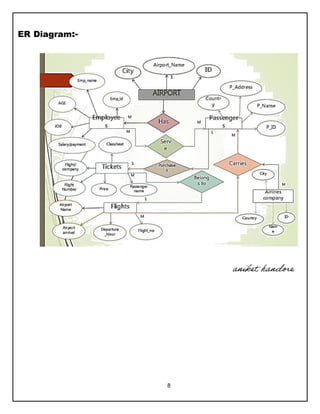
The document provides a comprehensive overview of database management systems (DBMS) and their application in an airline management system, highlighting the benefits, implementation steps, and data organization through ER diagrams and SQL. It emphasizes the efficiency, data independence, and security advantages of using DBMS while also addressing potential issues such as data duplication. Additionally, it outlines required entities and their attributes relevant to the airline industry, as well as basic SQL commands for data manipulation.