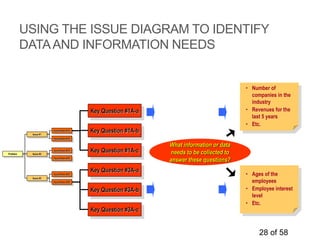
This document discusses analytical thinking and the scientific approach to problem solving, which includes defining the problem, formulating hypotheses, collecting facts, conducting analysis, and developing a solution. It provides details on various tools and techniques for each step of the process. For defining the problem, it describes techniques like problem identification, root cause analysis using the five whys method and fishbone diagrams. For formulating hypotheses, it recommends using an issue diagram to break down problems into key issues and formulate hypotheses and questions to test each hypothesis. It cautions that issue diagrams, hypotheses and questions need to be carefully crafted to be relevant, testable and not too broad or narrow in scope. Brainstorming is also presented as a method for identifying issues