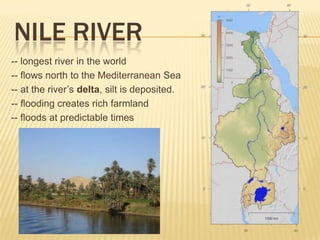
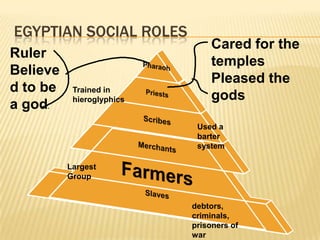
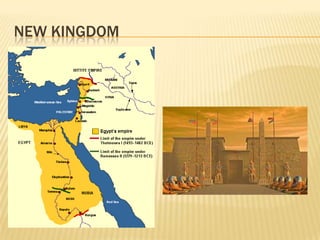
The document provides information about ancient Egypt, including its economy and society. The Egyptian economy depended heavily on agriculture along the fertile banks of the Nile River, which was used for irrigation, fishing, transportation, and trade. Egyptian society was stratified, with rulers and priests at the top who believed themselves to be gods, and laborers, artisans, and debtors at the bottom. Ancient Egypt reached the height of its power during the New Kingdom period under powerful pharaohs like Hatshepsut, Akhenaten, and Ramses II.