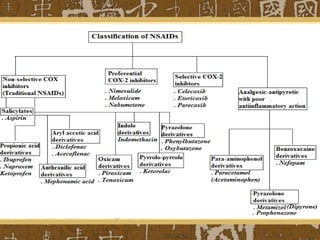
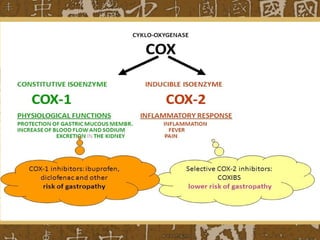
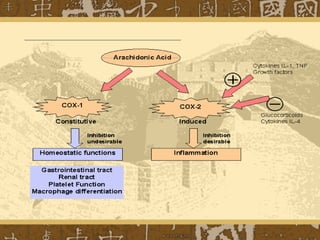
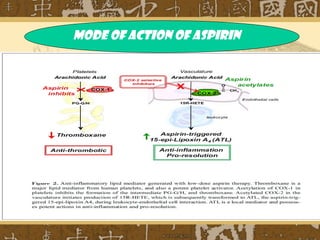
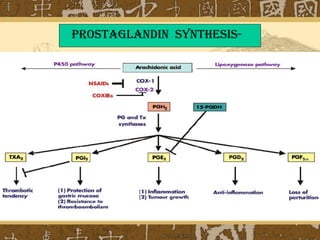
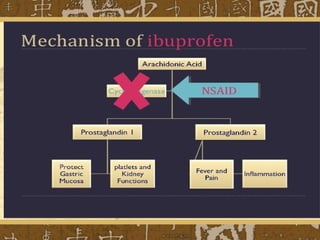
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) work by blocking cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which reduces prostaglandin production and consequently decreases inflammation, pain, and fever. NSAIDs are used to treat conditions like arthritis, gout, and postoperative pain but can cause side effects like gastrointestinal ulceration and bleeding by inhibiting protective prostaglandins in the stomach. They may also increase risks of cardiovascular and renal issues. Care must be taken with NSAID combinations or when used with other drugs that impact renal function.