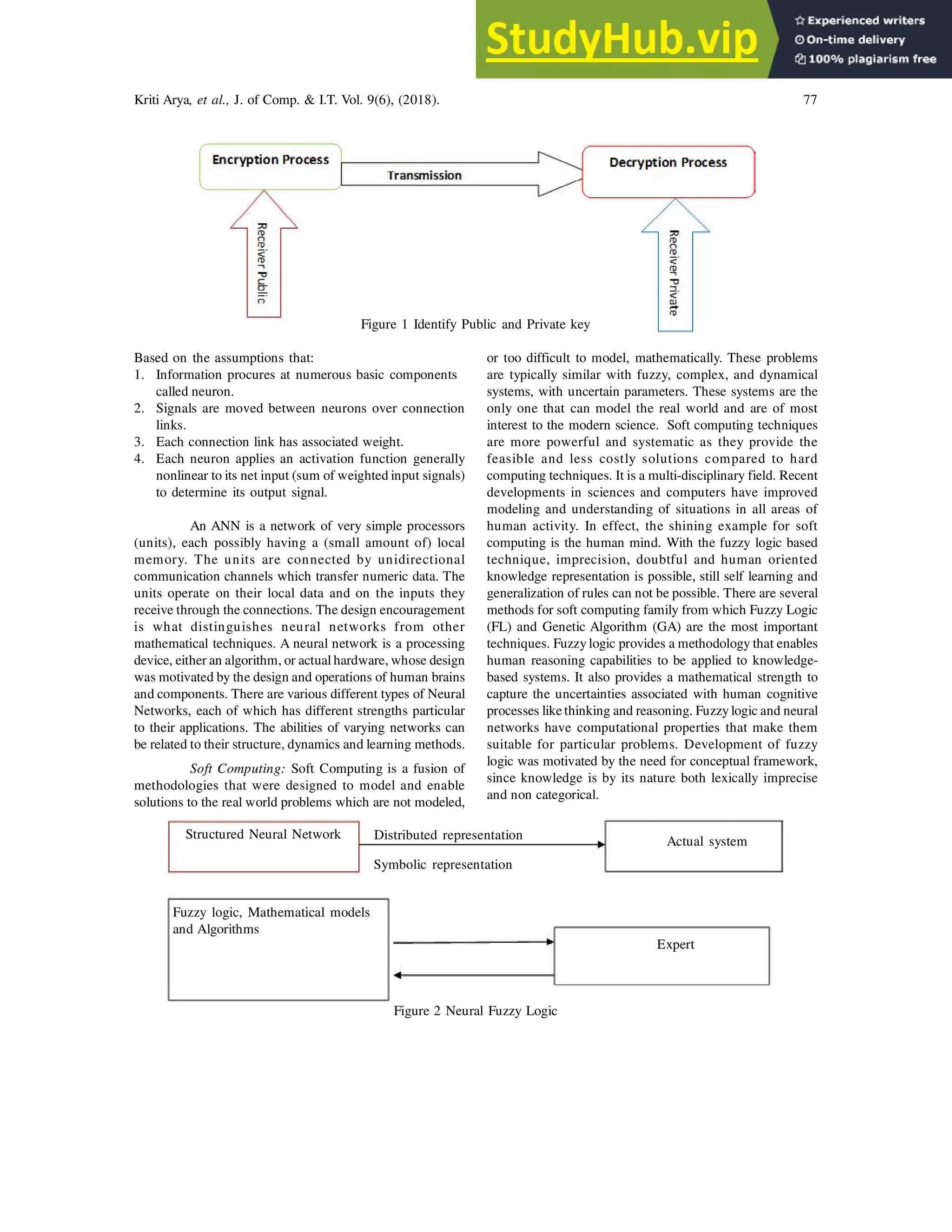
This document analyzes the use of artificial neural networks in cryptography. It discusses how neural networks can be used for secret key exchange and encryption. Specifically, it examines how synchronizing two neural networks through mutual learning can generate a secret key that is then used to encrypt and decrypt messages. The document also reviews various soft computing techniques like fuzzy logic that can be integrated with neural networks for cryptography applications. It concludes that artificial neural networks have potential for building more secure and effective cryptographic systems by overcoming some of the drawbacks of traditional approaches.