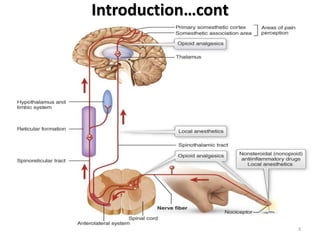
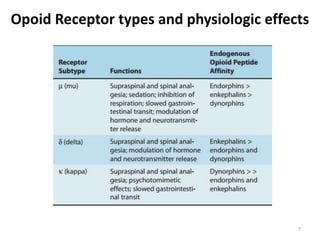
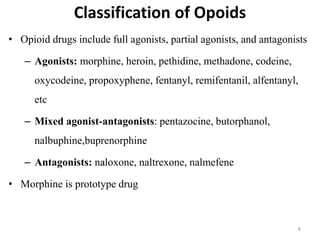
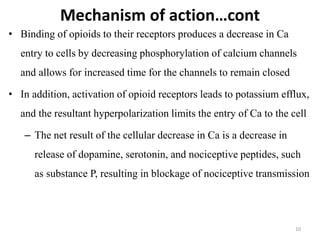
Pharmacology of analgesics
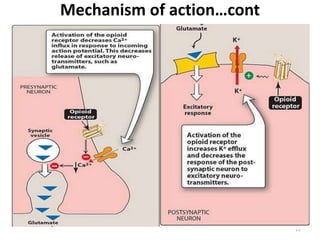
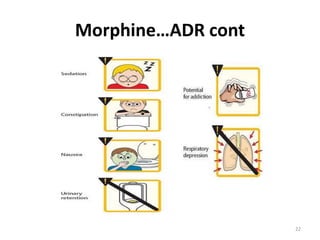
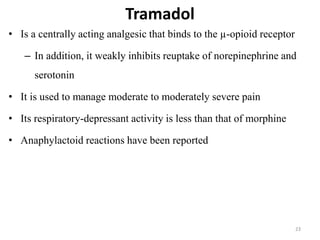
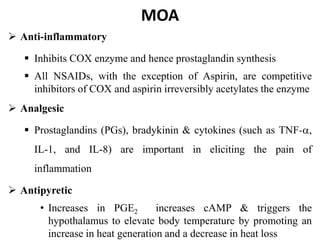
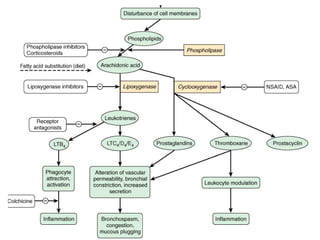
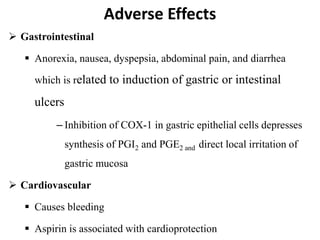
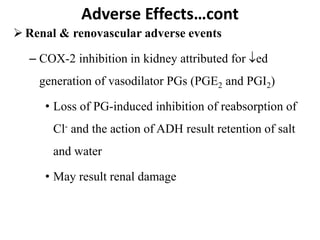
The document discusses various classes of analgesic drugs including opioids, NSAIDs, and acetaminophen. It describes the mechanism of action, therapeutic uses, and adverse effects of representative drugs from each class such as morphine, tramadol, aspirin, and acetaminophen. Specifically, it details how opioids like morphine produce analgesia by binding to mu receptors in the brain and spinal cord, while NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes to reduce inflammation and pain. Both classes can cause gastrointestinal adverse effects, though COX-2 selective NSAIDs have fewer GI side effects. Acetaminophen is largely devoid of anti-inflammatory effects compared to other NSAIDs.