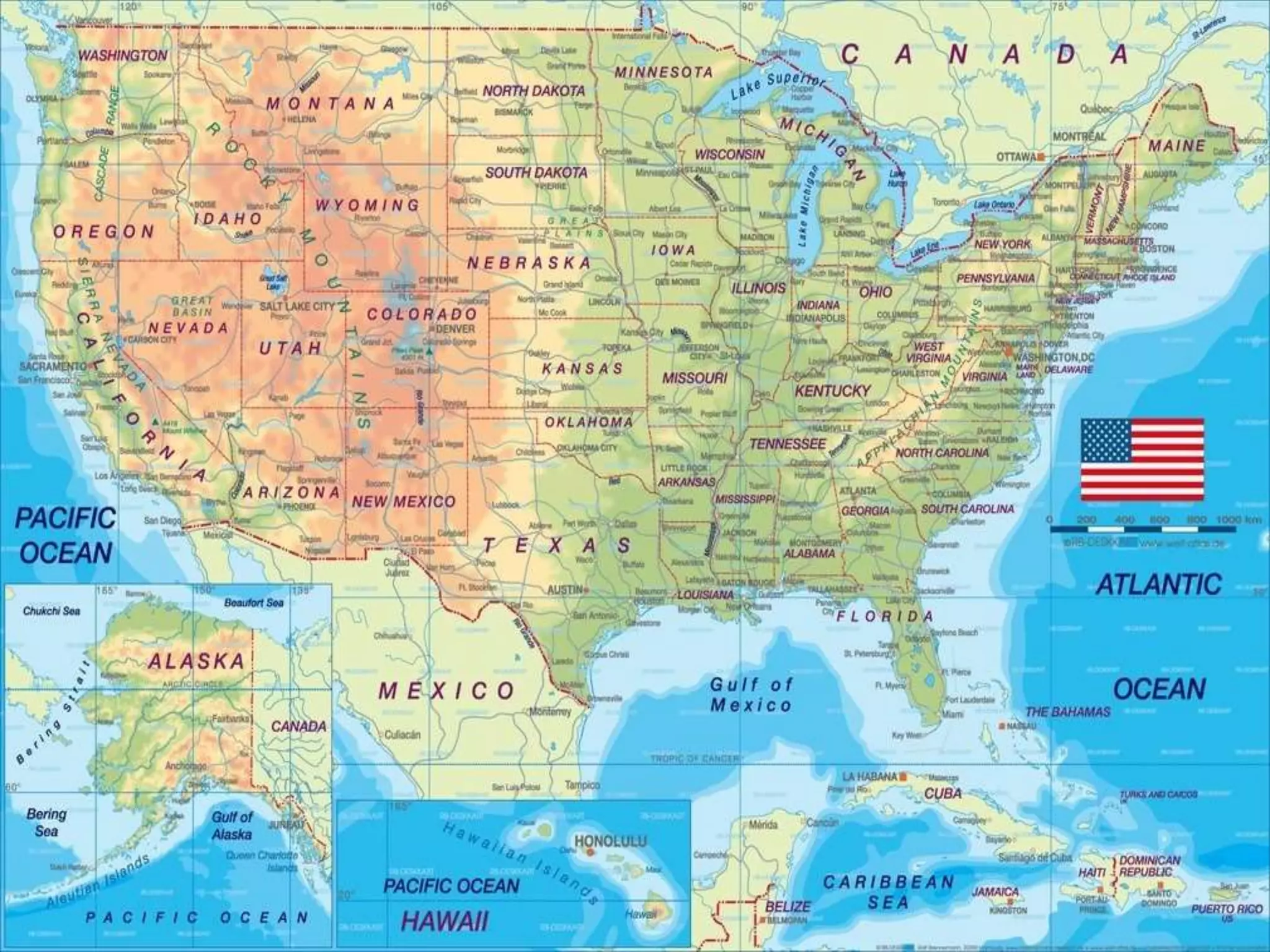
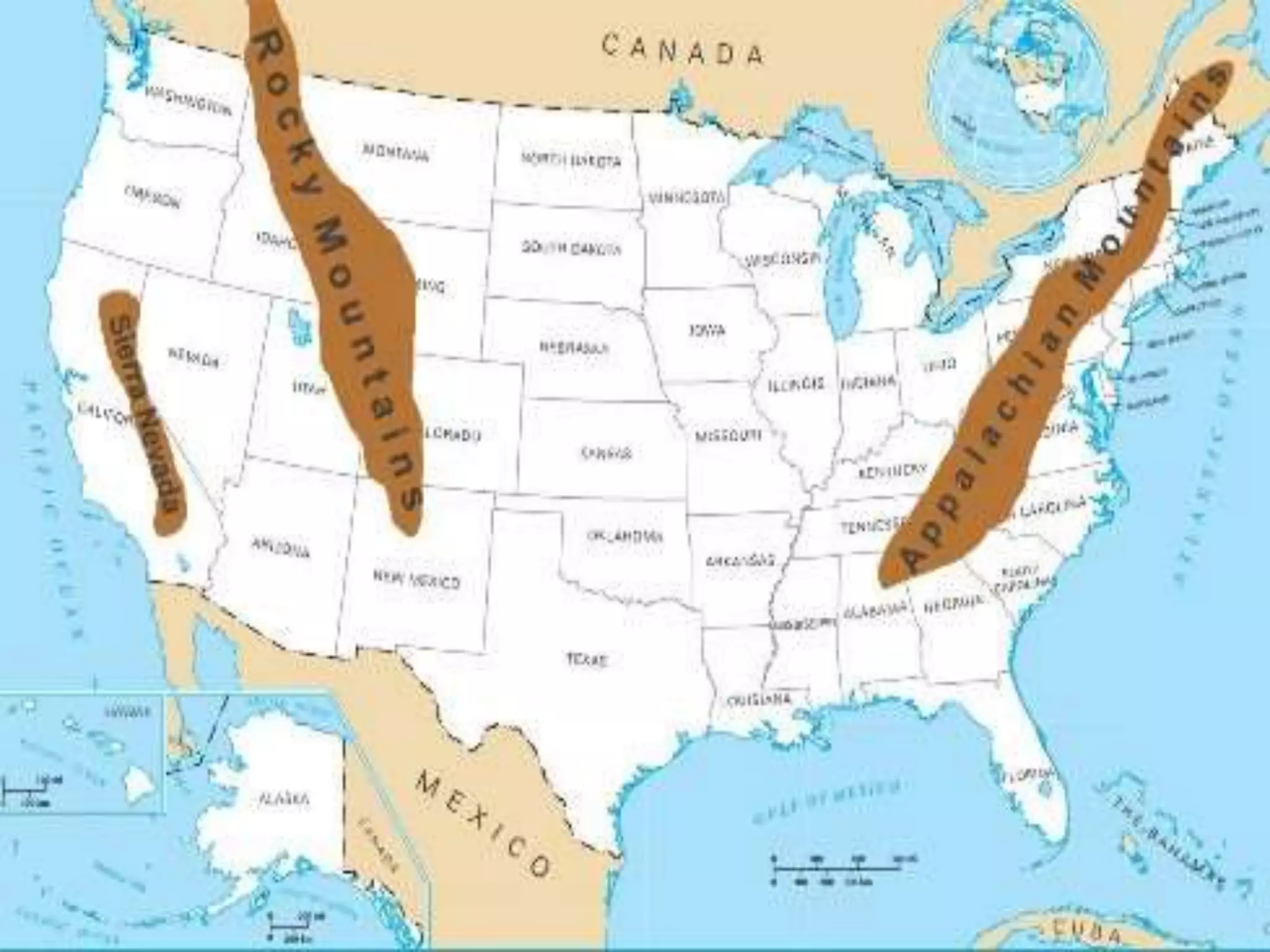
The document provides an overview of the geography of the United States. It describes the country's location between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, as well as its varied climate and terrain features, which include mountains like the Rocky Mountains and Appalachians, plains, deserts, and farmland. It also discusses the US' water resources like rivers and Great Lakes, mineral resources, national parks including Yellowstone which was the first, and regional divisions of the country.














![Yellowstone National Park is an American national
park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest
corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was
established by the U.S. Congress and signed into law by
President Ulysses S. Grant on March 1, 1872.[5][6] Yellowstone was
the first national park in the U.S. and is also widely held to be the
first national park in the world.[7] The park is known for
its wildlife and its many geothermal features, especially Old
Faithful geyser, one of its most popular.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geographicalpositionoftheusa-230318215626-c4dc7adc/75/Geographical-position-of-the-USA-ppt-17-2048.jpg)





