1) Alcohol is a depressant that impairs physical and mental functioning. It is absorbed quickly into the bloodstream and affects every organ, including the brain.
2) Chronic alcohol use can lead to alcoholism, a disease characterized by cravings, loss of control over drinking, physical dependence, and tolerance requiring greater amounts over time.
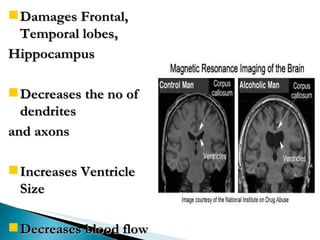
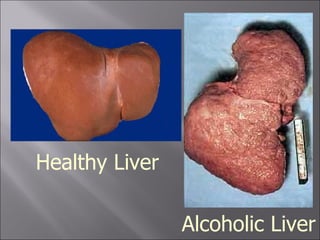
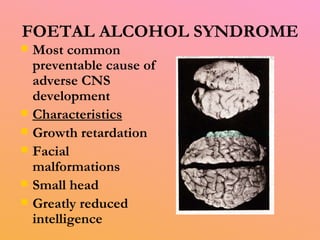
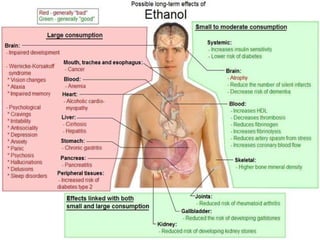
3) Alcohol damages many organs like the brain, liver, heart, and pancreas and can increase risks of health issues like cancers, strokes, and pancreatitis. Fetal alcohol syndrome is also a risk if a woman drinks during pregnancy.