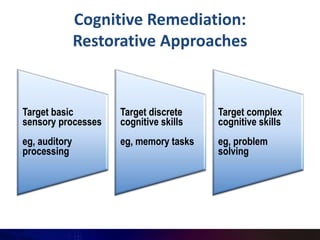
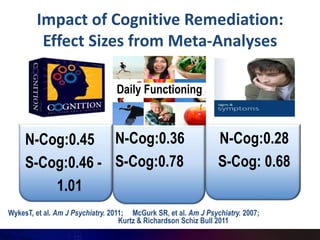
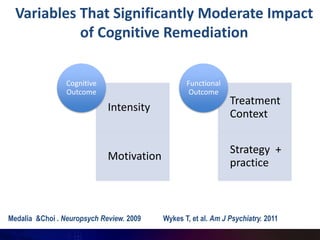
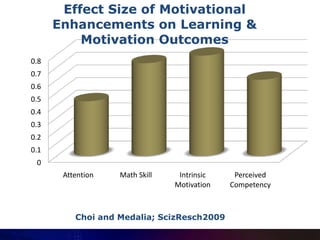
This document summarizes a presentation on cognitive remediation for schizophrenia. Cognitive remediation aims to improve cognitive processes like attention, memory, and executive function through behavioral training interventions. It relies on neuroplasticity to strengthen connections in the brain. Exercises target basic sensory skills, discrete cognitive abilities, and more complex skills. Studies find cognitive remediation improves cognition, functioning, and motivation, especially when treatment is more intensive, motivational factors are incorporated, and exercises are personalized. Typical programs involve cognitive assessment, goal setting, group sessions 2+ times per week for 3-4 months using drill and strategy practice, and bridging to real-world skills.