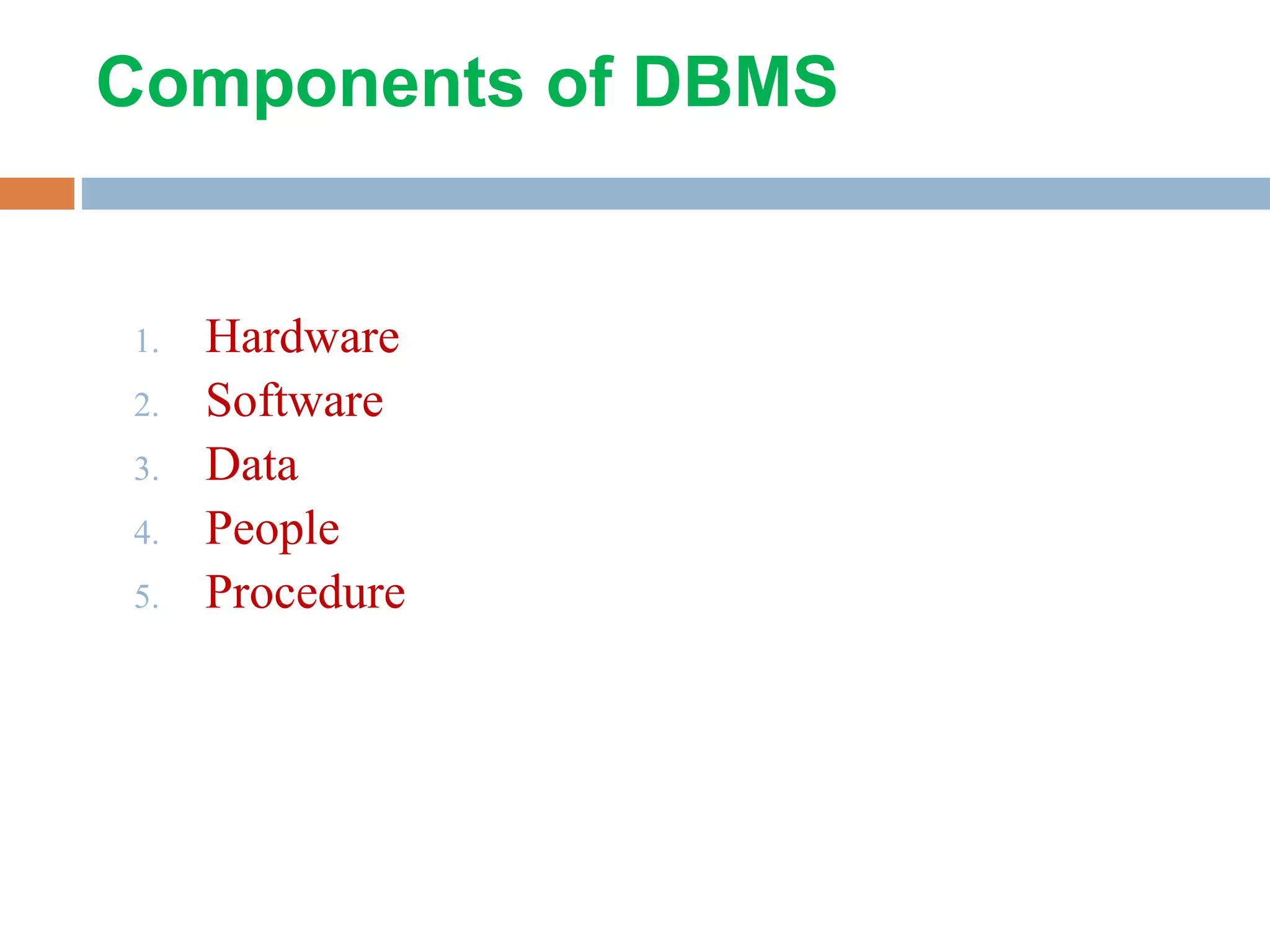
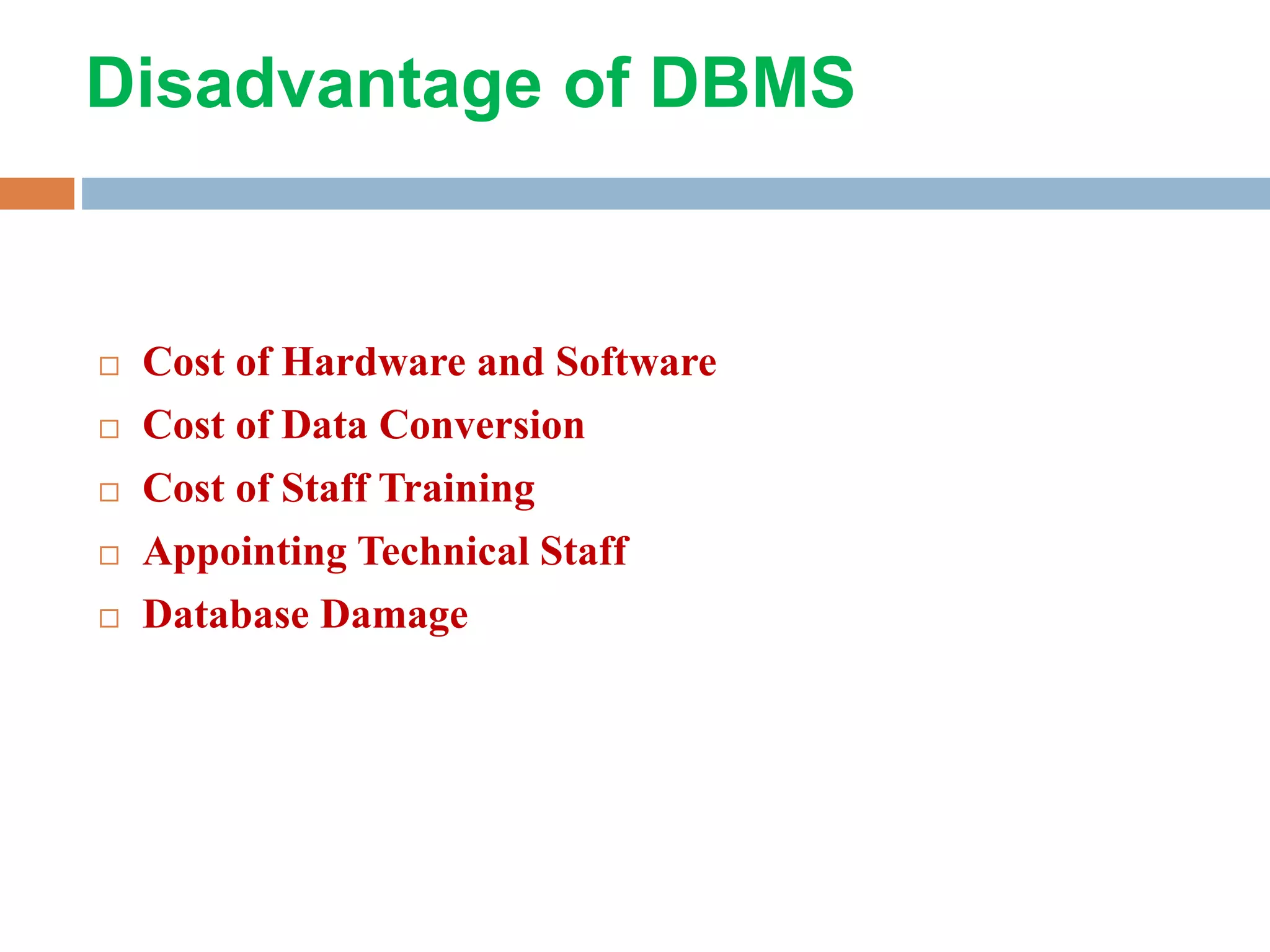
This document discusses database management systems (DBMS). It defines a DBMS as consisting of a collection of interrelated data and a set of programs to access, update and manage that data. The purposes of a DBMS are to reduce data redundancy, inconsistencies, and isolation while improving security, integrity and sharing of data. A DBMS has several components including hardware, software, data, people and procedures. It provides advantages such as data consistency, integration and security while also having costs such as equipment, conversion and training. The document also describes the different layers and languages of a DBMS, including data definition languages to define schemas and data manipulation languages to manage data.