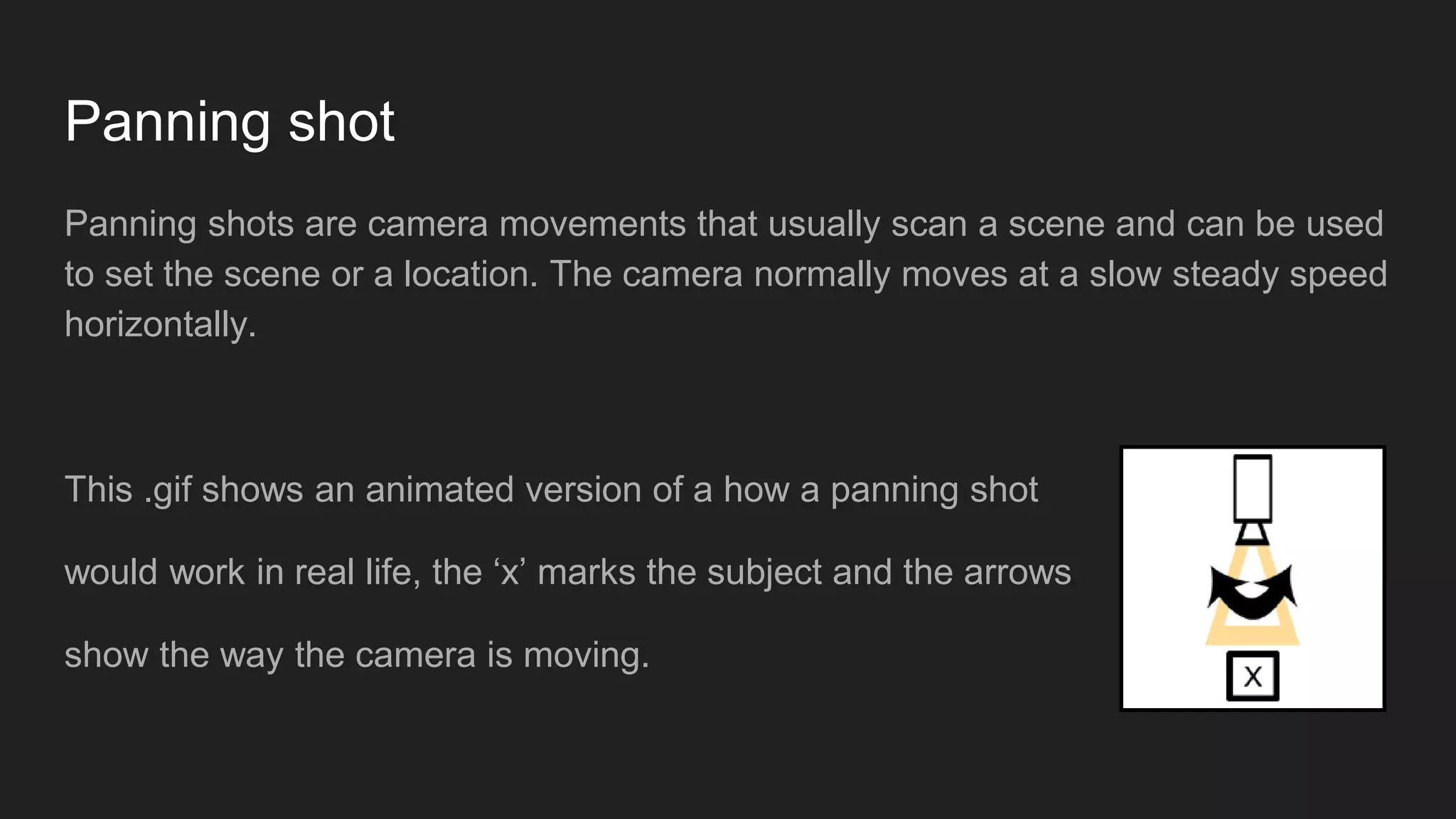
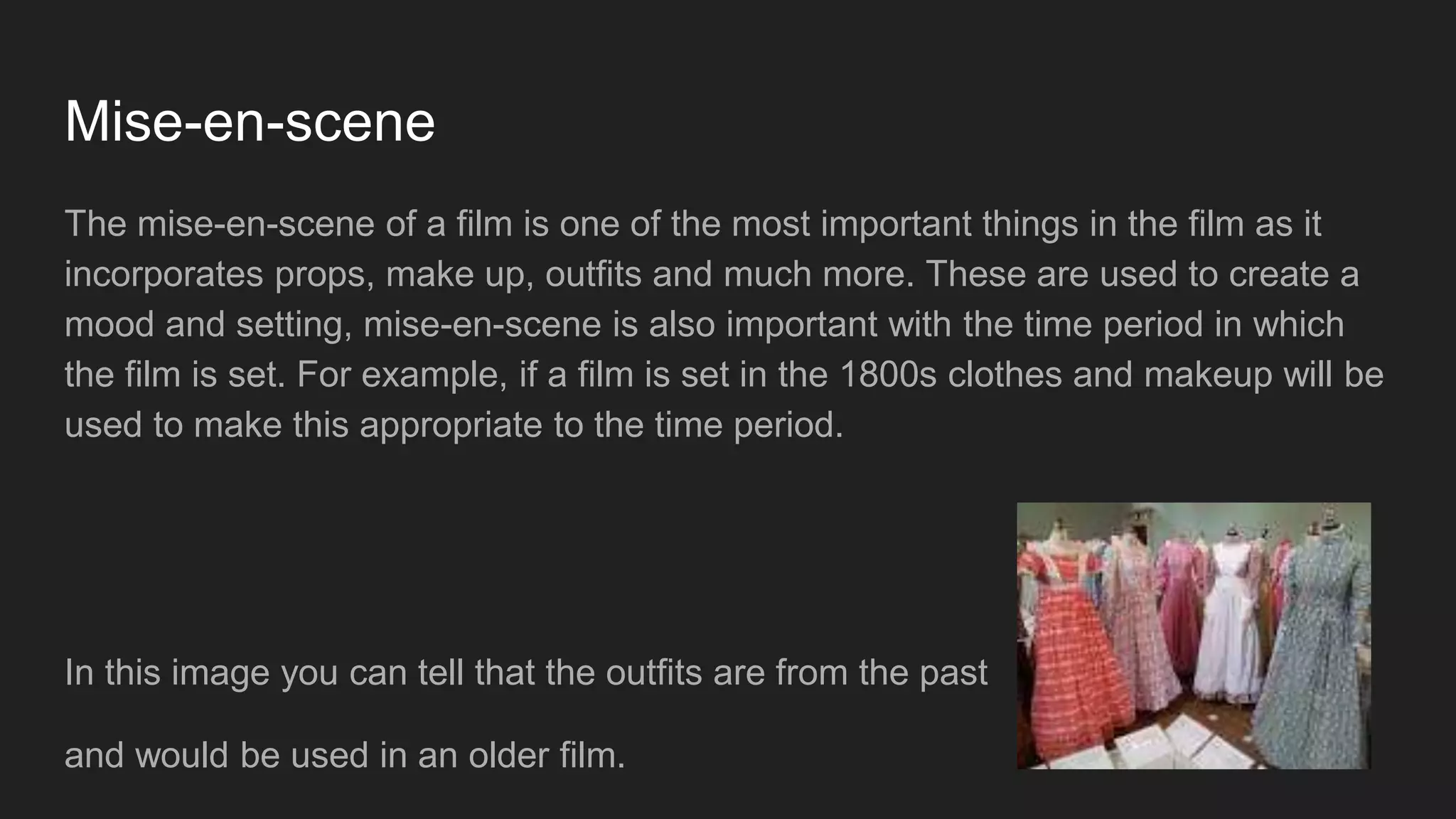
1) The document discusses various microelements of film including camera shots, angles, movements, and sounds.
2) It provides examples and definitions for extreme close-ups, close-ups, medium shots, long shots, extreme long shots, tracking shots, panning shots, tilt shots, zooms, cuts, and diegetic and non-diegetic sounds.
3) The author explains that understanding these microelements will help them apply different techniques to scenes in their own media assignment, such as using tracking shots and zoom shots in the opening of a horror film.