Embed presentation
Download to read offline








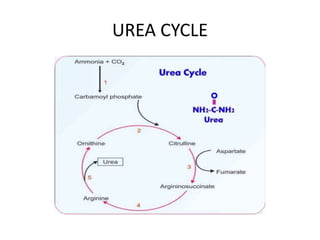

The document discusses ammonia toxicity and the role of the liver in filtering and converting ammonia into urea for excretion. It highlights the consequences of impaired liver function, which can lead to high ammonia levels in the blood and potentially fatal outcomes. The document also covers both acquired and inherited forms of hyperammonemia, emphasizing the significance of the urea cycle in preventing toxicity.