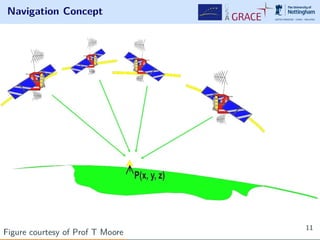
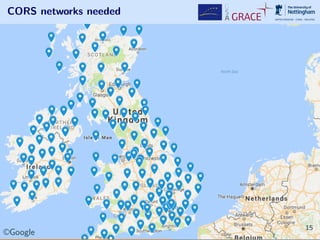
The document discusses how Android provides location services using GNSS, the advantages of using the Galileo system, and various applications of this technology. It highlights the integration of Android's APIs for enhanced positioning accuracy and discusses tools available for developers. The presentation emphasizes the potential for new applications and market opportunities in GNSS positioning with smartphones.