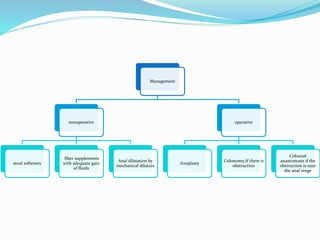
The anal canal is the terminal part of the lower GI tract located below the rectum. It is approximately 4 cm long and develops from both endoderm and ectoderm tissues. The pectinate line marks the transition between these tissues. The anal canal has longitudinal folds called columns, which contain glands and openings. Blood supply comes from the superior, middle, and inferior rectal arteries. Anal stenosis has various causes like surgery, inflammation, radiation, and trauma. Symptoms are constipation and painful defecation. Diagnosis involves visual, digital, and proctoscopic exams. Treatment depends on severity and includes dilatation, anoplasty surgery, or colostomy.