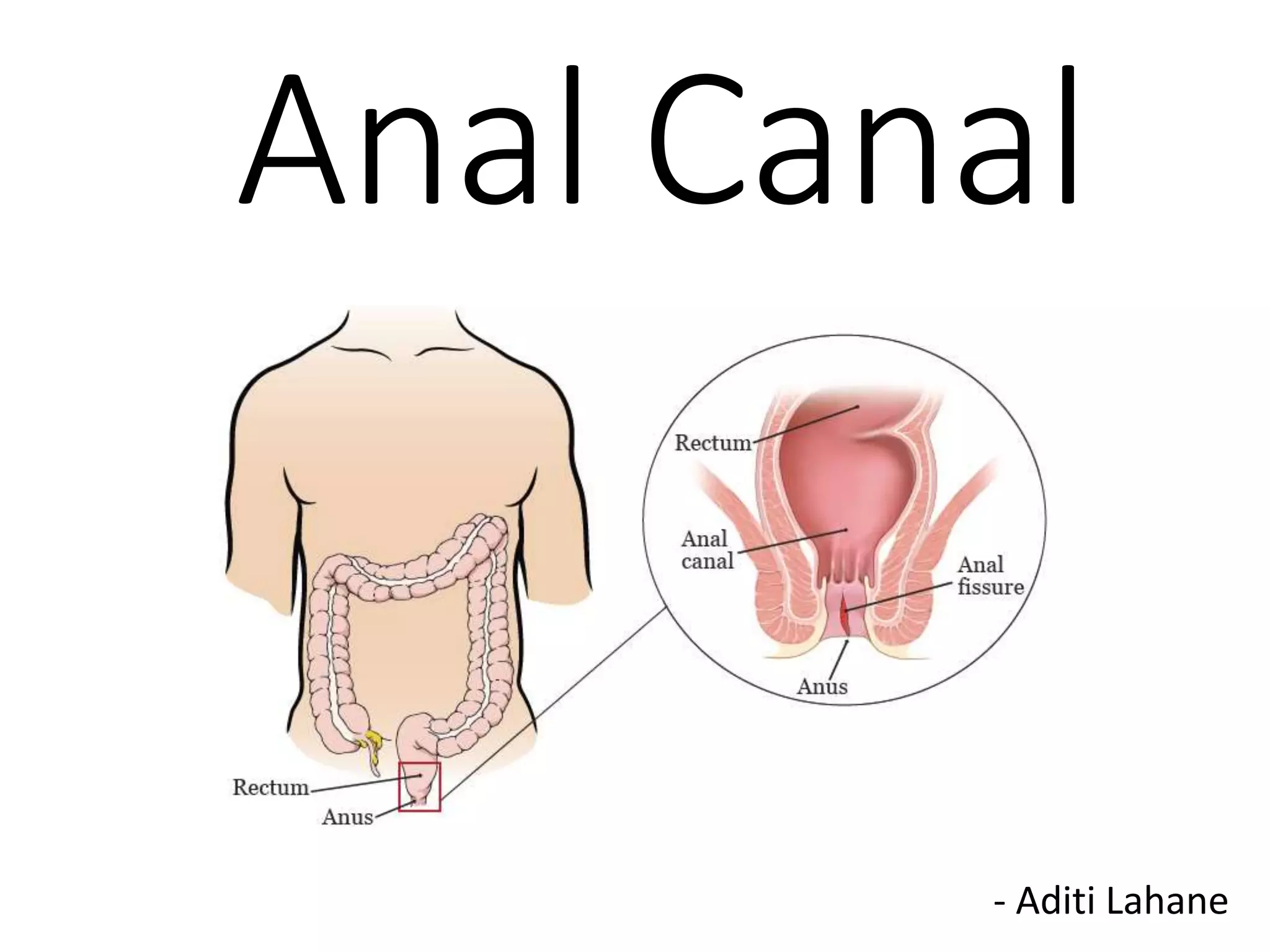
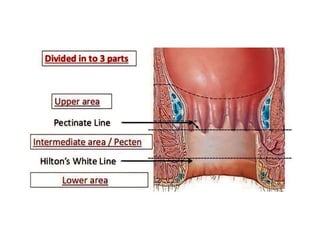
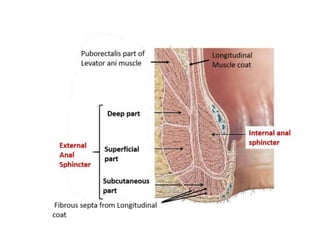
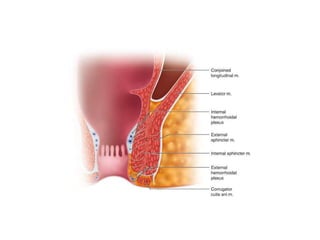
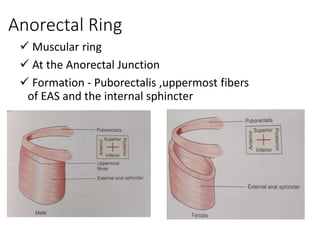
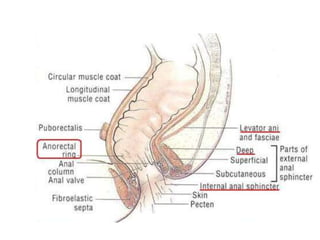
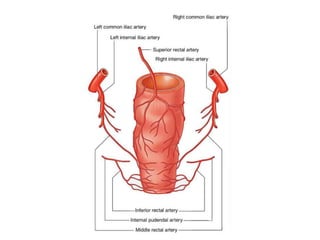
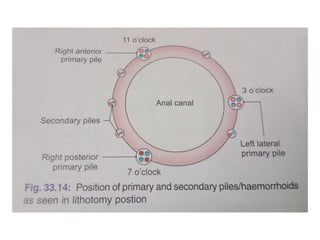
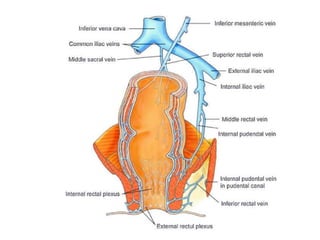
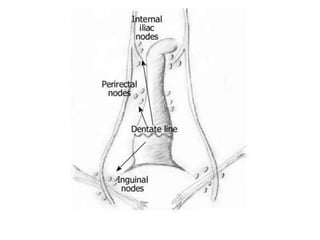
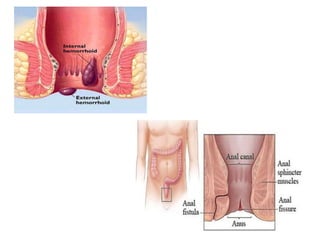
The anal canal is located below the pelvic diaphragm and extends from the anorectal junction to the anus. It is surrounded by inner involuntary and outer voluntary sphincter muscles and is around 3.8 cm long. The anal canal has three parts - the upper mucous part lined by columnar epithelium, the middle transitional zone, and the lower cutaneous part lined by skin. It receives blood supply from the inferior and superior rectal arteries and drains into internal iliac and inguinal lymph nodes. Nerve supply includes autonomic nerves above the pectinate line and somatic nerves below.