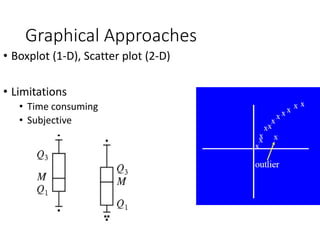
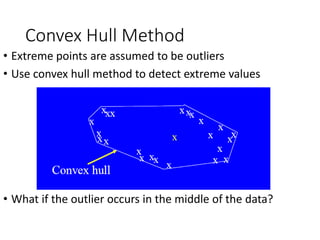
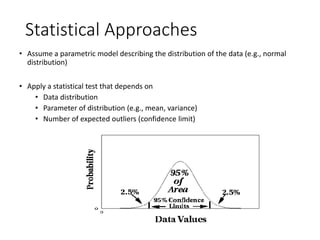
Anomaly detection identifies data points that significantly differ from the rest of the dataset and can involve various methods such as unsupervised techniques and graphical approaches. Applications range from credit card fraud detection to network intrusion detection, although there are challenges in validation and determining the number of outliers. Different methods include statistical approaches, distance-based techniques, and graphical methods, each with its own limitations.