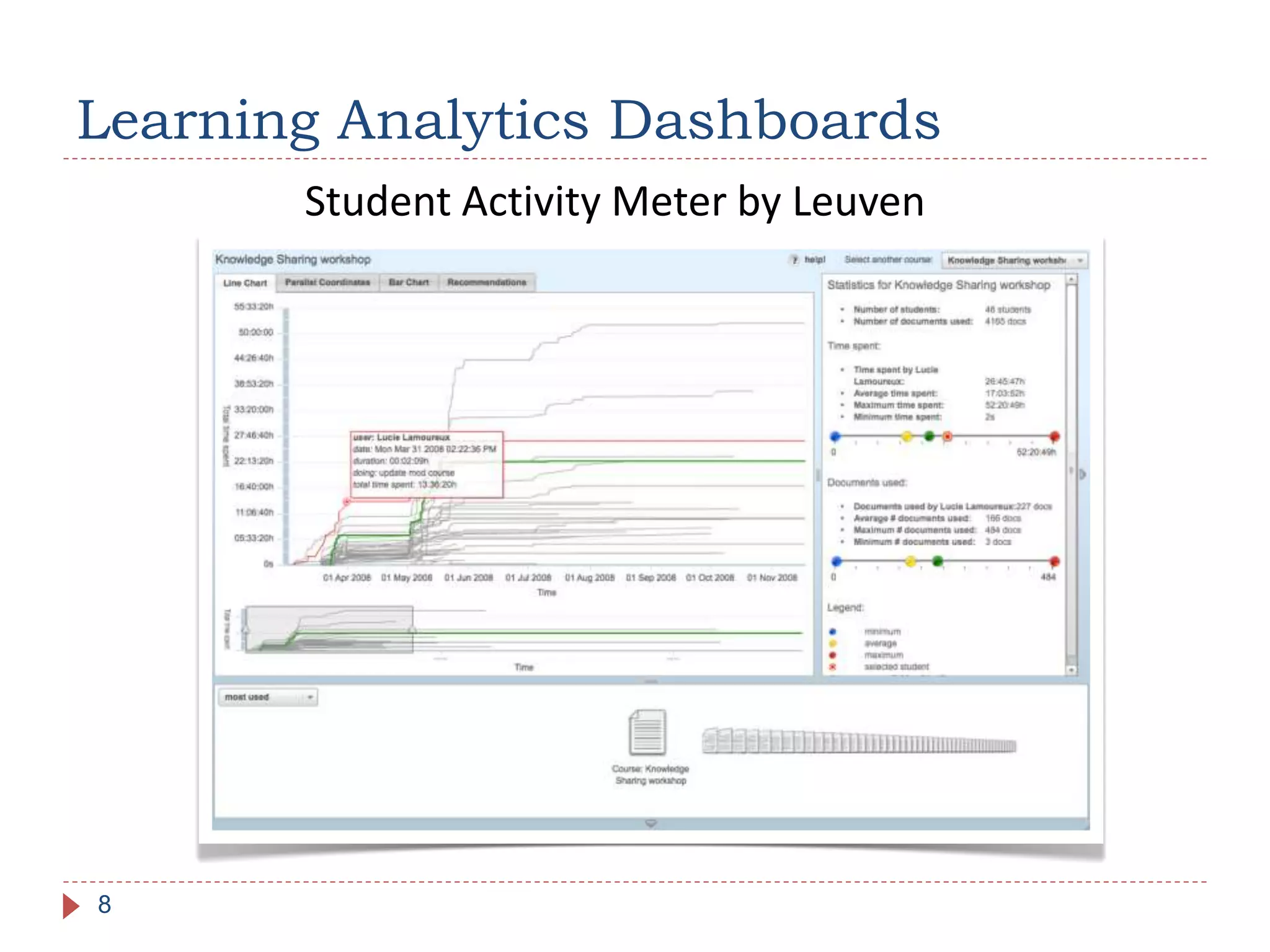
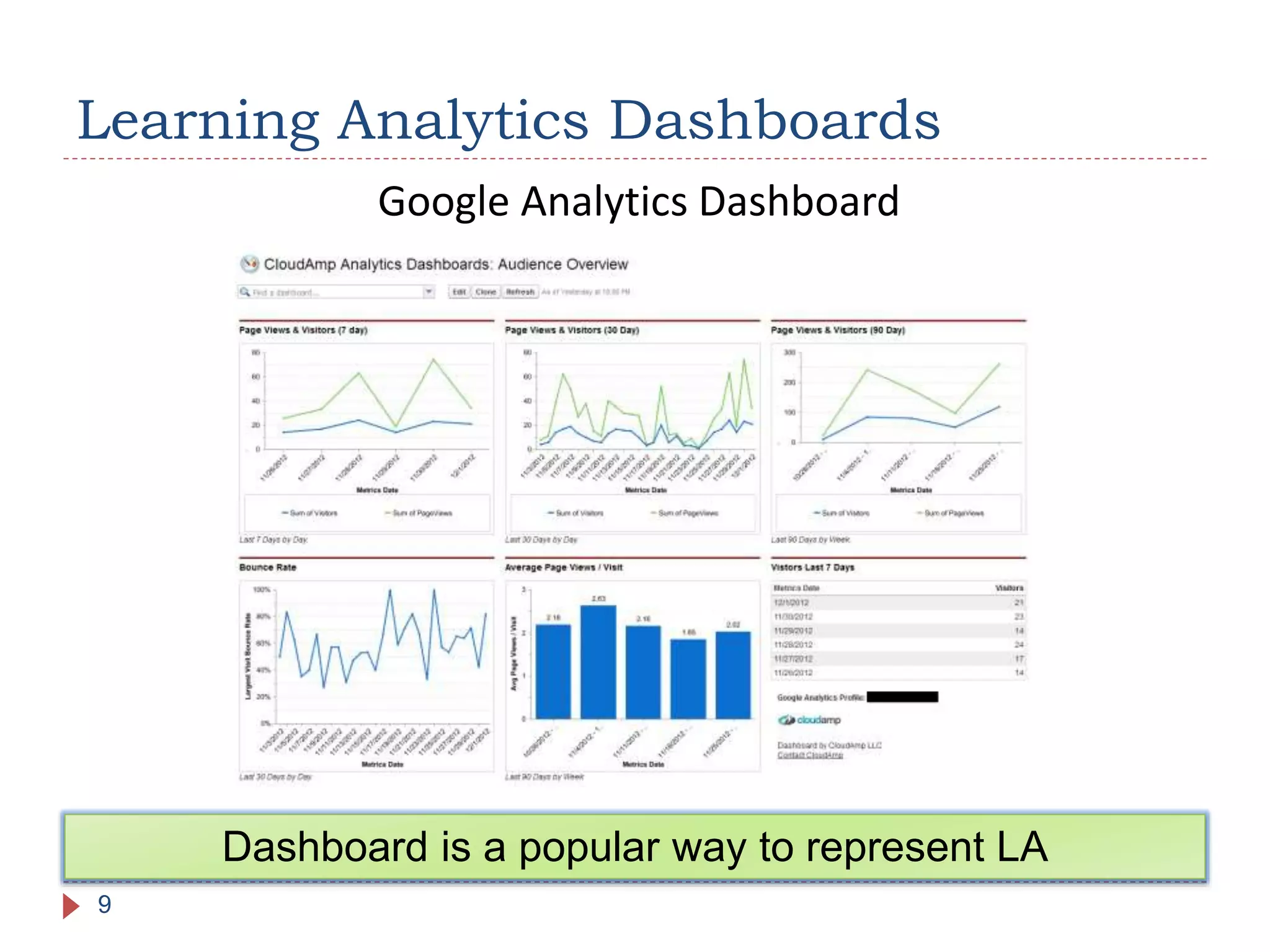
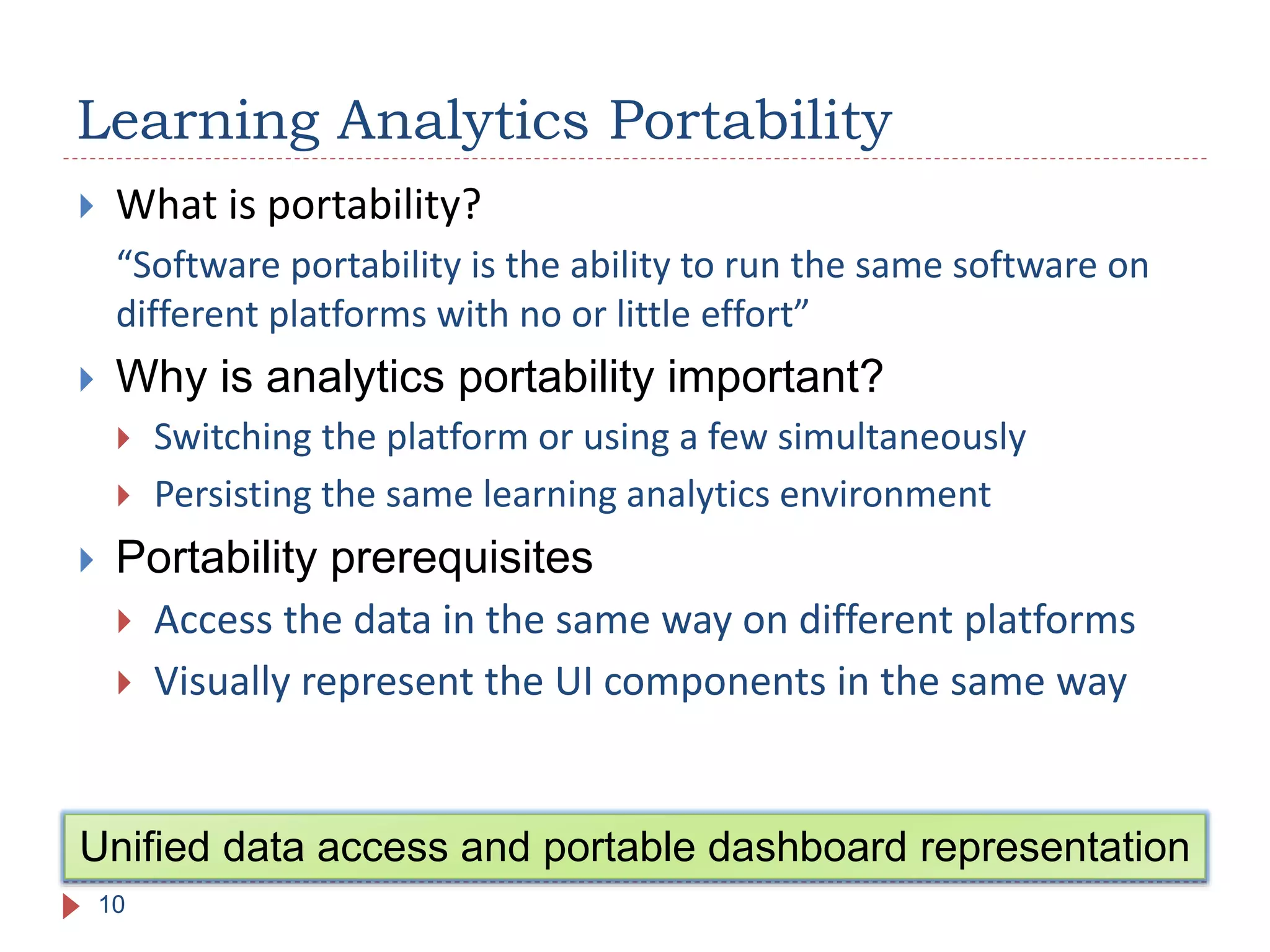
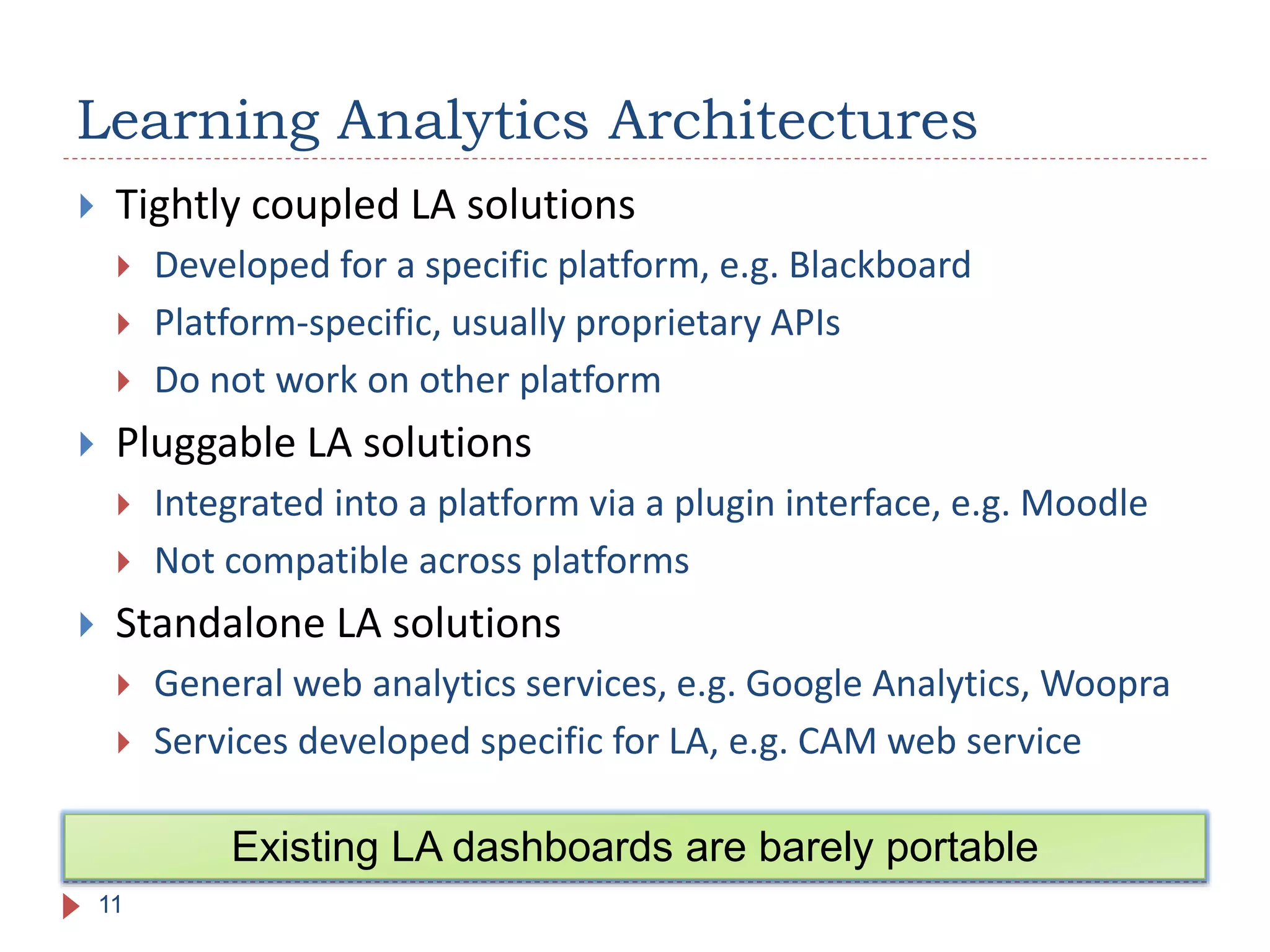
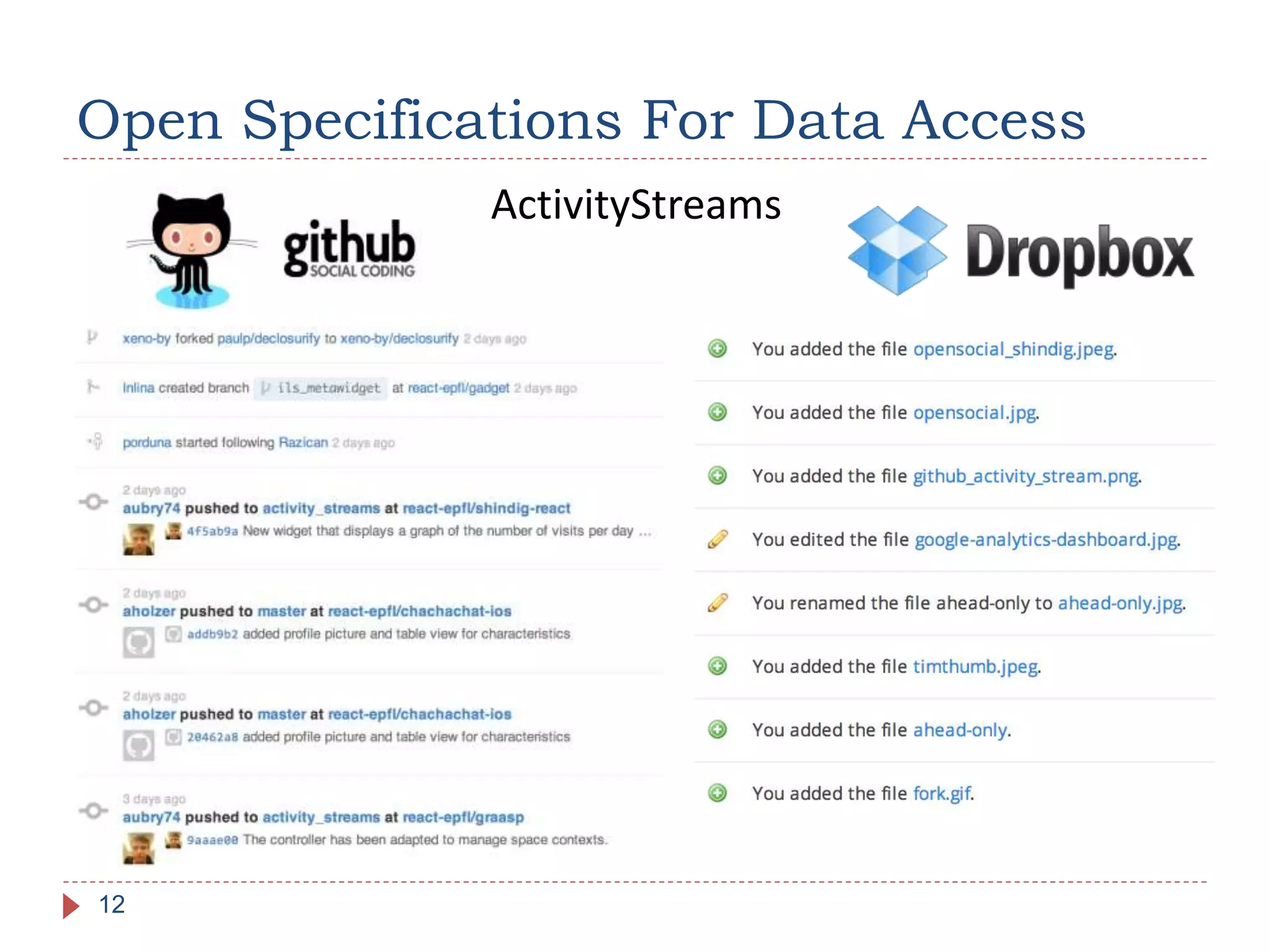
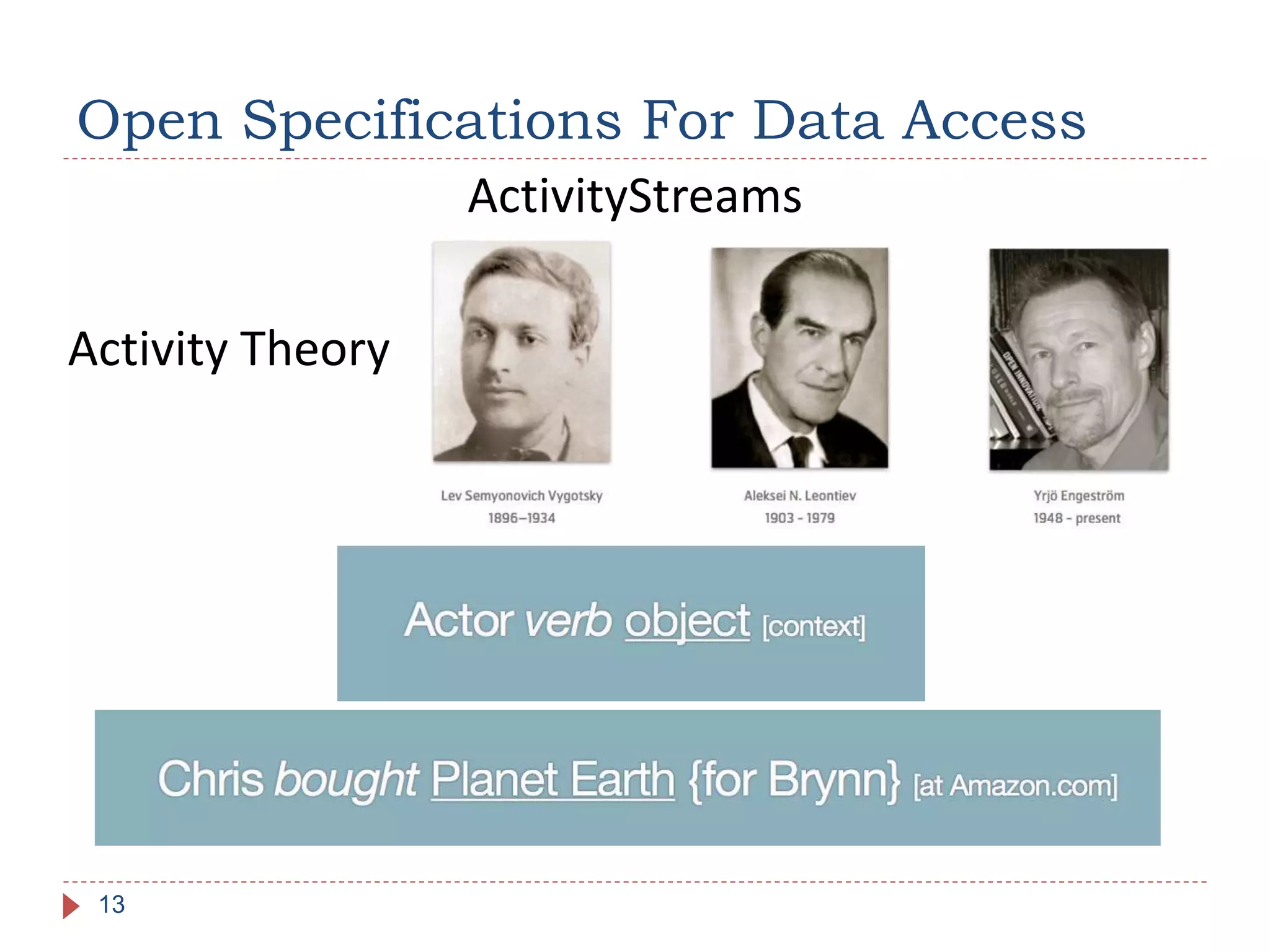
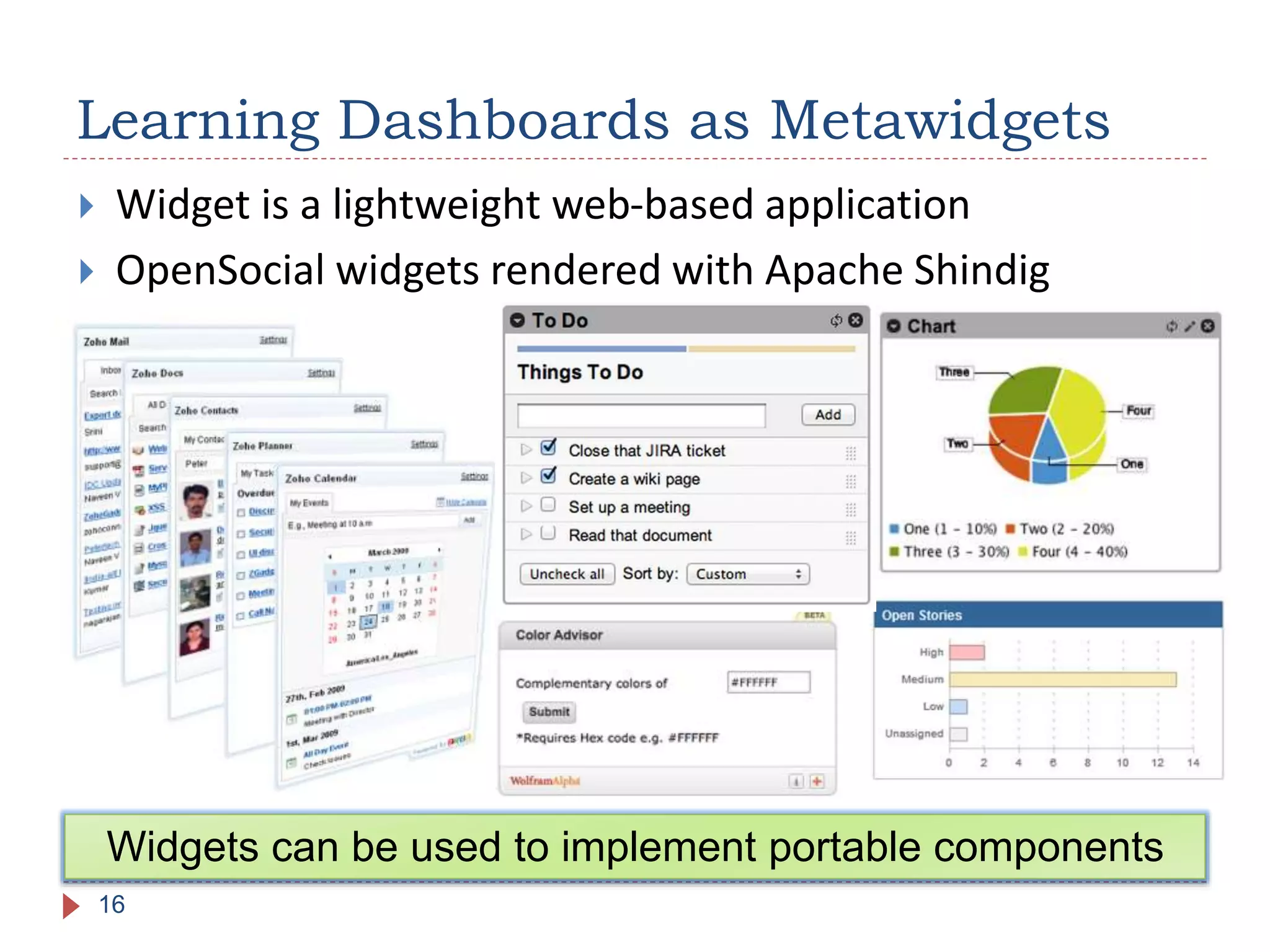
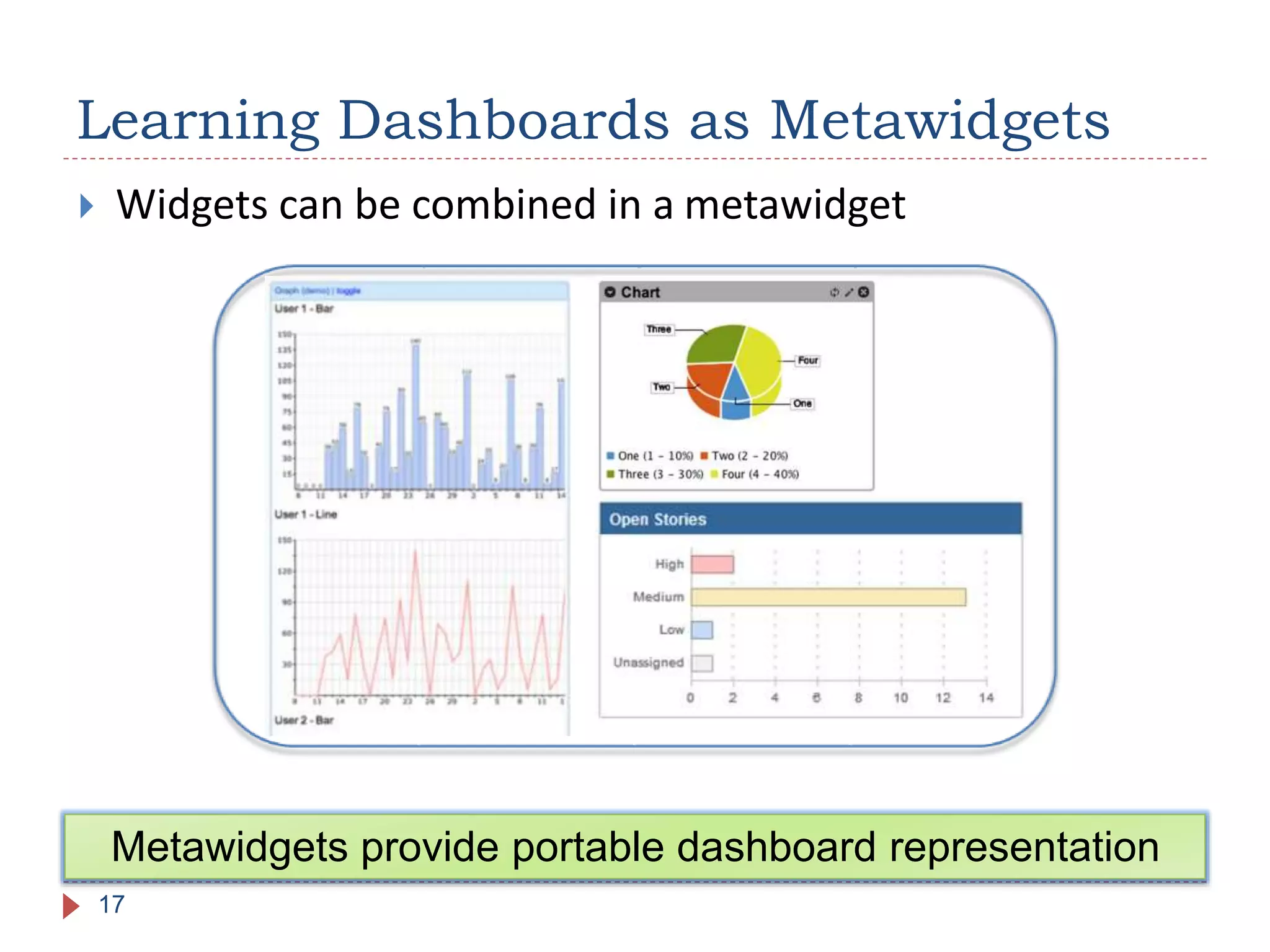
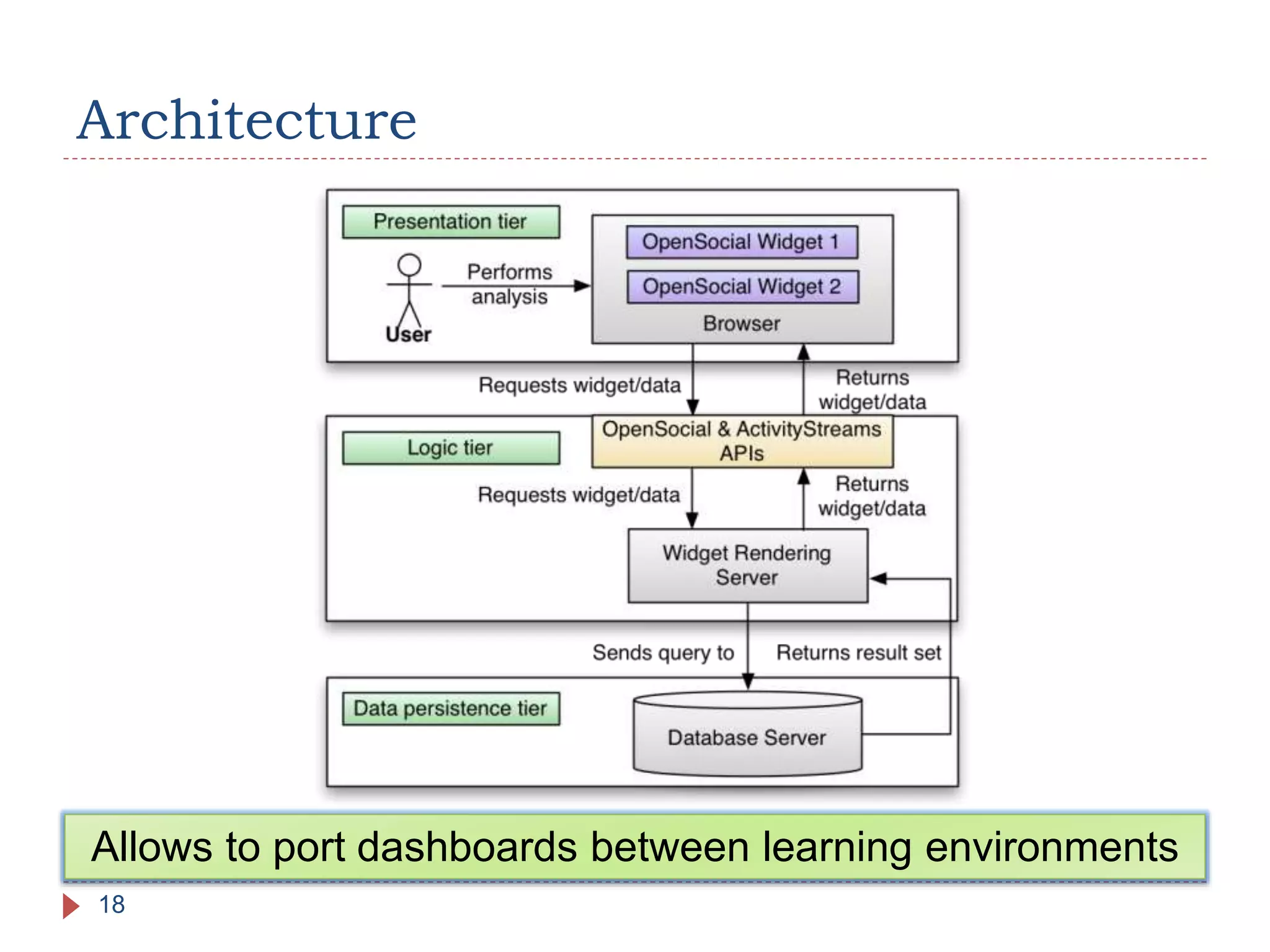
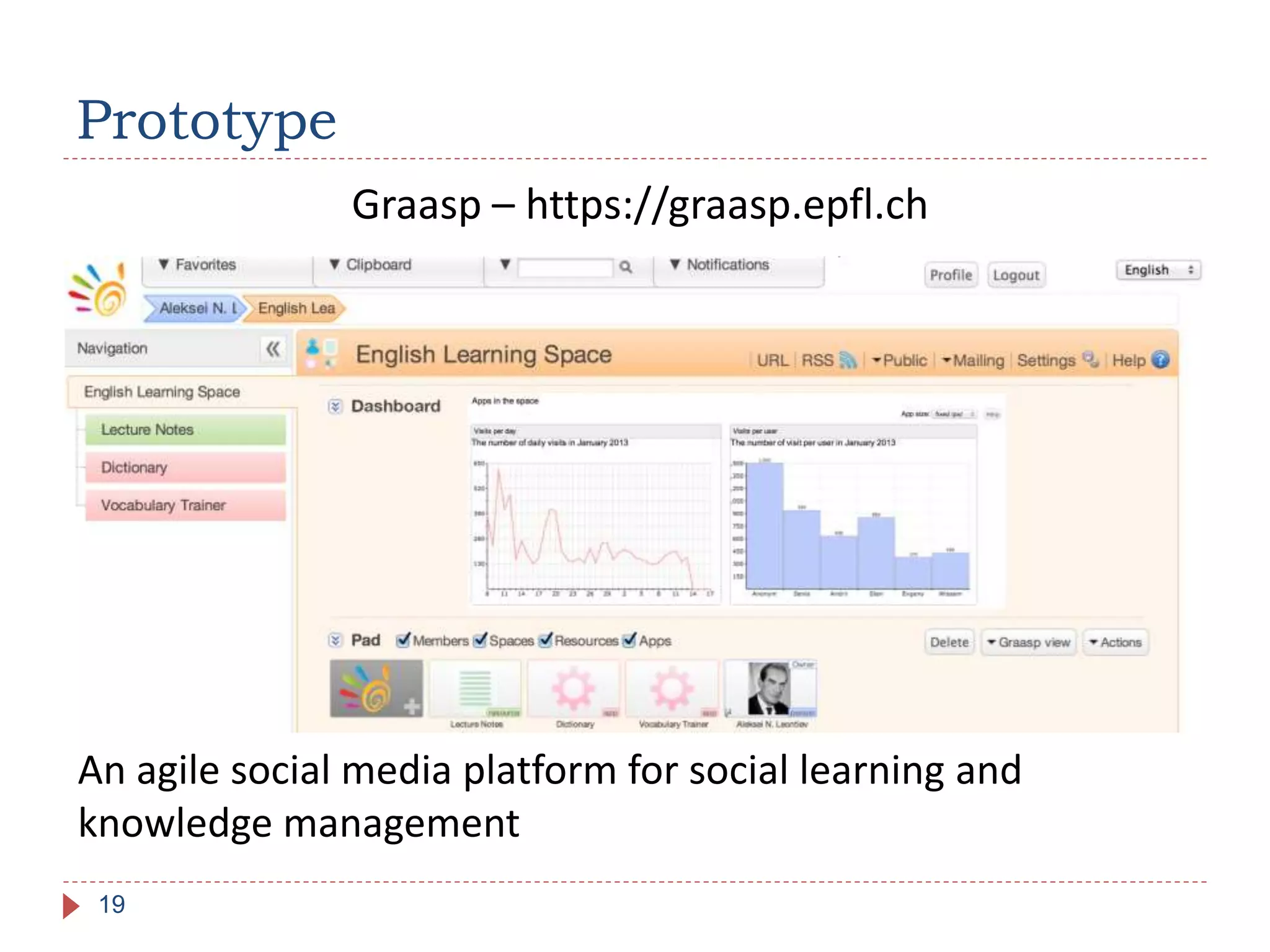
The document discusses the development of portable learning analytics dashboards that harness data to optimize the learning experience. It emphasizes the importance of software portability across learning environments and introduces various methods for unified data access, such as OpenSocial and ActivityStreams. The proposed solutions leverage open standards to allow the integration of analytics across multiple platforms, exemplified by the prototype implemented in the Graasp platform.