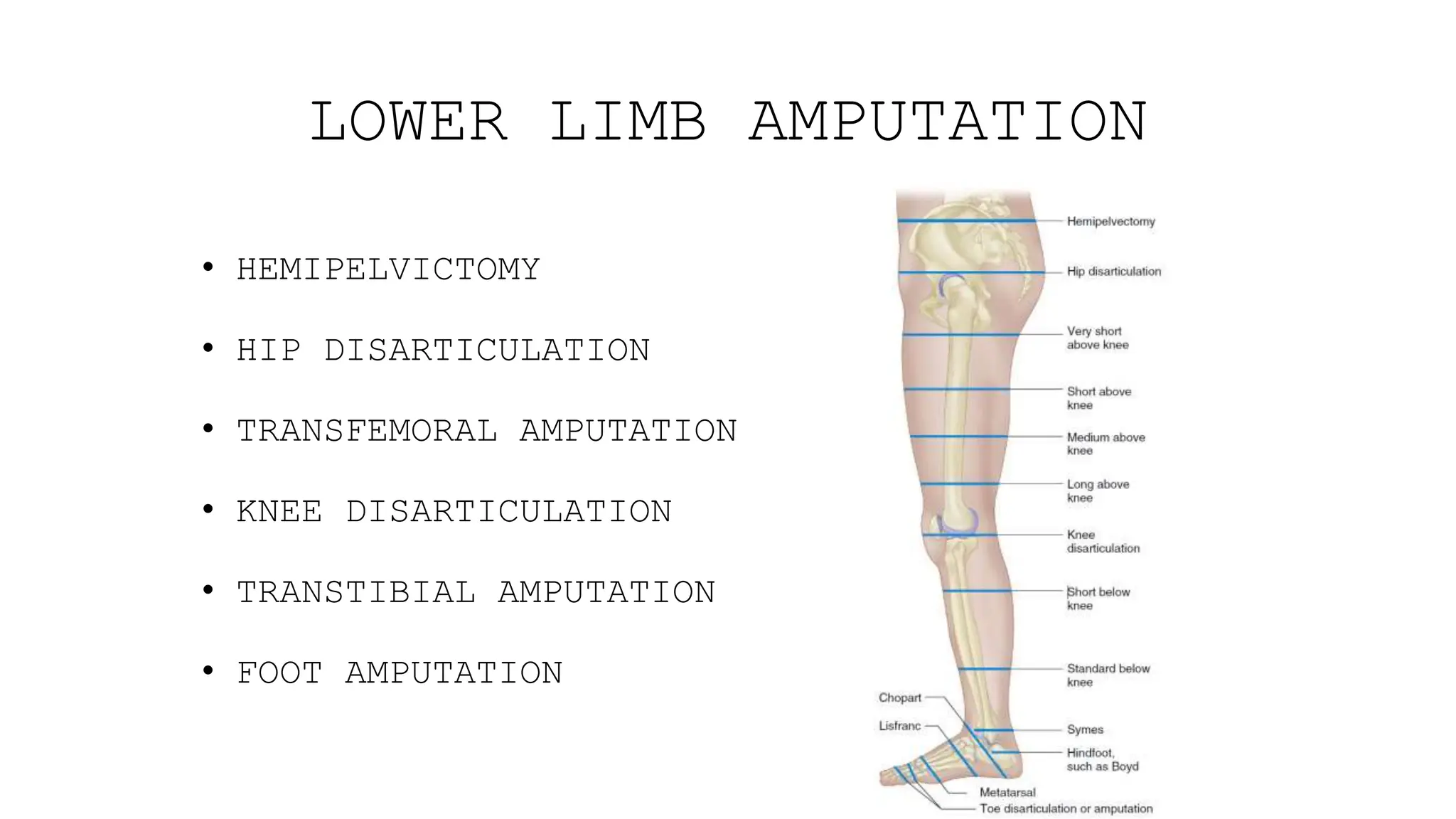
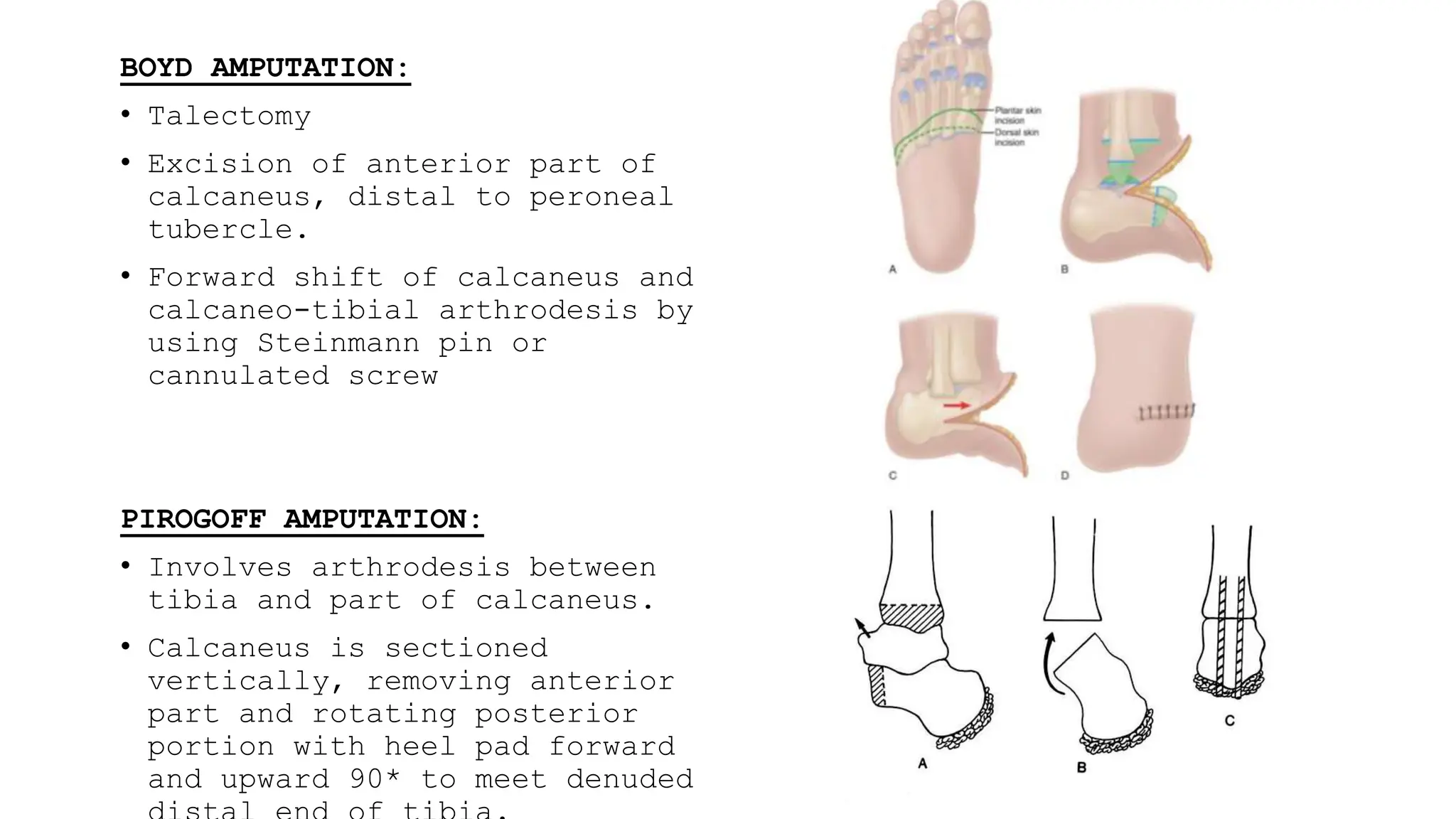
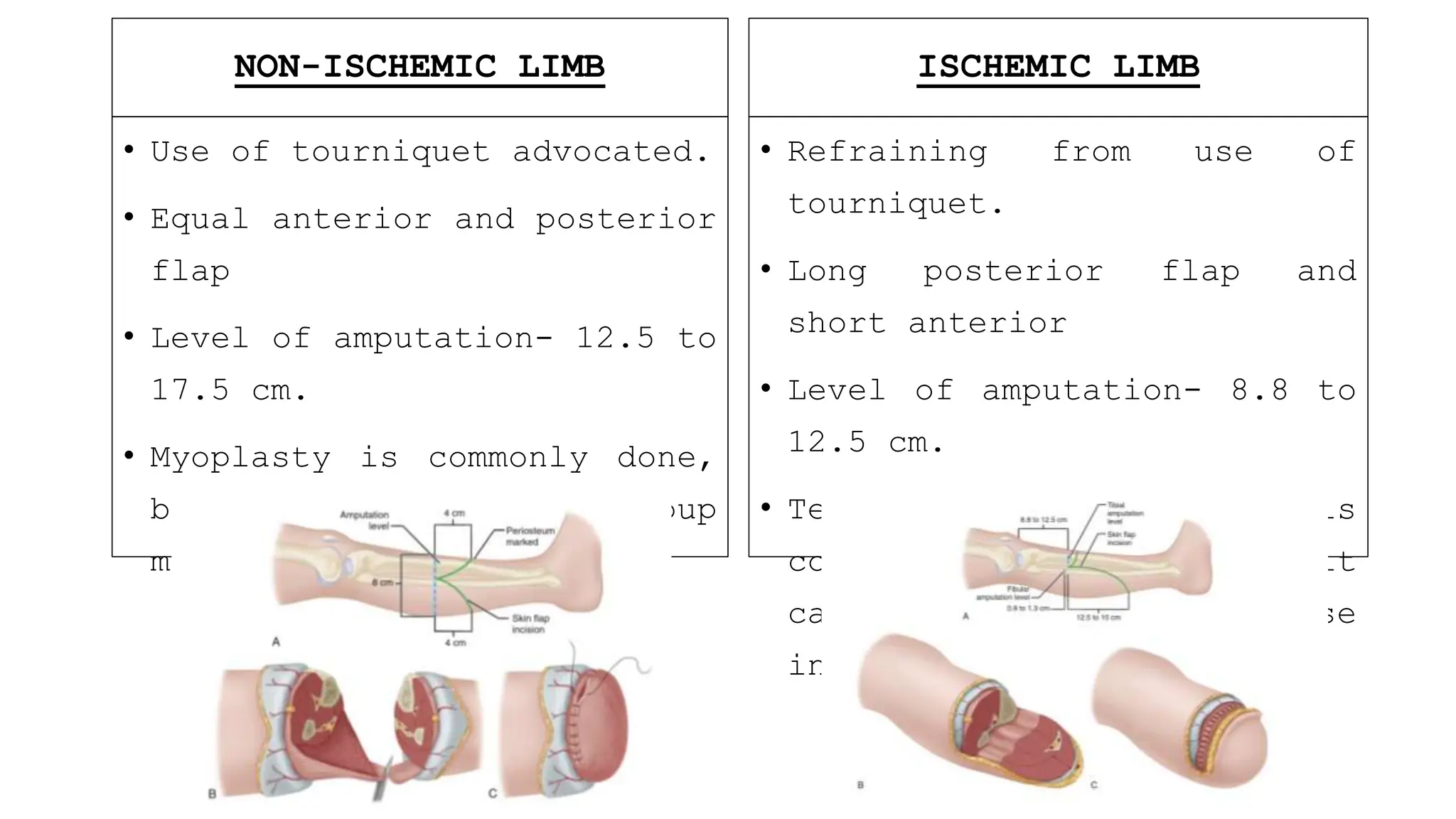
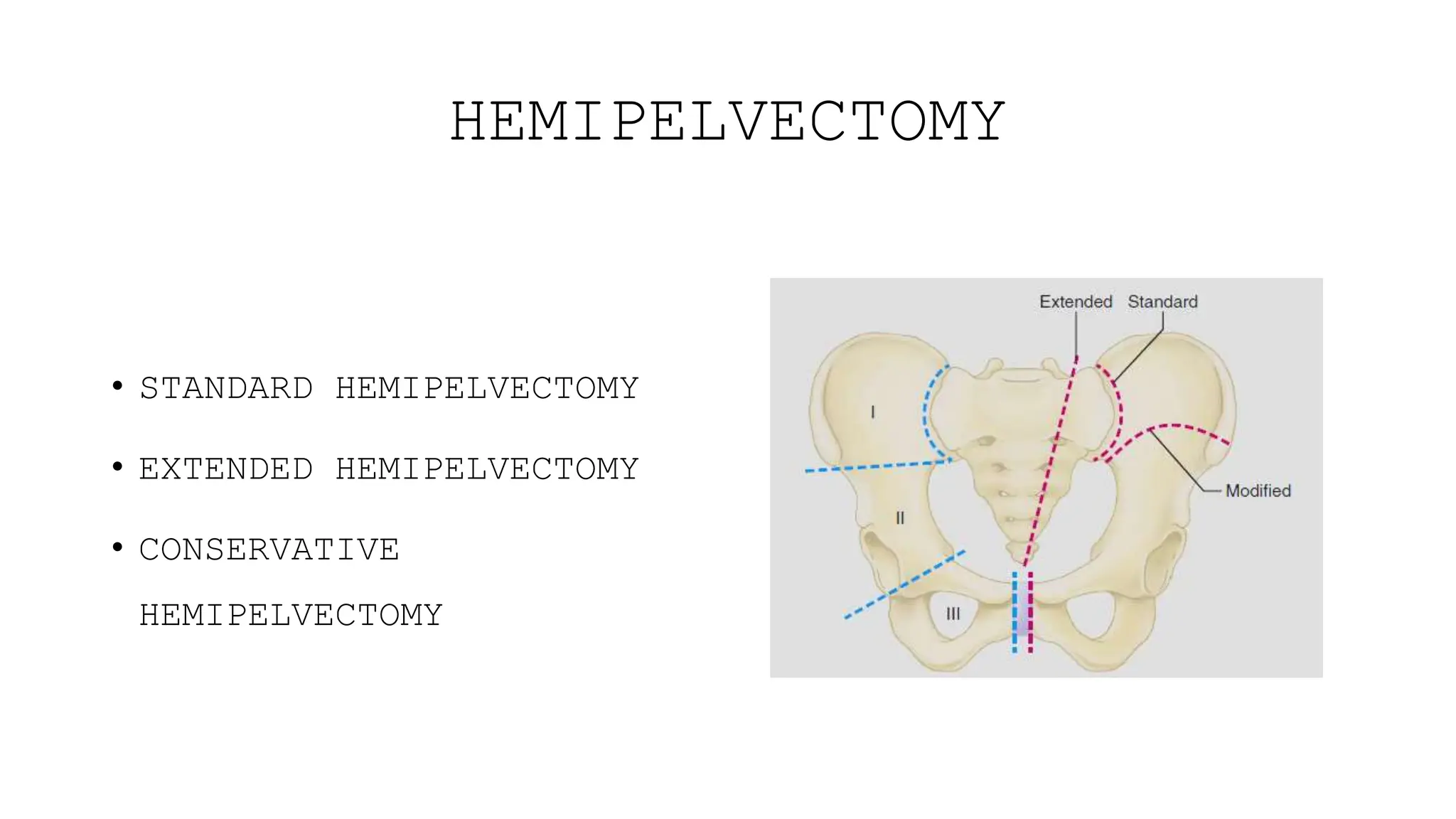
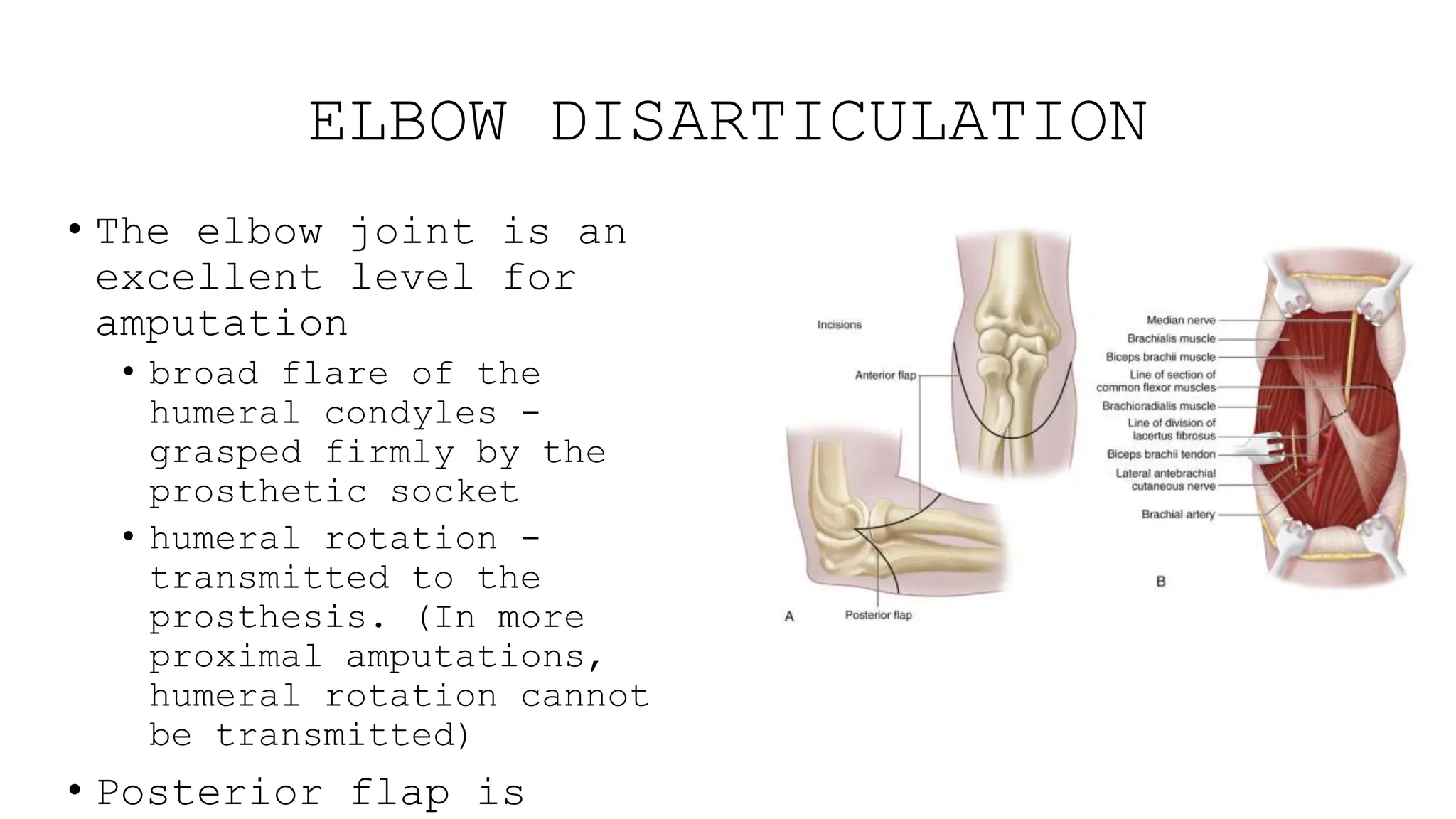
This document provides information about amputation indications, surgical principles, and post-operative care. It discusses various types of amputations for both lower and upper limbs. The main indications for amputation include peripheral vascular disease, trauma, malignancy, infection, burns, and frostbite. The surgical principles focus on choosing an amputation level for optimal function, creating adequate skin and muscle flaps, and hemostasis. Post-operative care involves pain management, rigid dressings, physiotherapy, and prosthetic training to prevent complications like infection, contractures, and phantom limb pain.