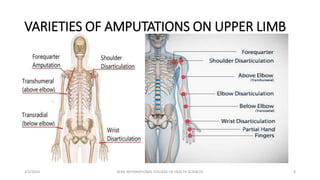
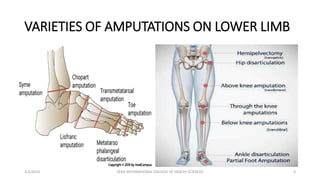
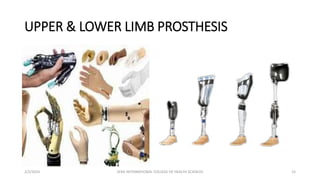
This document discusses amputations, including definitions, goals, types, indications, and complications. Amputation involves surgically removing a limb or part of a limb through the bone or joint. It is performed to reduce pain, provide independence, and restore function. The main goals of amputation are to preserve functional length and sensation while preventing issues like neuromas or contractures. Major types include open/guillotine and closed amputations. Common indications are non-viable or dangerous limbs due to issues such as gangrene. Risk factors often involve vascular insufficiency. Potential complications range from early issues like hemorrhage to longer-term problems such as infection, contracture, or phantom limb sensations.