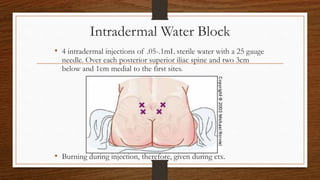
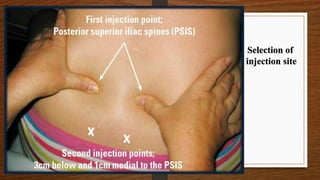
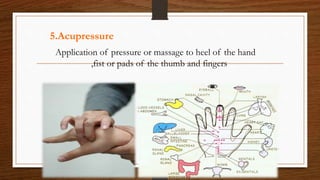
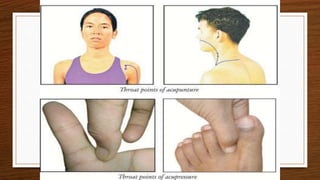
The document discusses various alternative therapies in maternity care, including Ayurveda, homeopathy, acupuncture, and more, highlighting their benefits for pregnancy and labor. It emphasizes the importance of holistic care through specific behavioral practices, dietary guidelines, and non-pharmacologic pain management techniques during childbirth. The text also covers supportive measures such as the role of doulas and the efficacy of different therapeutic approaches in enhancing the birthing experience.