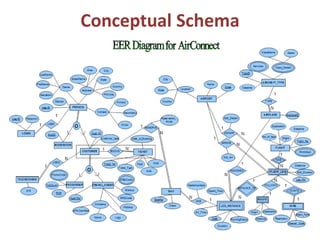
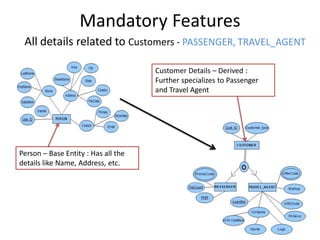
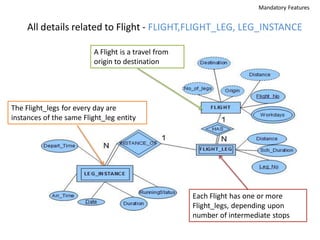
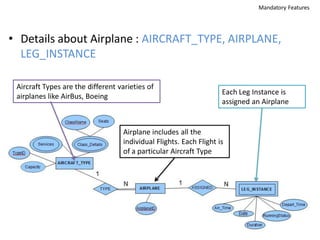
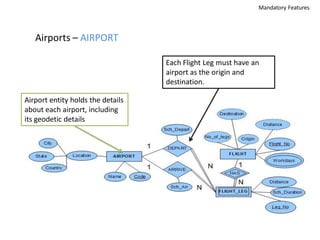
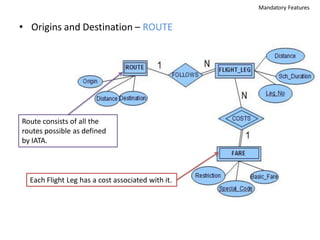
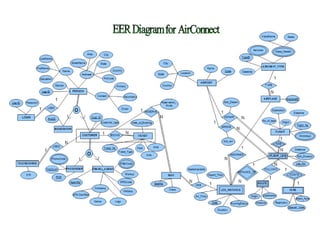
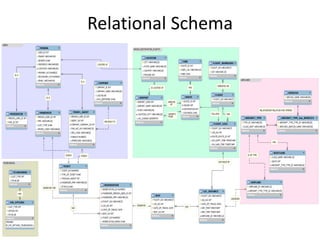
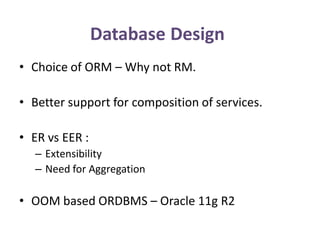
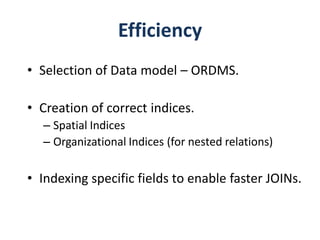
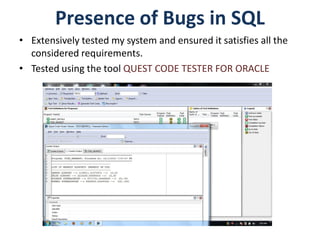
The document outlines a project for designing a renewed database structure for Airconnect, a low-cost airline, emphasizing the gathering and analysis of requirements, key entities, and relationships. It includes specifics on mandatory features related to customers, flights, airports, routing, security measures, and testing methodologies, as well as best practices throughout the system development life cycle. Additionally, it discusses the implementation using Oracle 11g and the significance of data modeling approaches such as ORM.