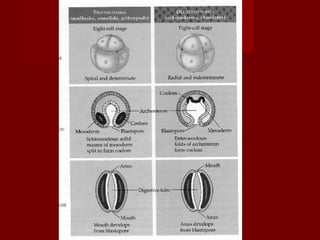
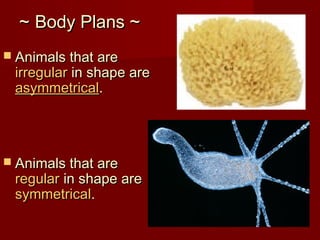
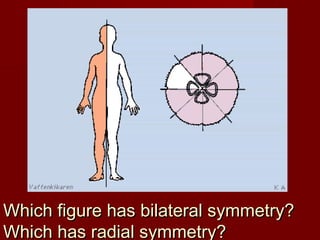
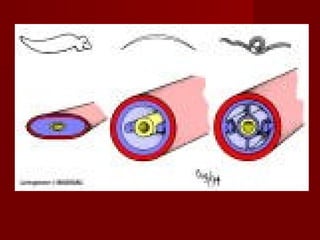
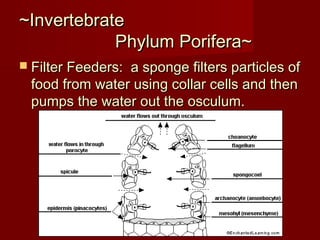
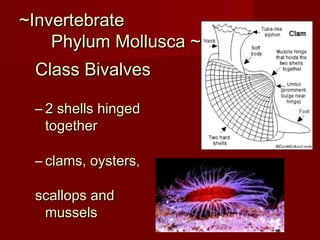
The document describes key characteristics of Kingdom Animalia. Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that lack cell walls. They have nervous systems and locomotion to obtain food as heterotrophs. Most animals develop from a zygote into a gastrula with three germ layers - ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm. Animals are also classified based on their body plan, symmetry, development of mouth/anus, and presence of coelom. The major invertebrate phyla include porifera, cnidaria, platyhelminthes, nematoda, mollusca, annelida, echinodermata, arthropoda and their characteristics are described