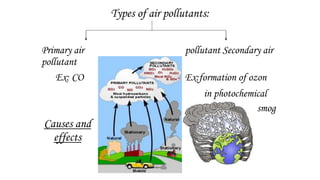
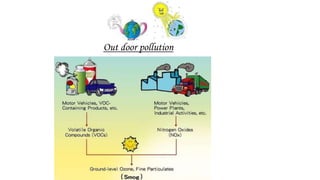
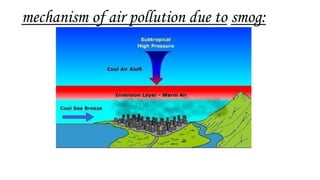
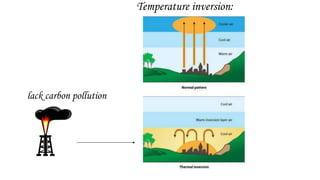
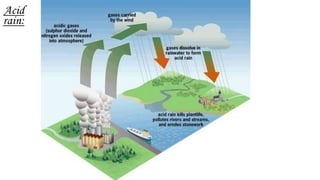
This document discusses air pollution, including its definition, types of pollutants, sources, and health effects. It defines air pollution as physical, chemical, and biological agents that can modify the natural atmosphere. There are primary pollutants emitted directly and secondary pollutants formed from atmospheric reactions between primary pollutants. Outdoor sources include combustion from power plants, vehicles, stoves, and fires. Indoor sources consist of aerosols, dust, refrigerants, and natural sources like wildfires and volcanoes. Pollutants listed are carbon monoxide, chlorofluorocarbons, hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and nitrogen and sulfur oxides. Both short and long term health effects are detailed, ranging from