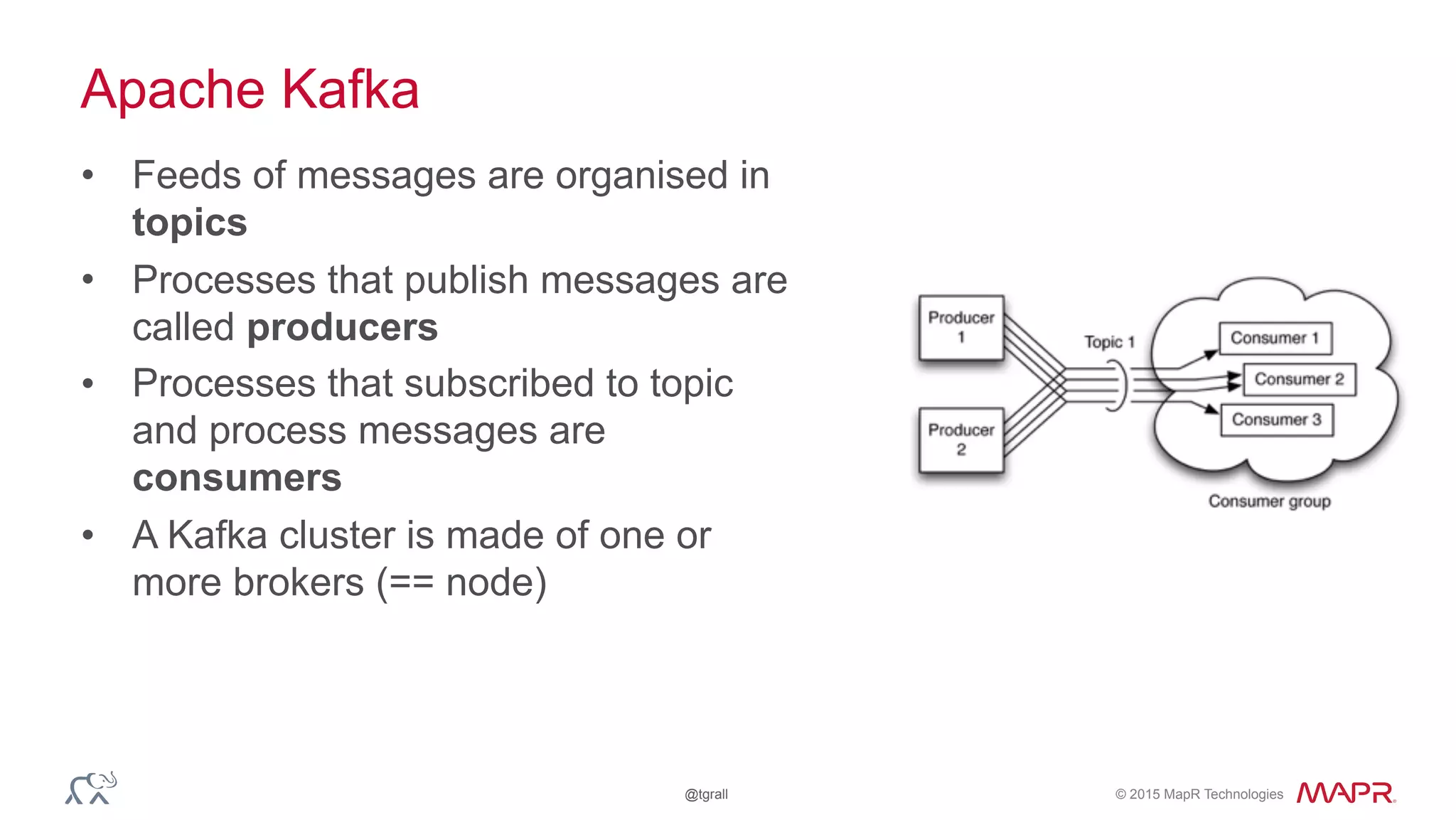
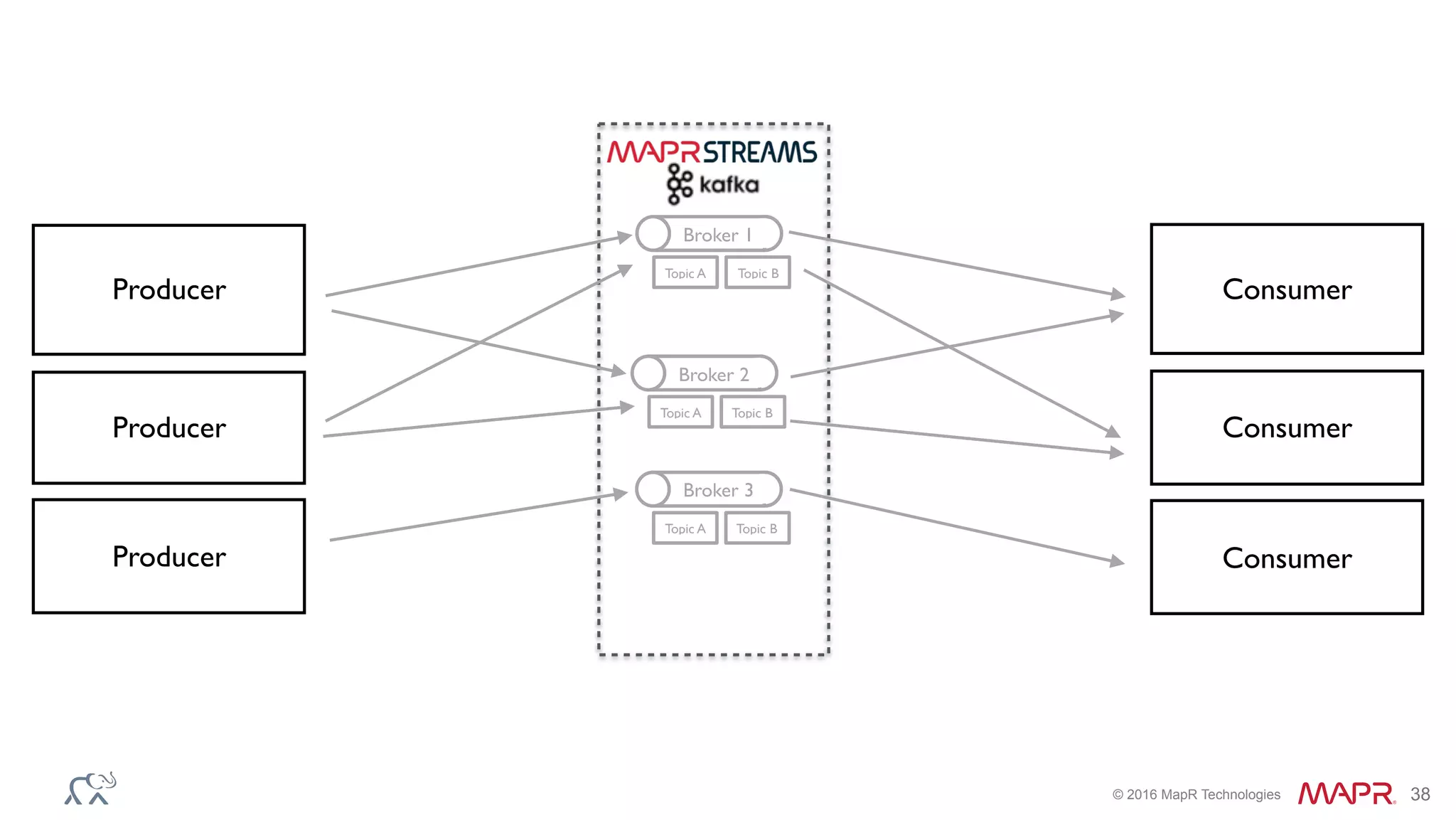
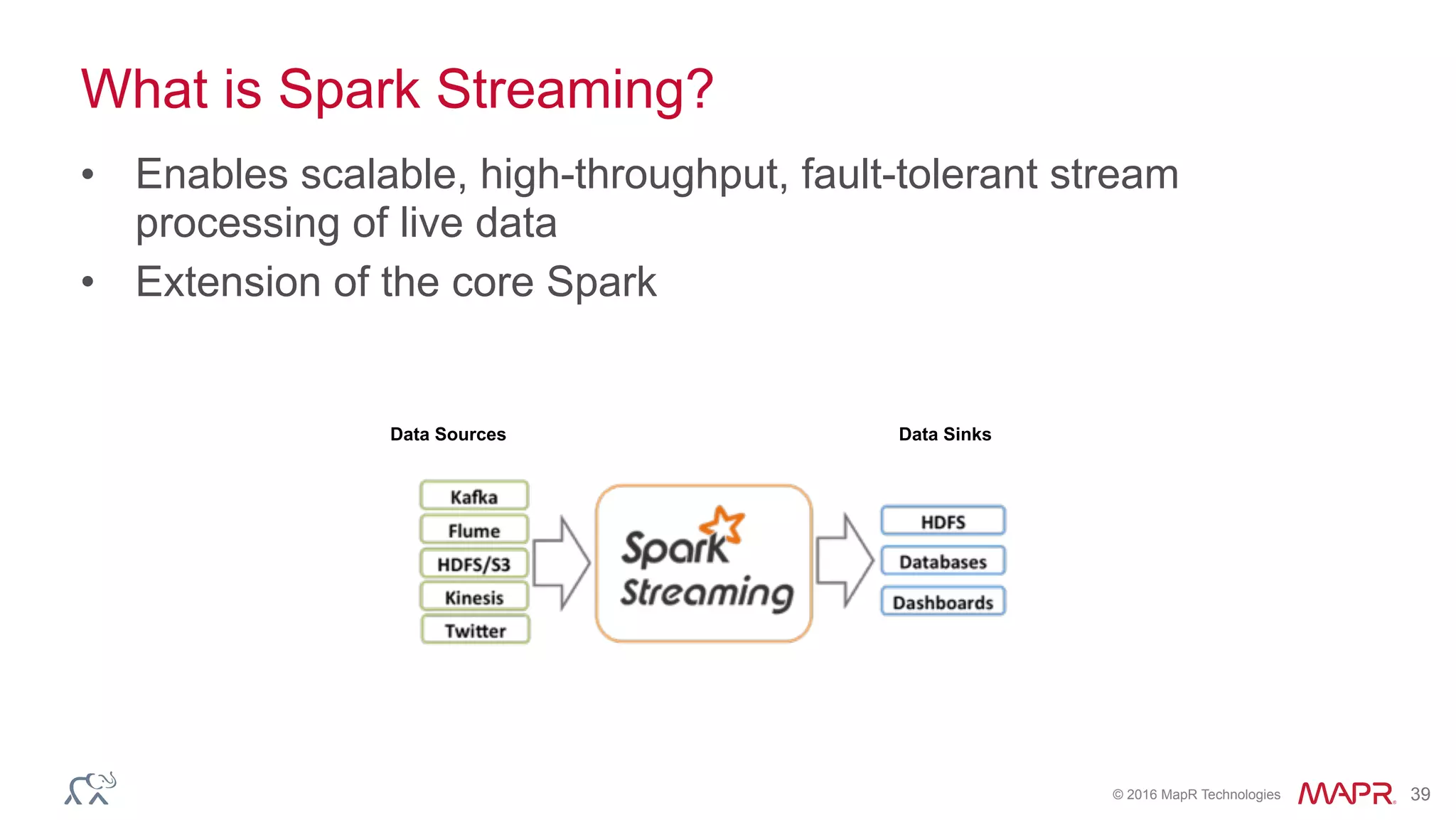
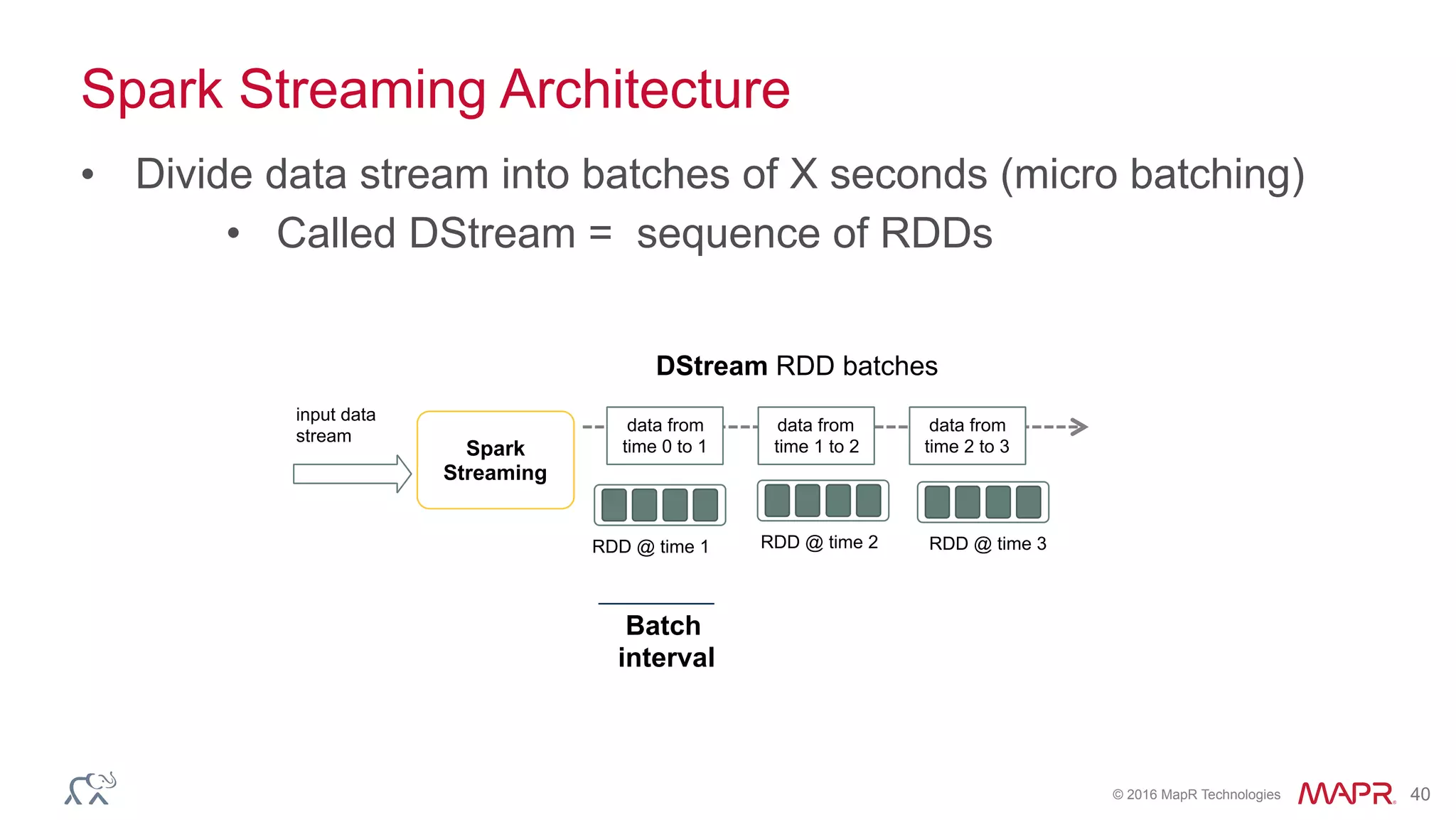
The document discusses anomaly detection in telecommunications using Spark, detailing its importance, methodologies, and application use cases. It outlines the process of defining 'normal' behavior, setting adaptive thresholds for alerts, and constructing a streaming application to analyze real-time data. Key technologies mentioned include Apache Kafka, Spark Streaming, and various machine learning techniques to effectively detect anomalies.