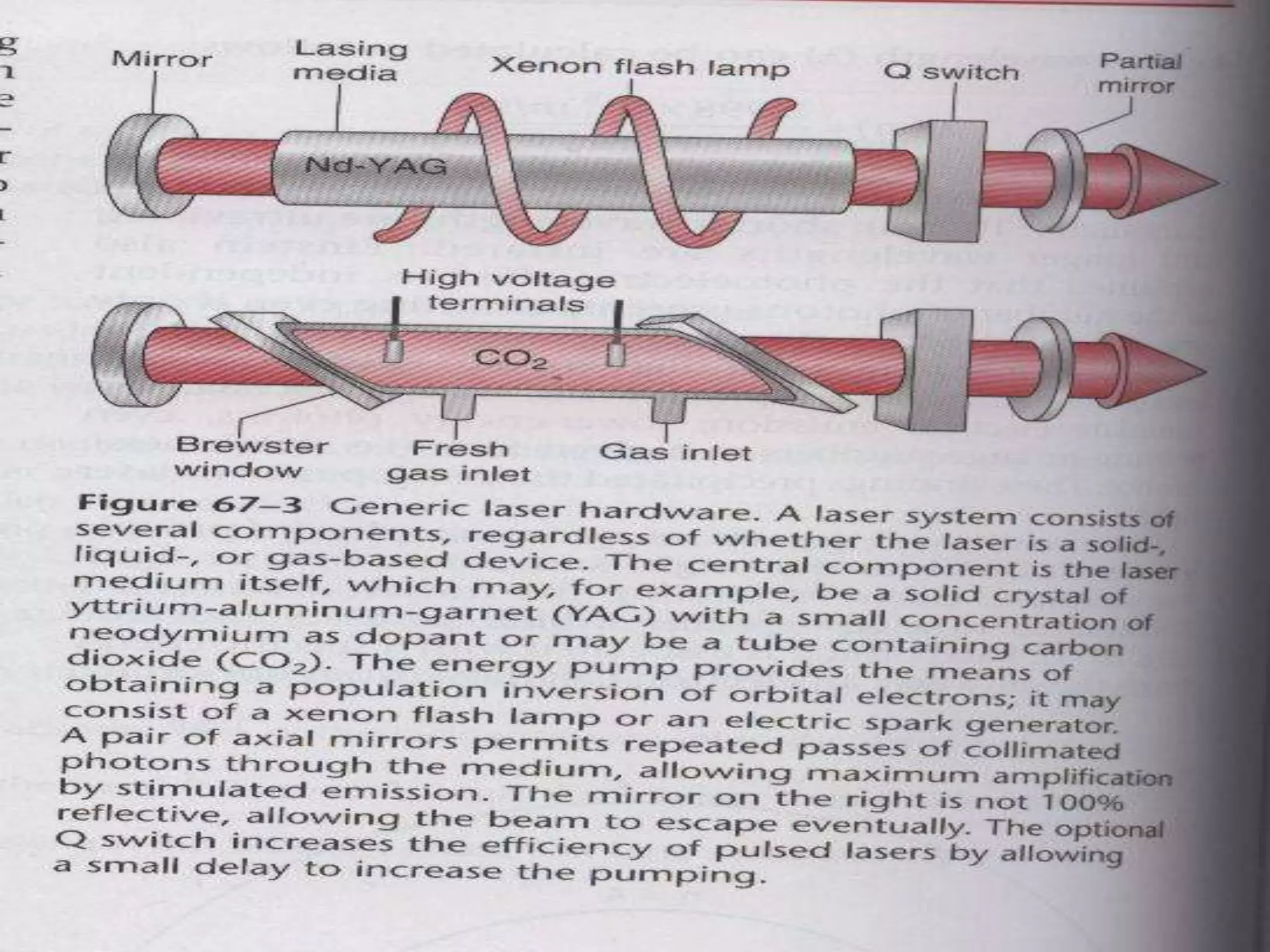
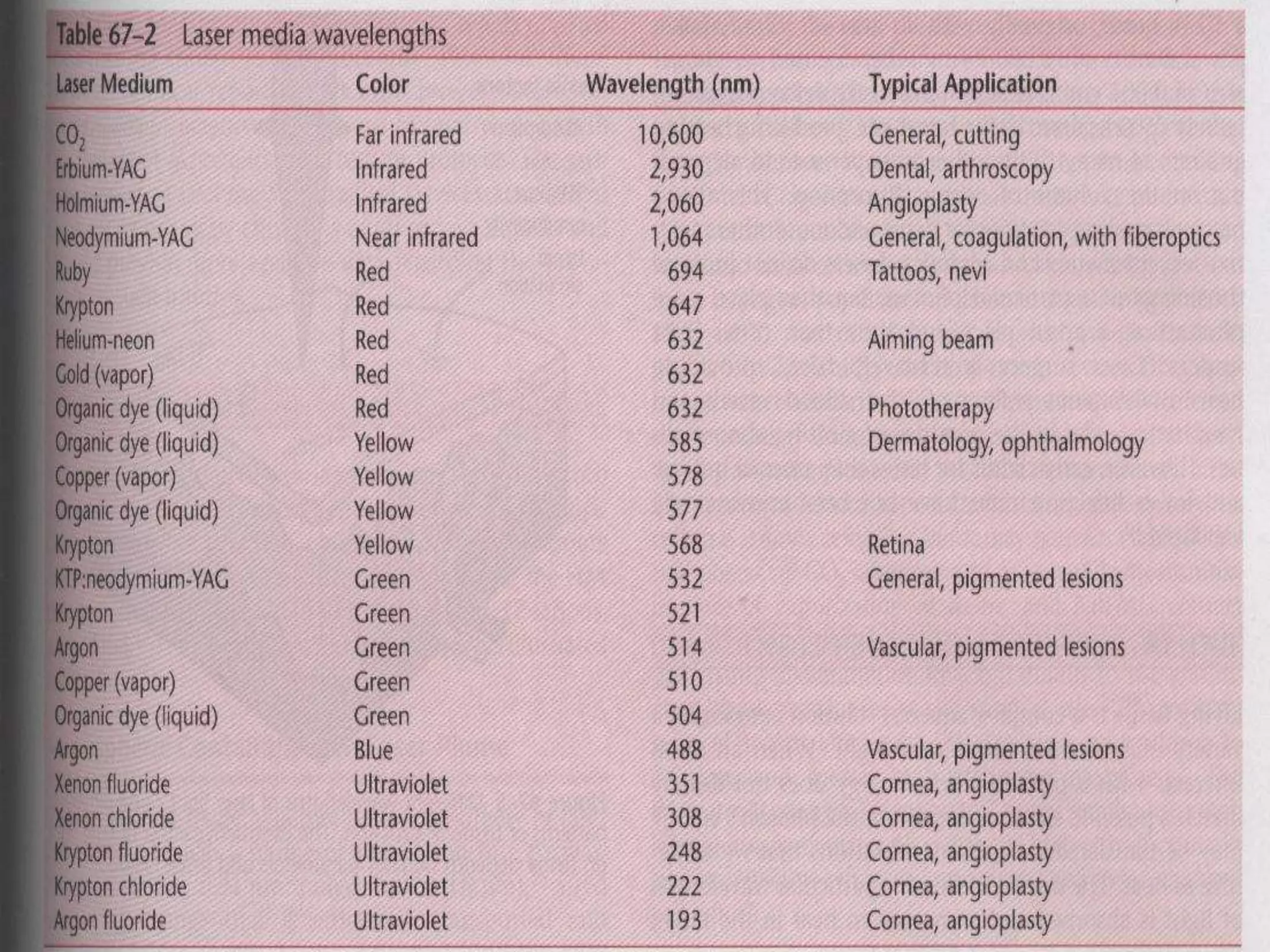
This document discusses anesthesia considerations for LASER surgery. It begins by describing how LASERs work and their properties. It then discusses the risks of LASER use including atmospheric contamination from tissue vaporization, perforation of vessels or structures, embolism, and inappropriate energy transfer. Techniques to secure the airway are presented, including non-intubation methods like apneic oxygenation and spontaneous ventilation, as well as intubation with special LASER-resistant endotracheal tubes. The goals of anesthesia are to provide a safe environment while minimizing complications, and various techniques are described to achieve these goals.