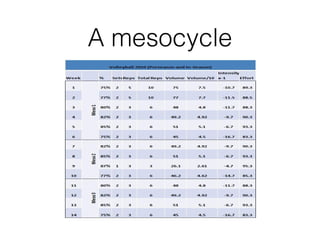
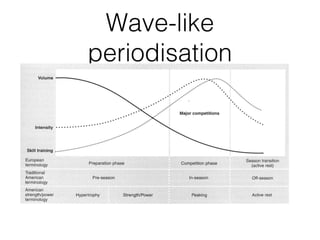
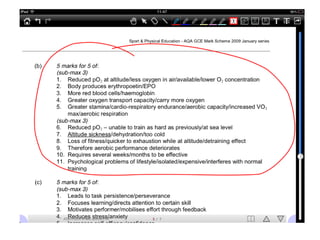
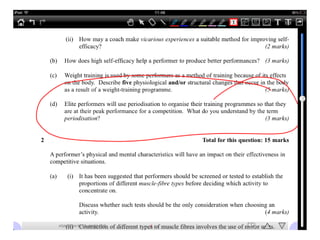
This document discusses altitude training and periodization. Altitude training involves living or training at high altitude to improve endurance performance through increased red blood cell concentration upon returning to sea level. The process involves acclimatization, primary training at altitude, and recovery upon returning to sea level. Problems with altitude training include physiological stresses and the disruption to an athlete's normal training. Periodization involves planning training in cycles to optimize performance and avoid overtraining. It includes tapering training loads before events to allow the body to peak and supercompensate.