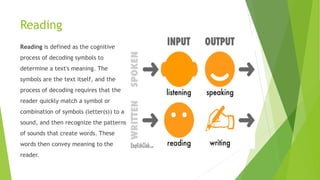
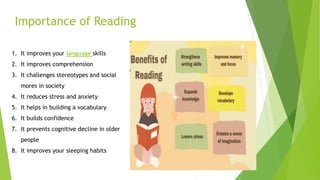
The document outlines the concept of analytical reading, highlighting its importance as a high-level cognitive skill that enhances comprehension and retention of texts. It details the steps and strategies for effective analytical reading, including surveying the text, formulating guiding questions, summarizing key ideas, and evaluating the author's arguments. Additionally, it contrasts analytical thinking with critical thinking, emphasizing the benefits of thorough text analysis for deep understanding and cognitive health.