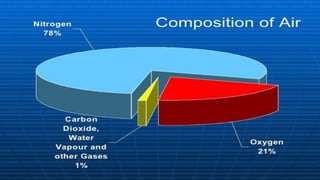
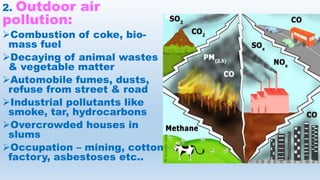
Air pollution is defined as the presence of harmful substances like gases, particles, or biological molecules in the atmosphere that negatively affect human health. There are two main types of air pollutants: chemical pollutants which include gases, particulate matter, and metals, and biological pollutants such as pathogens. Major sources of air pollution include industries, automobiles, and domestic activities like burning fuels. Air pollution causes both immediate and long term health effects in humans like respiratory illnesses and cancer. It also harms plants, soils, buildings and contributes to issues like global warming. Prevention and control of air pollution involves engineering controls at pollution sources, legislative standards and limits, and general public measures.