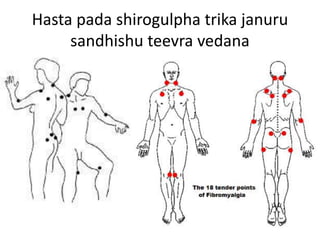
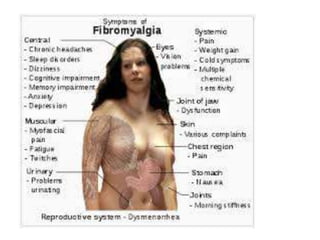
Fibromyalgia can be better correlated with Amavata than rheumatism based on symptoms. Amavata and fibromyalgia share key features - widespread persistent pain, stiffness, fatigue, non-refreshing sleep, cognitive difficulties, tenderness at specific points, and accompanying symptoms like mood issues. Both conditions involve defective metabolism and nervous system dysregulation leading to metabolic abnormalities and sensitization causing symptoms. Treatment of both focuses on correcting digestion and metabolism, reducing stress, and lifestyle modifications.