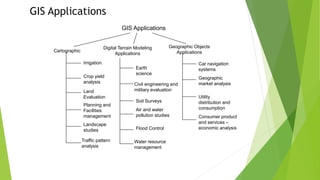
Geographic information systems (GIS) collect, model, and analyze spatial and non-spatial data to represent physical features and socio-economic data. GIS can be divided into cartographic, digital terrain modeling, and geographic objects applications used for civil engineering, planning, natural resource management, and more. GIS requires data modeling, integration from multiple sources, analysis, and special operators to conduct tasks like interpolation, interpretation, and proximity analysis.