This document provides an agenda for a presentation on Big Data Analytics with Cassandra, Spark, and MLLib. The presentation covers Spark basics, using Spark with Cassandra, Spark Streaming, Spark SQL, and Spark MLLib. It also includes examples of querying and analyzing Cassandra data with Spark and Spark SQL, and machine learning with Spark MLLib.




![codecentric AG
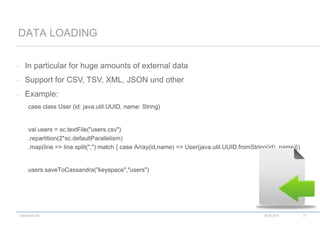
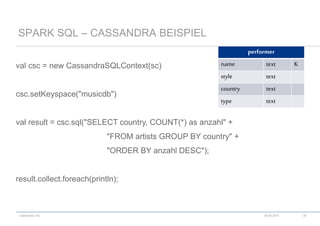
scala> val textFile = sc.textFile("README.md")
textFile: spark.RDD[String] = spark.MappedRDD@2ee9b6e3
scala> val linesWithSpark = textFile.filter(line => line.contains("Spark"))
linesWithSpark: spark.RDD[String] = spark.FilteredRDD@7dd4af09
scala> linesWithSpark.count()
res0: Long = 126
RDD EXAMPLE
18.06.2015 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswithcassandrasparkfrankfurt-150618181941-lva1-app6892/85/Analytics-with-Cassandra-Spark-MLLib-Cassandra-Essentials-Day-7-320.jpg)

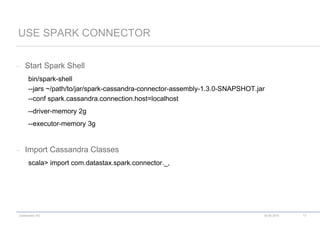
![codecentric AG
– Read complete table
val movies = sc.cassandraTable("movie", "movies")
// Return type: CassandraRDD[CassandraRow]
– Read selected columns
val movies = sc.cassandraTable("movie", "movies").select("title","year")
– Filter Rows
val movies = sc.cassandraTable("movie", "movies").where("title = 'Die Hard'")
READ TABLE
18.06.2015 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswithcassandrasparkfrankfurt-150618181941-lva1-app6892/85/Analytics-with-Cassandra-Spark-MLLib-Cassandra-Essentials-Day-11-320.jpg)
))
– As Scala tuple
sc.cassandraTable[(String,Int)]("movie","movies")
.select("title","year")
or
sc.cassandraTable("movie","movies").select("title","year")
.as((_: String, _:Int))
CassandraRDD[(String,Int)]
READ TABLE
18.06.2015 19
getString,
getStringOption,
getOrElse, getMap,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswithcassandrasparkfrankfurt-150618181941-lva1-app6892/85/Analytics-with-Cassandra-Spark-MLLib-Cassandra-Essentials-Day-12-320.jpg)

.select("title","year")
sc.cassandraTable("movie","movies").select("title","year")
.as(Movie)
CassandraRDD[Movie]
READ TABLE – CASE CLASS
18.06.2015 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswithcassandrasparkfrankfurt-150618181941-lva1-app6892/85/Analytics-with-Cassandra-Spark-MLLib-Cassandra-Essentials-Day-13-320.jpg)

![codecentric AG
( [atomic,collection,object] , [atomic,collection,object])
val fluege= List( ("Thomas", "Berlin") ,("Mark", "Paris"), ("Thomas", "Madrid") )
val pairRDD = sc.parallelize(fluege)
pairRDD.filter(_._1 == "Thomas")
.collect
.foreach(t => println(t._1 + " flog nach " + t._2))
PAIR RDD‘S
18.06.2015 23
key – not unique value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswithcassandrasparkfrankfurt-150618181941-lva1-app6892/85/Analytics-with-Cassandra-Spark-MLLib-Cassandra-Essentials-Day-15-320.jpg)

![codecentric AG
– keys(), values()
– mapValues(func), flatMapValues(func)
– lookup(key), collectAsMap(), countByKey()
– reduceByKey(func), foldByKey(zeroValue)(func)
– groupByKey(), cogroup(otherDataset)
– sortByKey([ascending])
– join(otherDataset), leftOuterJoin(otherDataset), rightOuterJoin(otherDataset)
– union(otherDataset), substractByKey(otherDataset)
SPECIAL OP‘S FOR PAIR RDD‘S
18.06.2015 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswithcassandrasparkfrankfurt-150618181941-lva1-app6892/85/Analytics-with-Cassandra-Spark-MLLib-Cassandra-Essentials-Day-17-320.jpg)

![codecentric AG
pairRDD.groupByCountry()
RDD[(String,Iterable[CassandraRow])]
val directors = sc.cassandraTable(..).map(r => r.getString("name"),r))
val movies = sc.cassandraTable().map(r => r.getString("director"),r))
directors.cogroup(movies)
RDD[(String,
(Iterable[CassandraRow], Iterable[CassandraRow]))]
CASSANDRA EXAMPLE
18.06.2015 27
director
name text K
country text
movie
title text K
director text
Director Movies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswithcassandrasparkfrankfurt-150618181941-lva1-app6892/85/Analytics-with-Cassandra-Spark-MLLib-Cassandra-Essentials-Day-19-320.jpg)
![codecentric AG
– Joins could be expensive
partitions for same keys in different
tables on different nodes
requires shuffling
val directors = sc.cassandraTable(..).map(r => (r.getString("name"),r))
val movies = sc.cassandraTable().map(r => (r.getString("director"),r))
movies.join(directors)
RDD[(String, (CassandraRow, CassandraRow))]
CASSANDRA EXAMPLE - JOINS
18.06.2015 28
director
name text K
country text
movie
title text K
director text
DirectorMovie](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswithcassandrasparkfrankfurt-150618181941-lva1-app6892/85/Analytics-with-Cassandra-Spark-MLLib-Cassandra-Essentials-Day-20-320.jpg)