Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




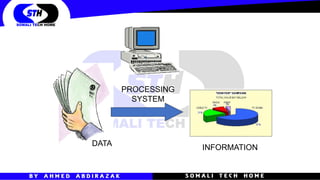


A computer is an electronic device that accepts data as input, manipulates and processes that data, and produces information as output based on instructions stored in its memory. Computers come in various types for different uses including supercomputers for processing extremely large amounts of data like weather predictions, mainframes for businesses and governments, and personal computers. Computers perform a cycle of inputting data, processing it, outputting information, and storing the results through their processing system. They are used for a variety of tasks in businesses, governments, schools, and personal life.






