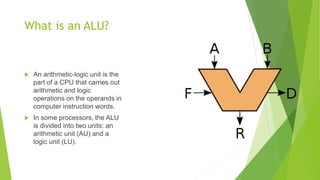
An ALU (arithmetic logic unit) carries out arithmetic and logic operations on operands in computer instructions. It receives an opcode and operands from memory and performs operations like addition, subtraction, AND, OR, XOR. An FPGA (field-programmable gate array) is a programmable integrated circuit that allows a user to implement custom logic functions. Verilog HDL (hardware description language) is used to describe the behavior of digital circuits, including how blocks are connected and data flows through an FPGA.