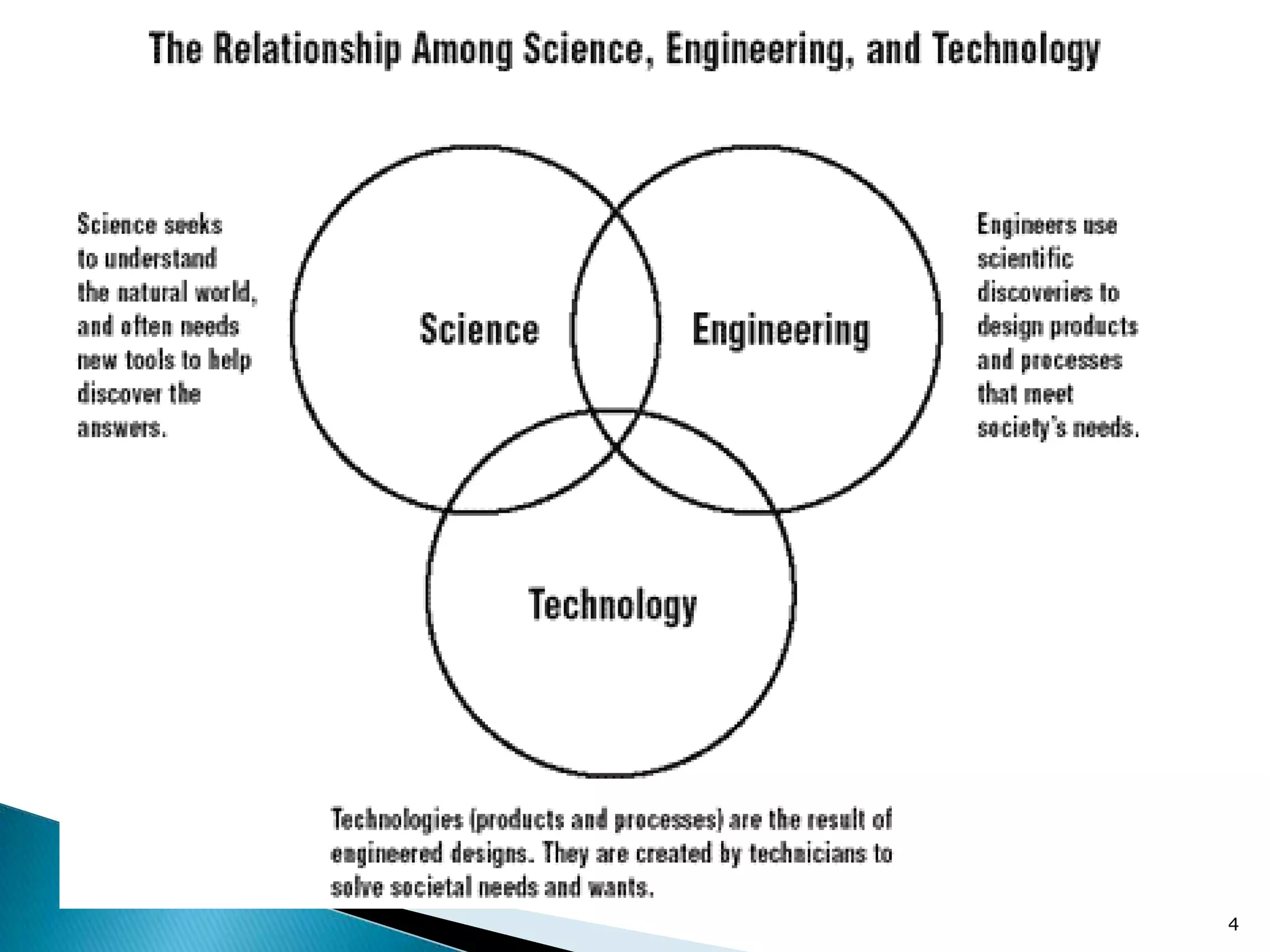
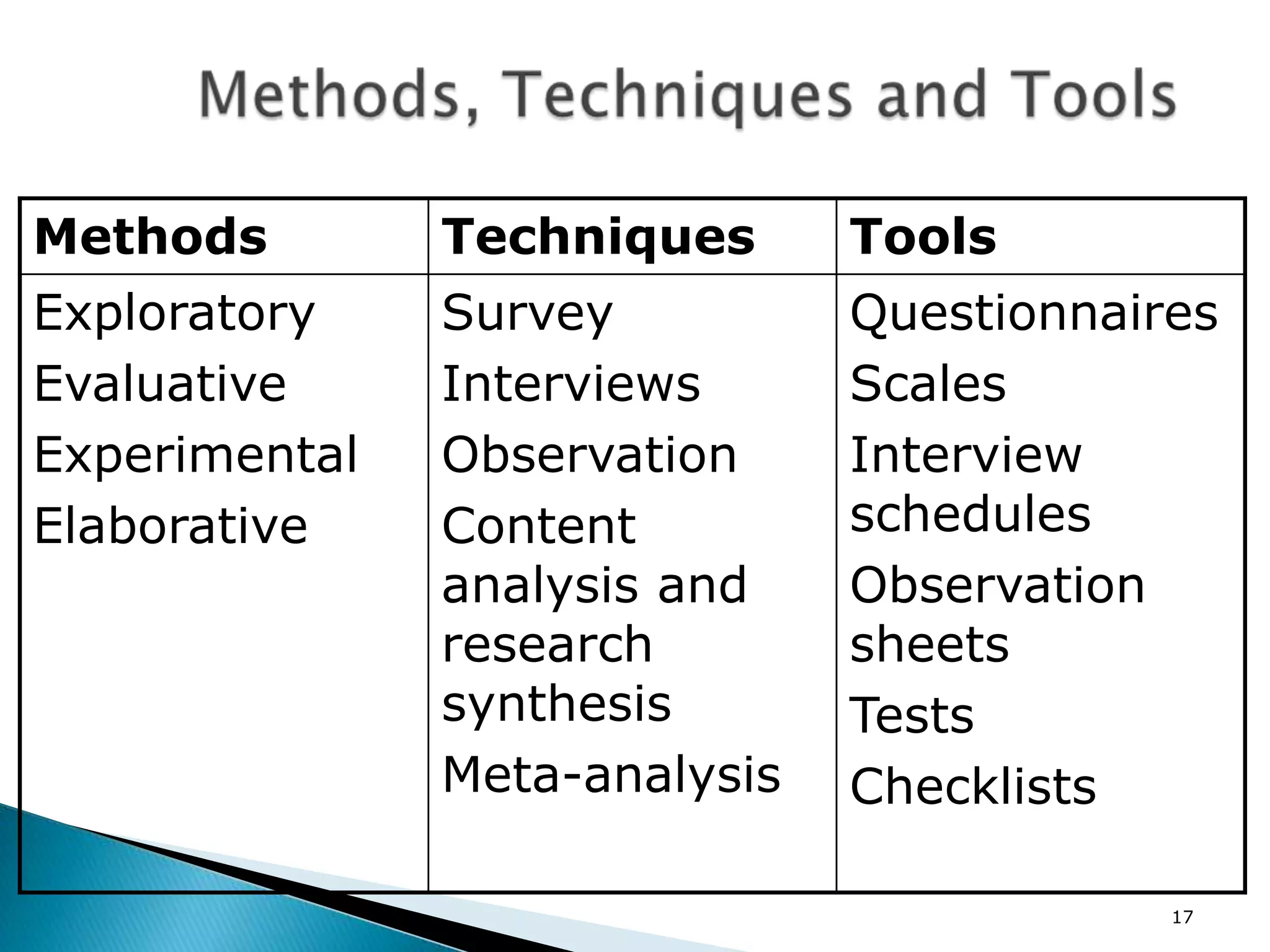
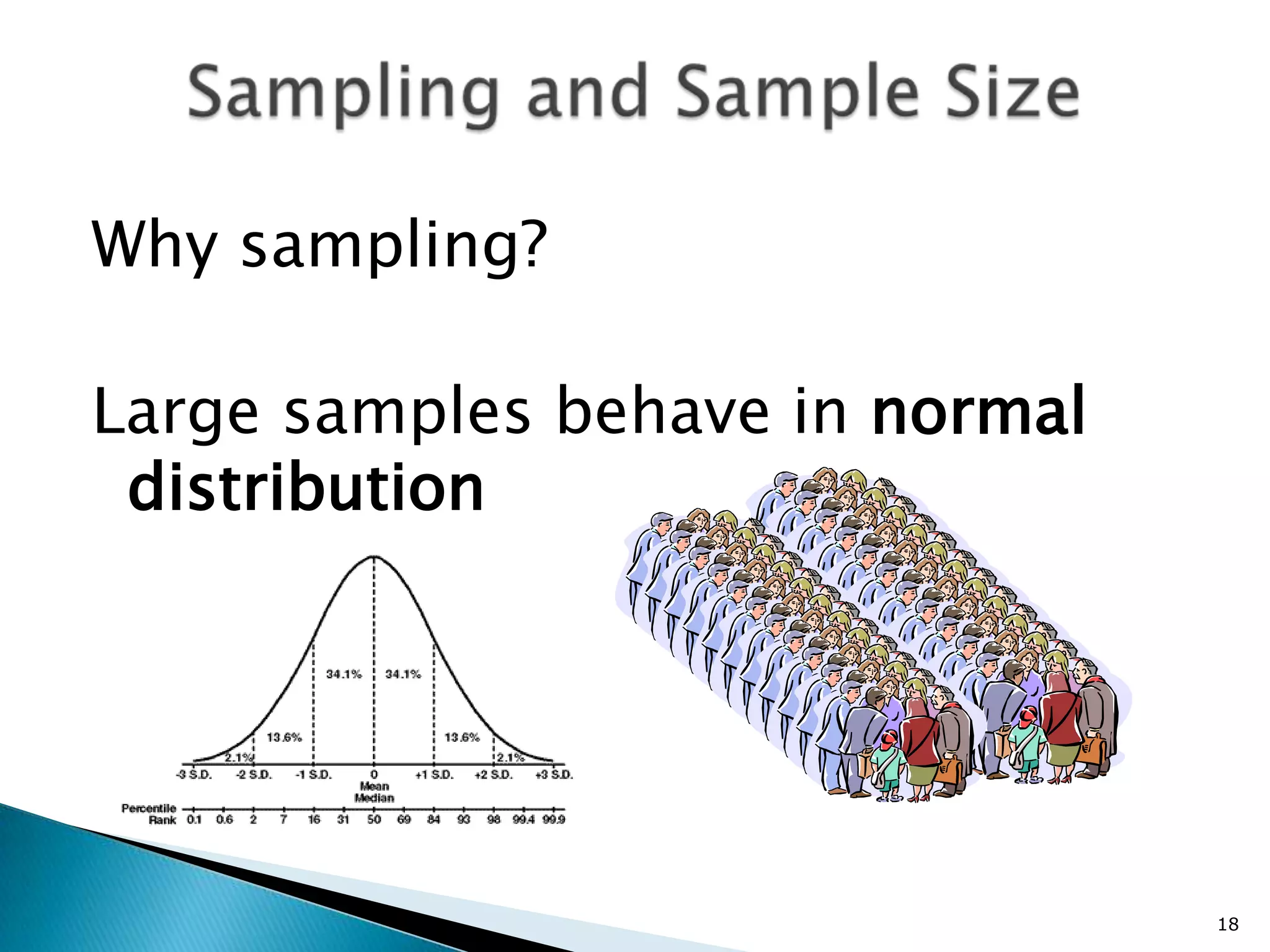
This document provides an overview of a research methods training workshop conducted by the Afghanistan Ministry of Higher Education at the Asian Institute of Technology Language Center. The 3-day workshop covered topics such as defining research, types of research, writing a research problem, developing a research design, and components of a research proposal. It also discussed qualitative and quantitative research methods, sampling techniques, developing a research proposal outline, and presenting a research project. The document provides details on the content covered each day of the workshop to help participants learn the steps for developing and conducting a research study.