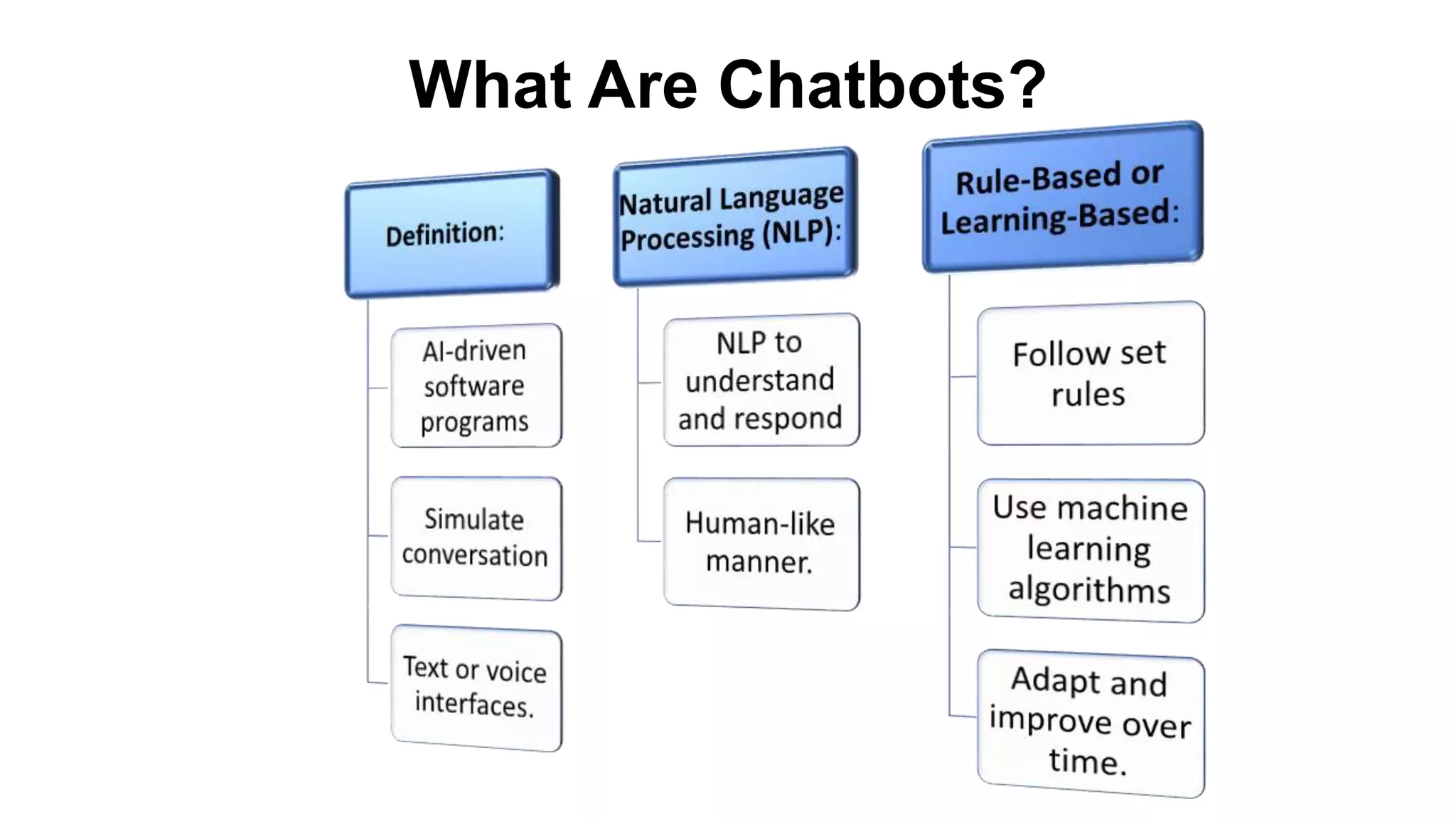
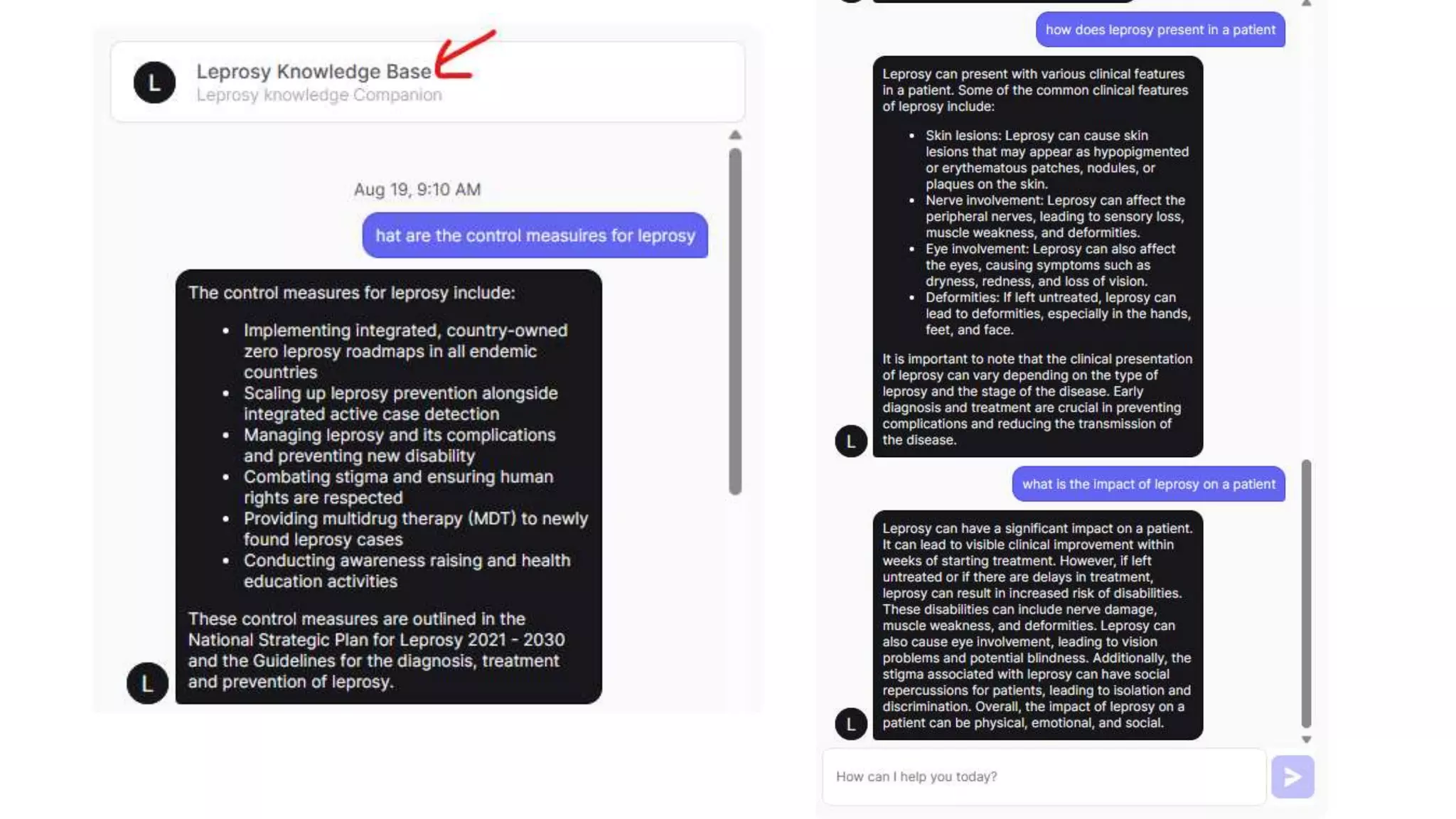
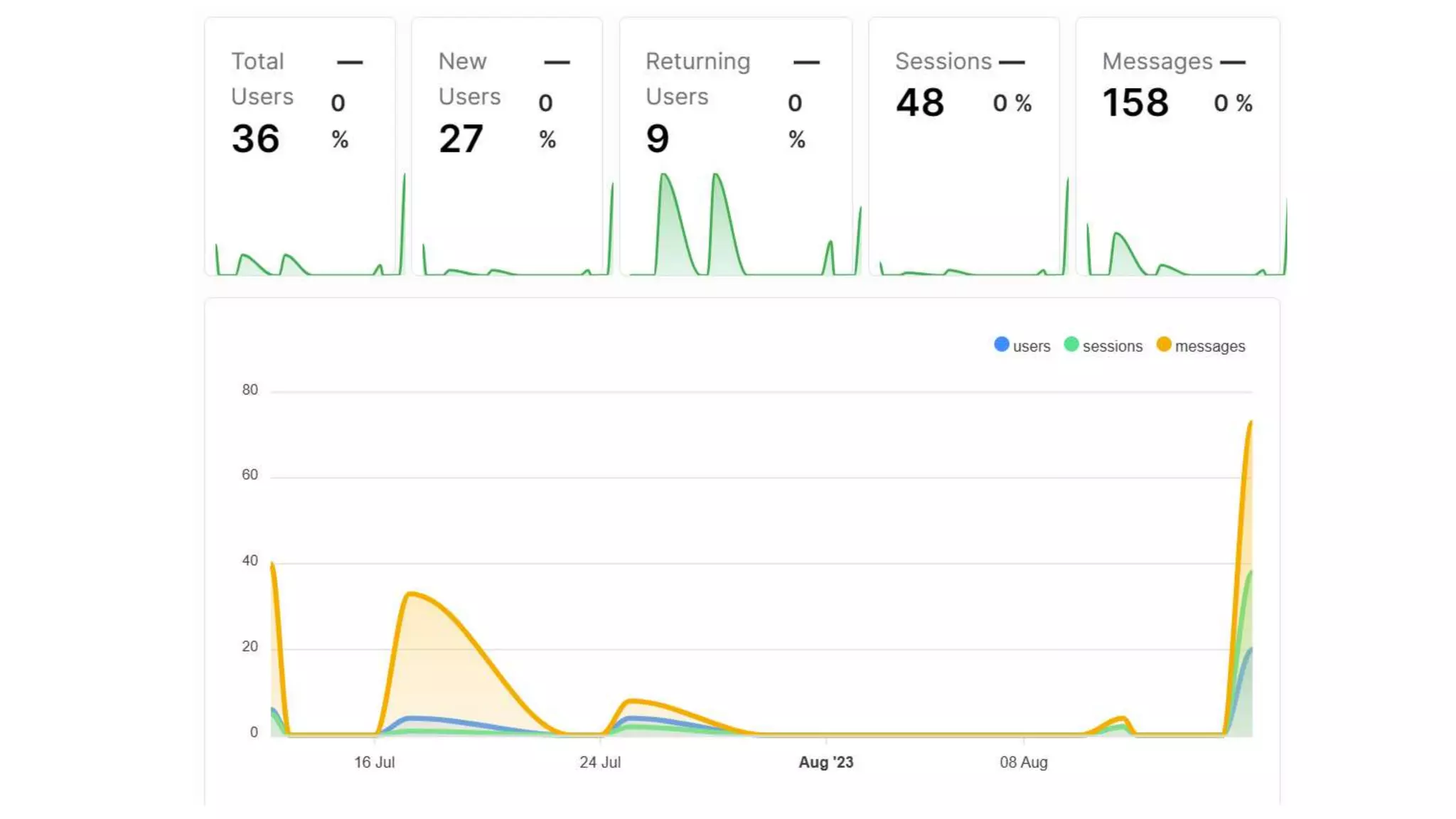
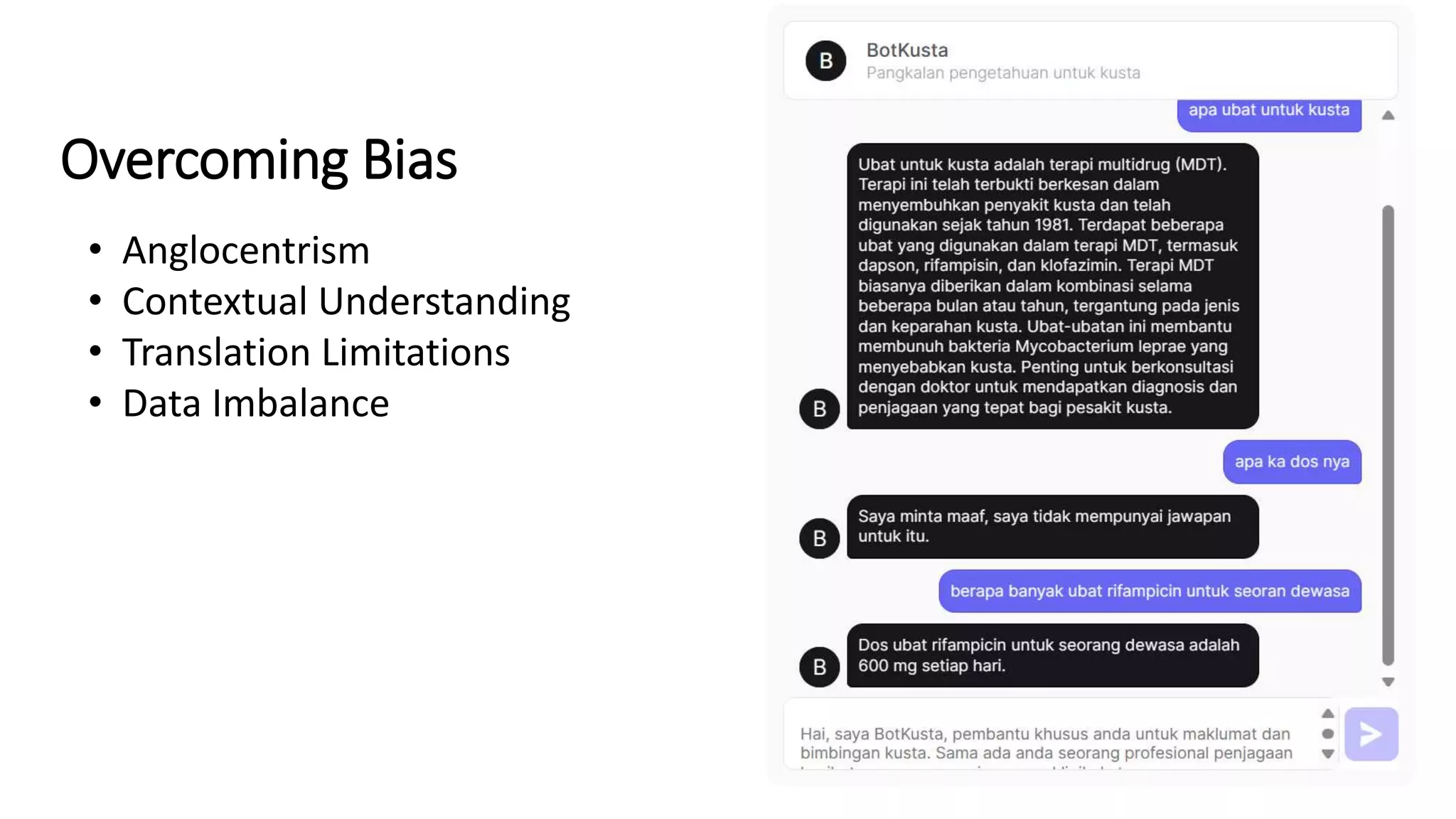
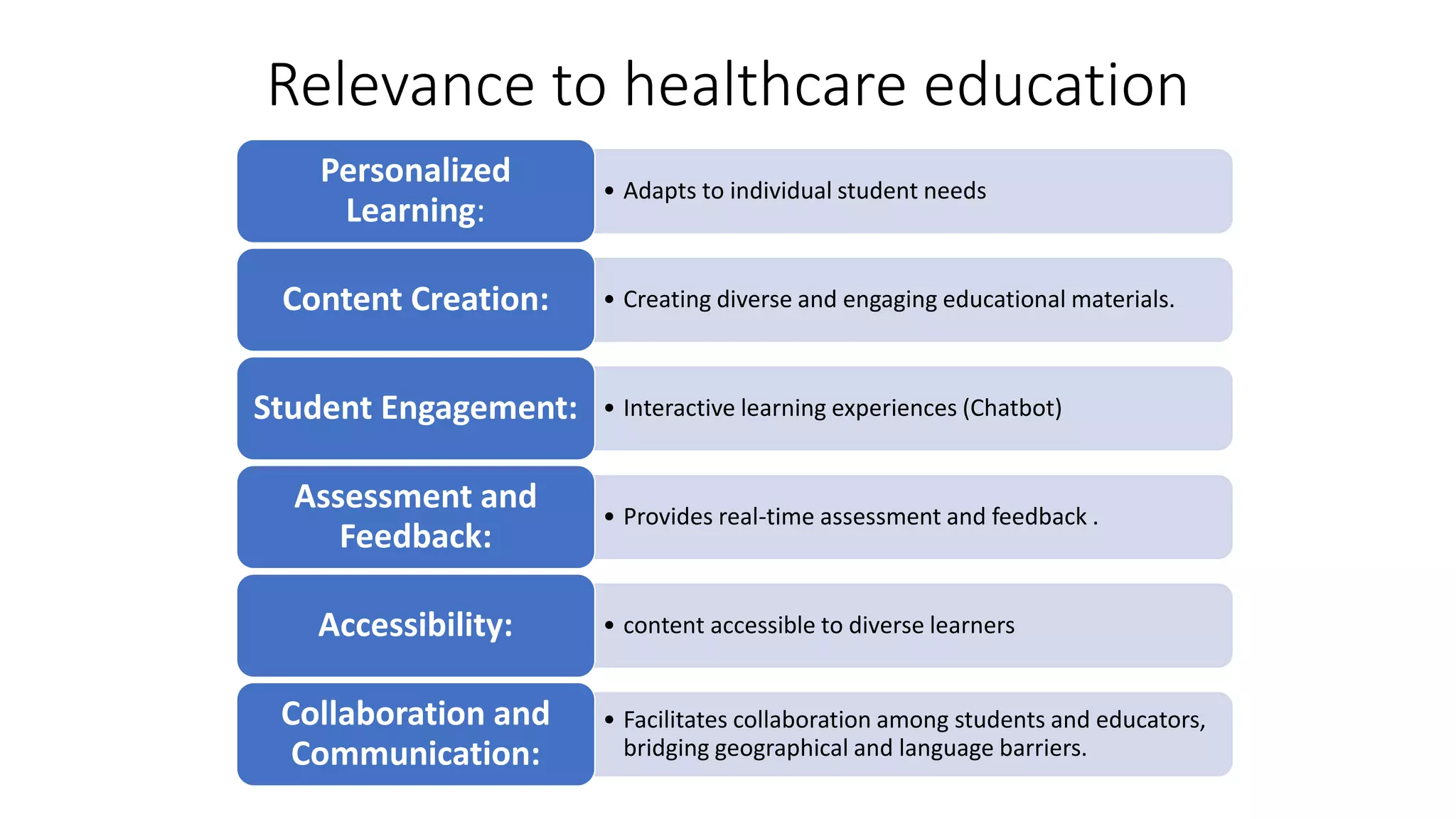
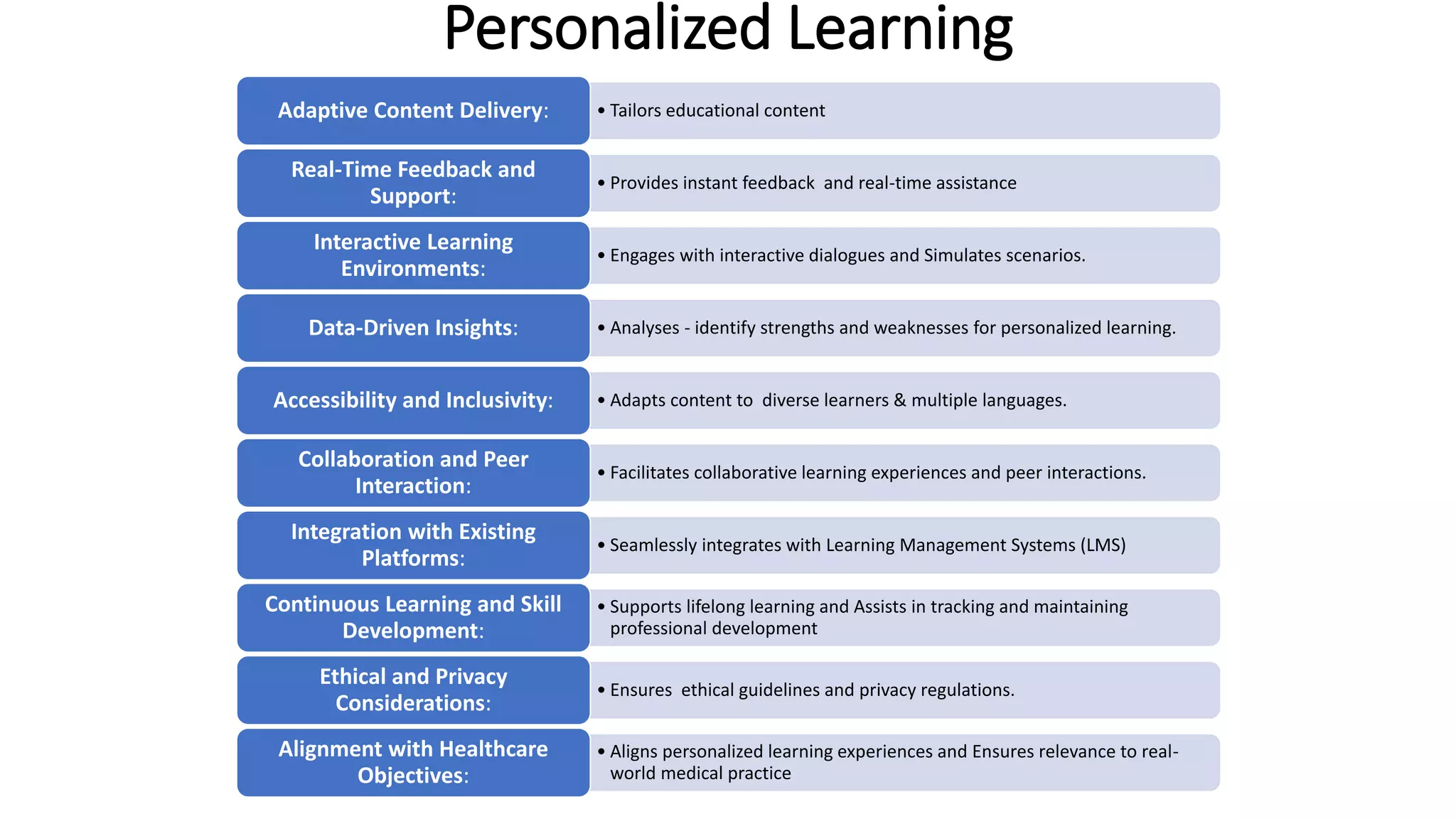
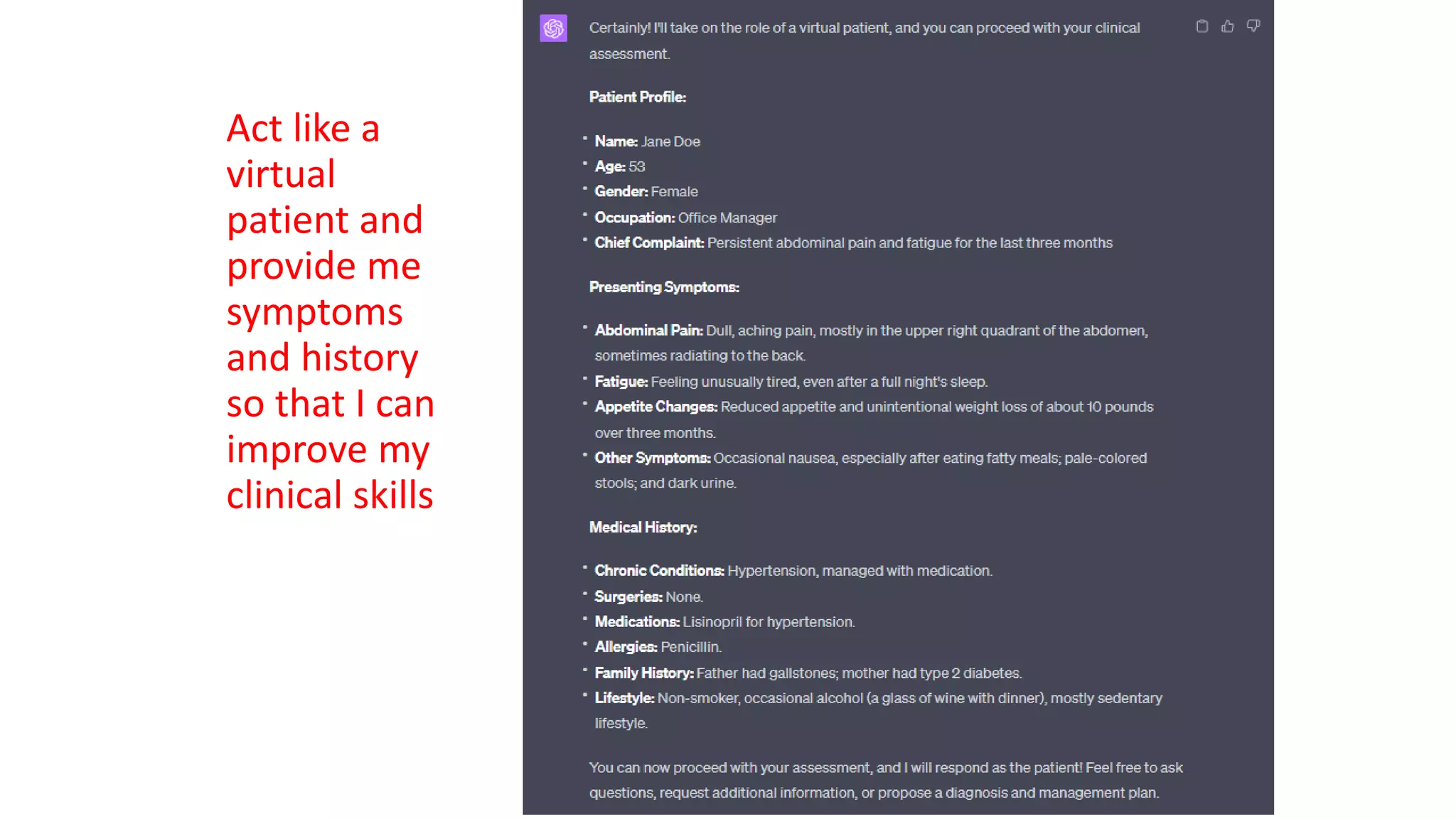
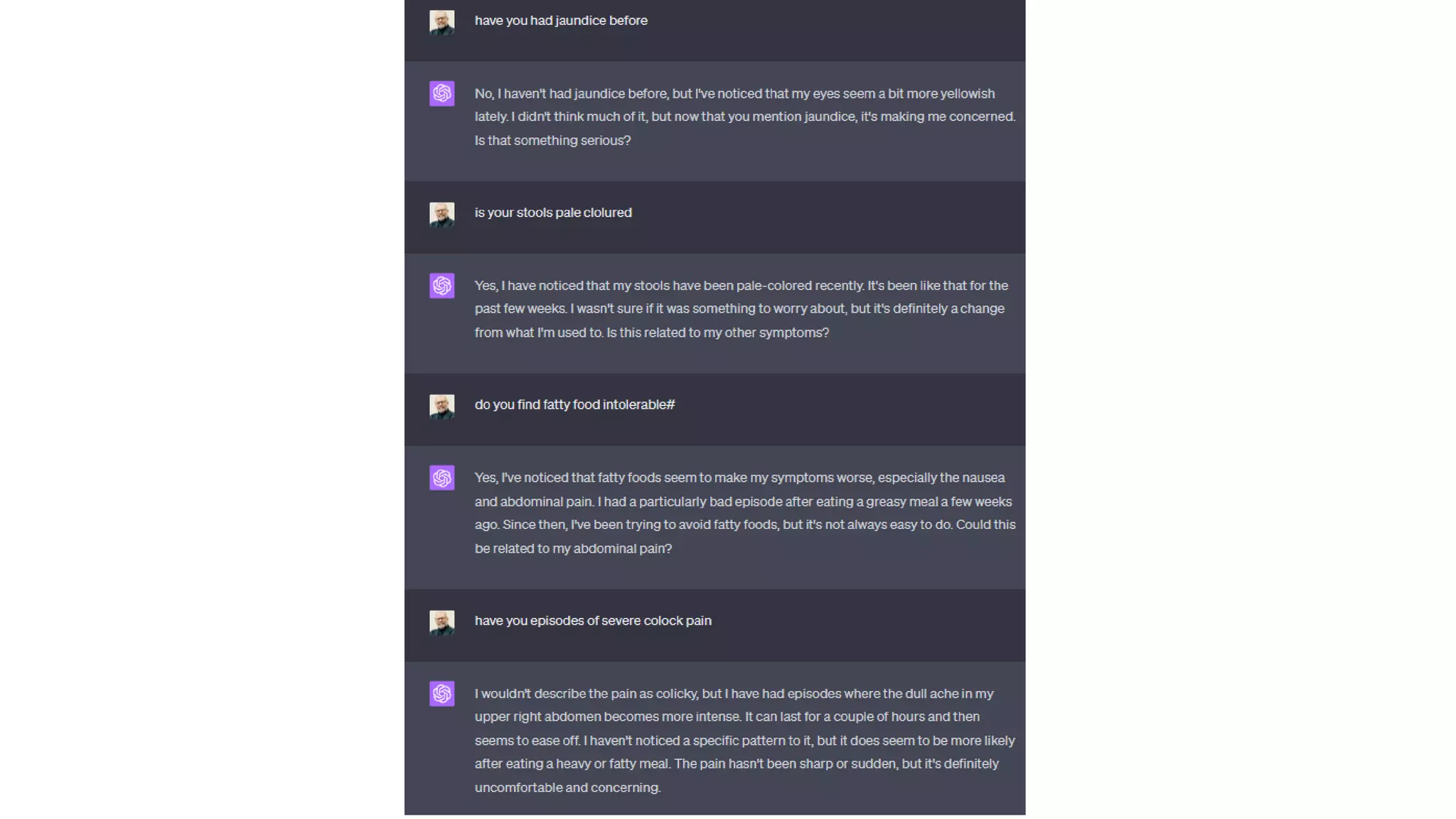
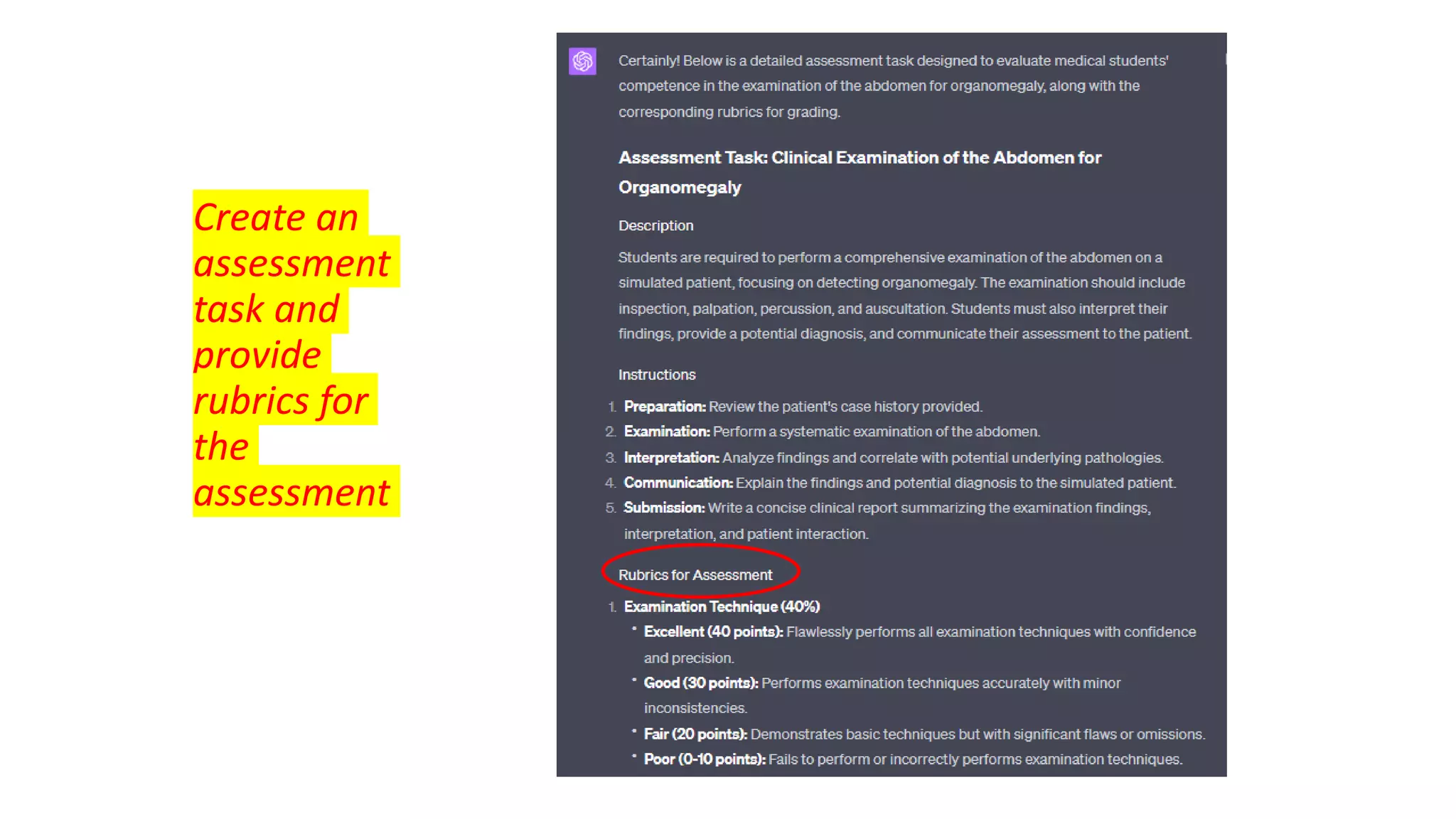
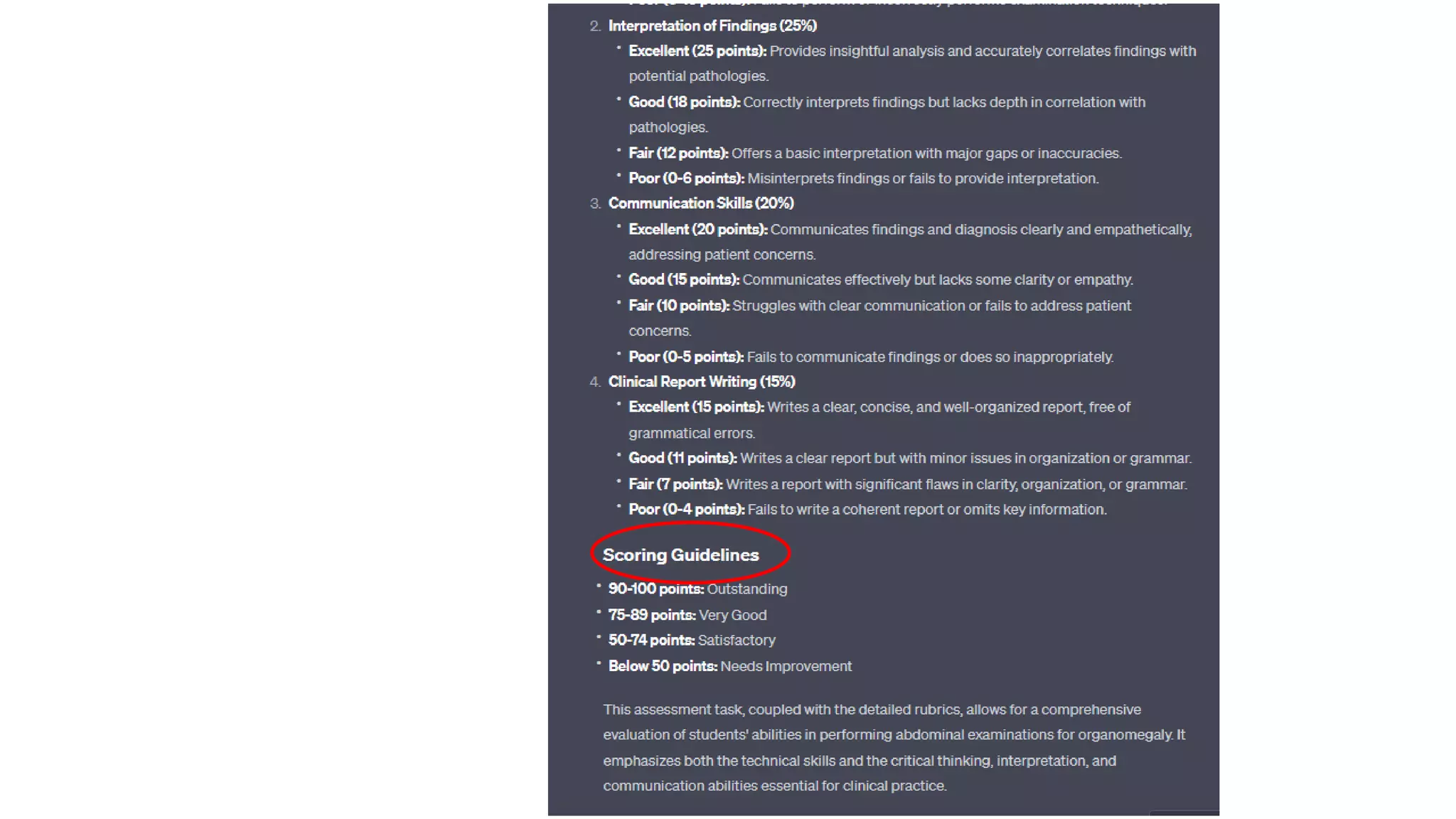
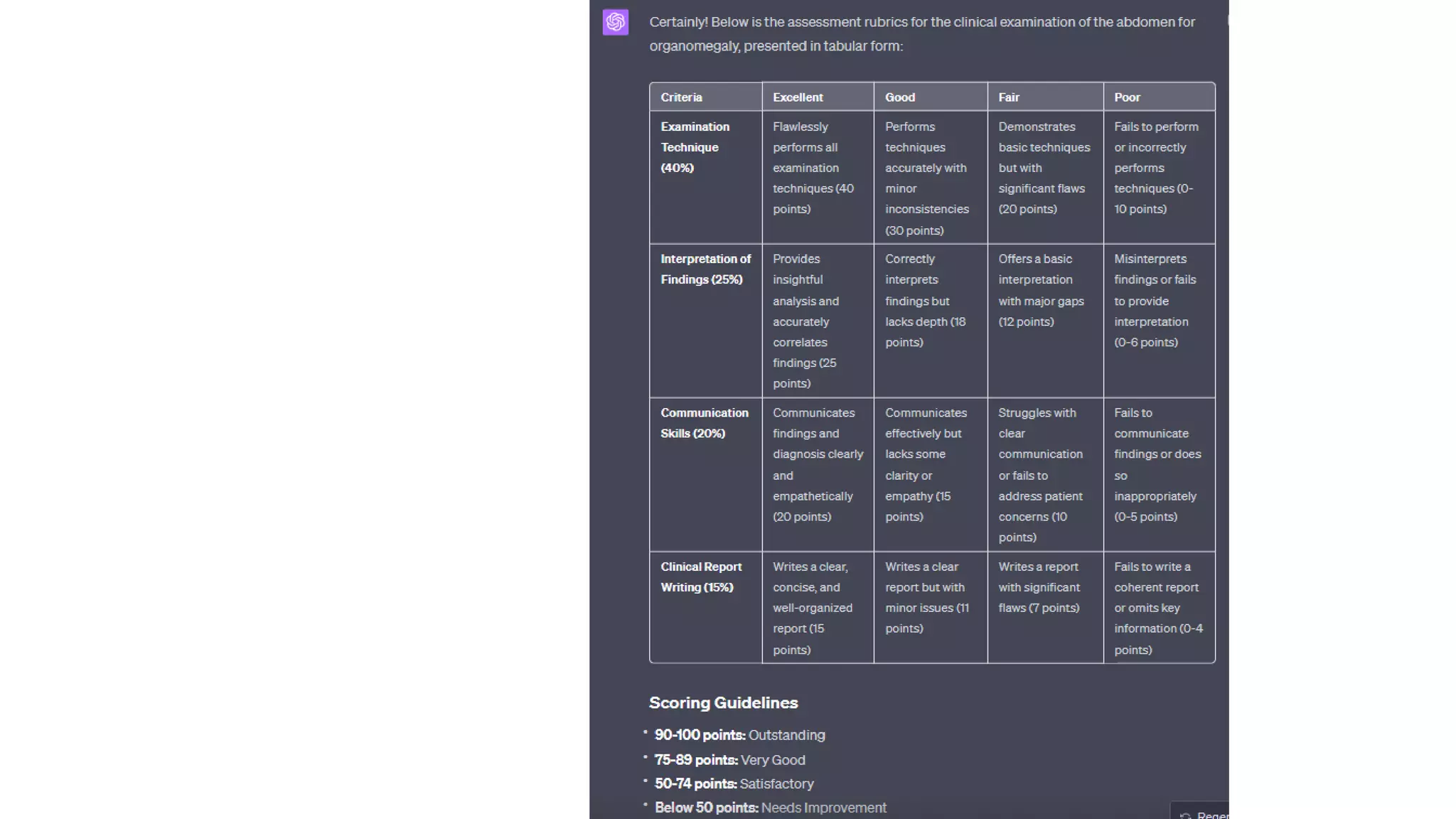
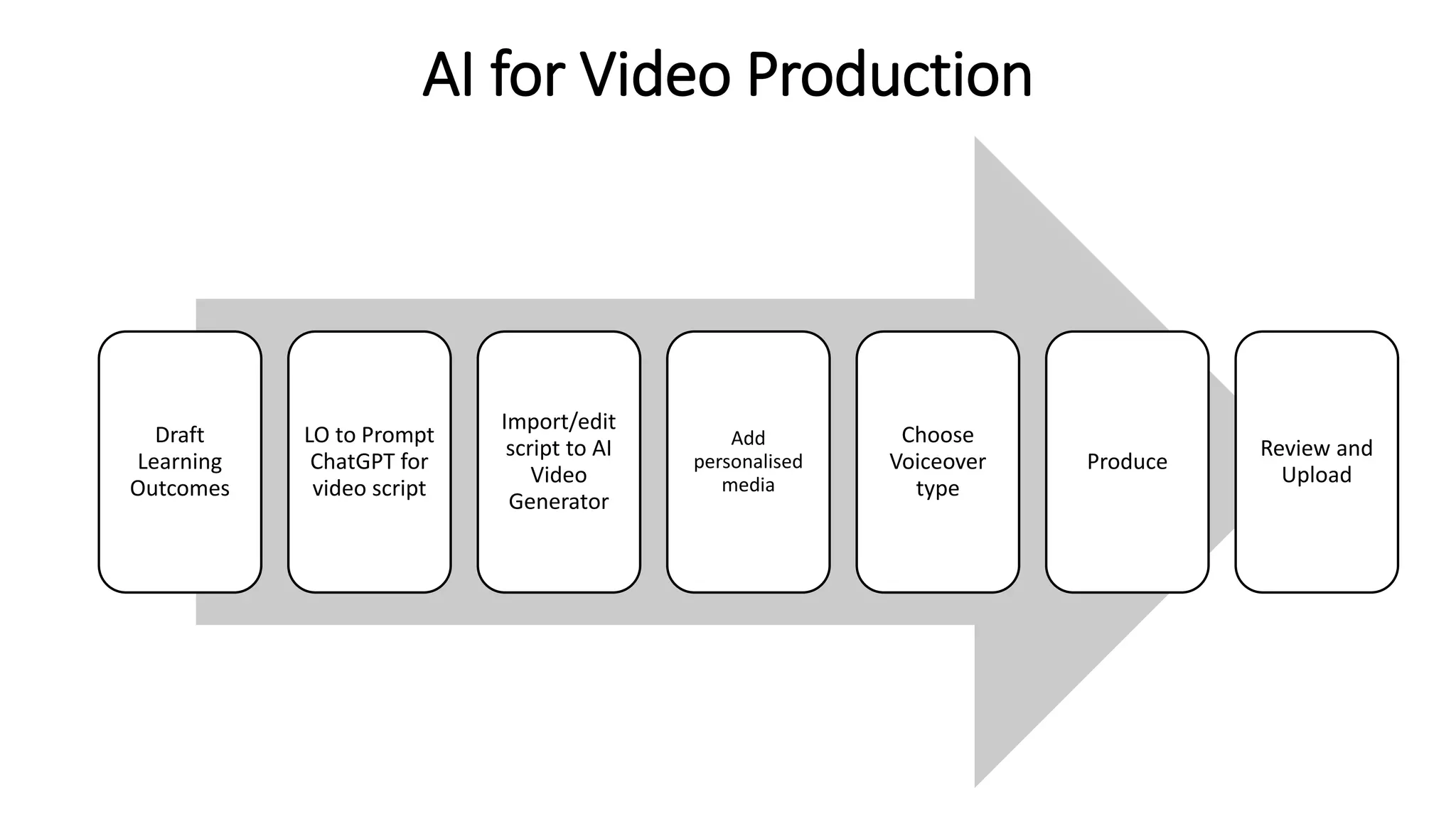
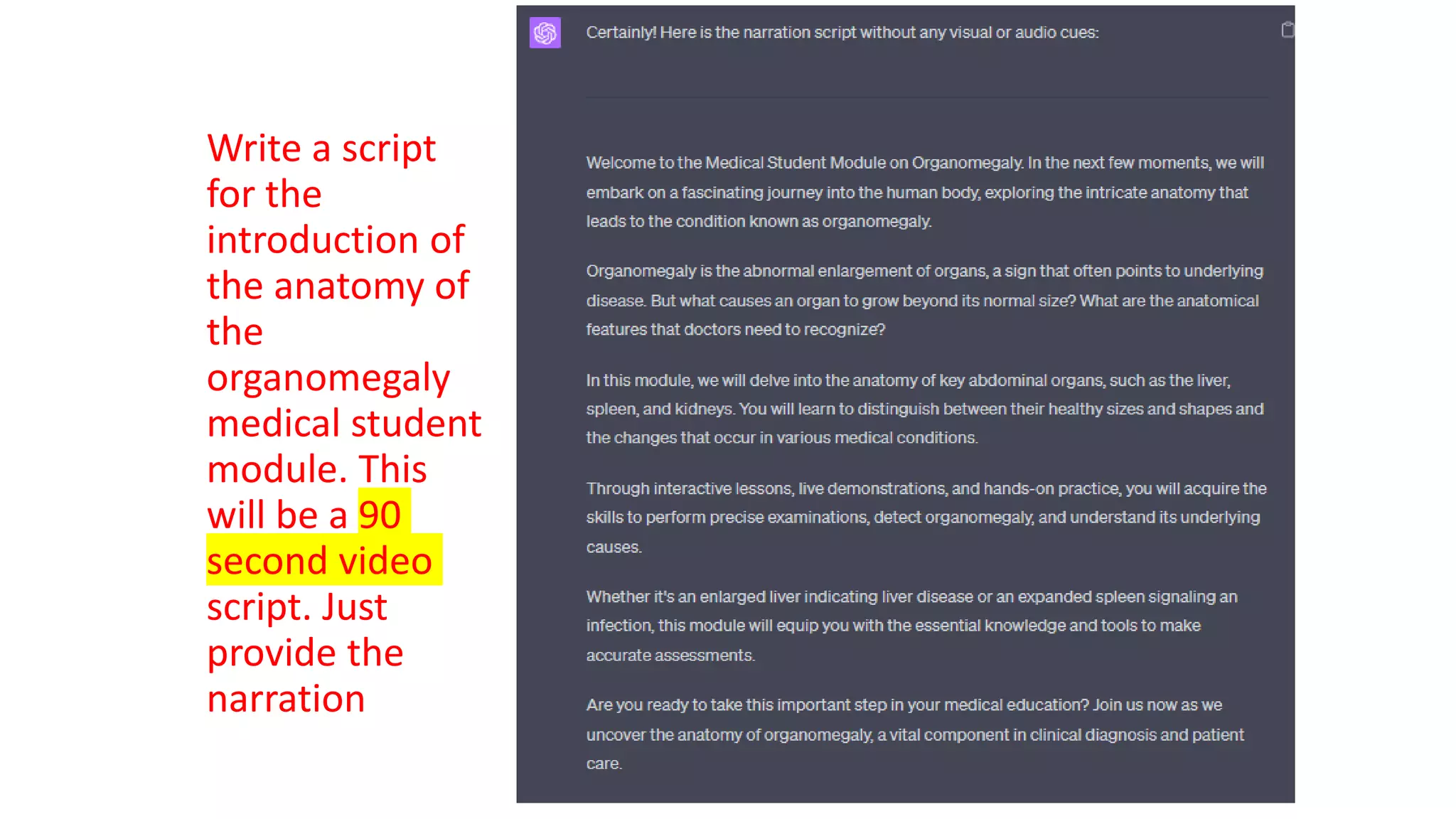
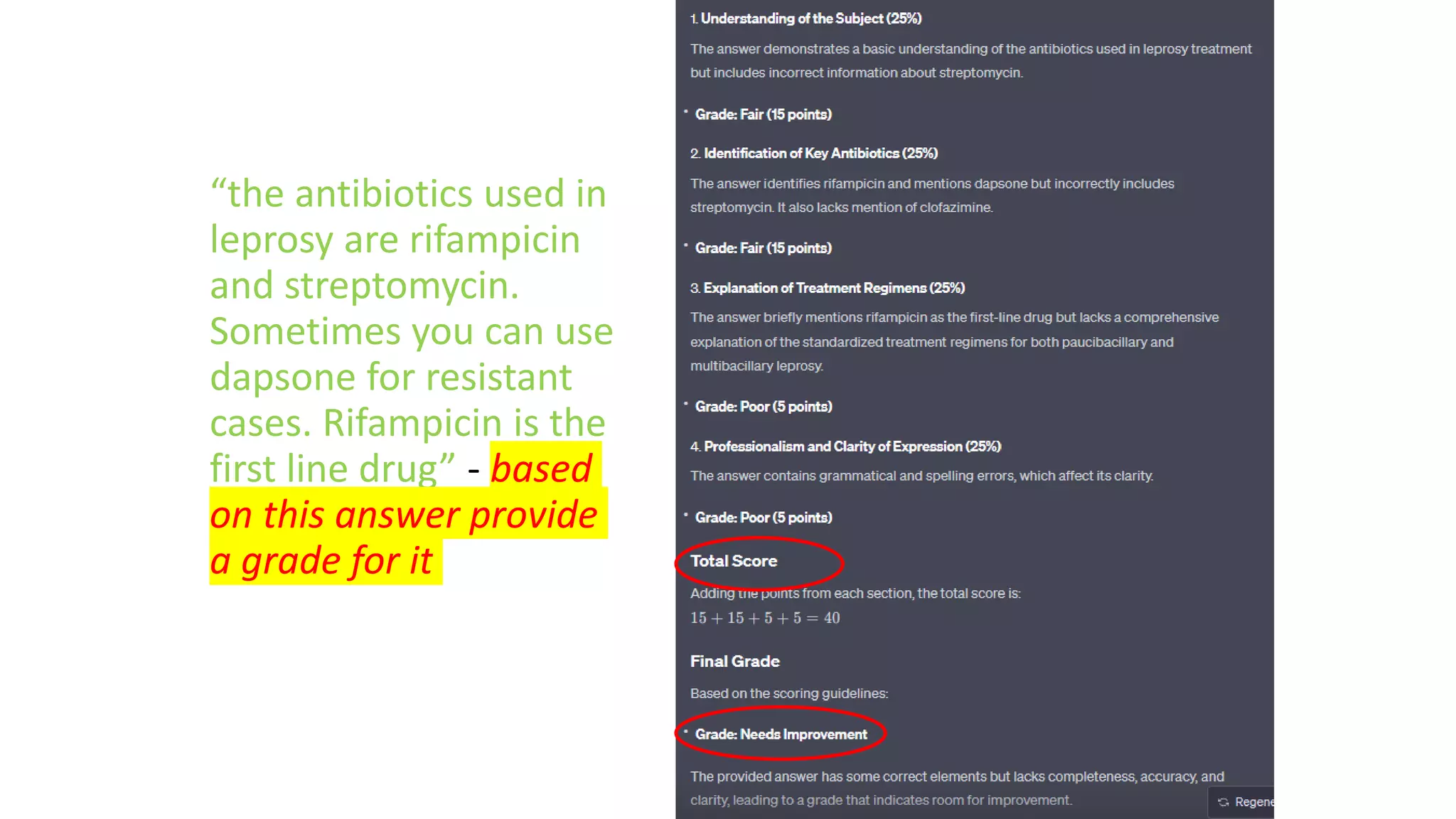
Here is a proposed rubric to assess answers to the question "What are the antibiotics for leprosy treatment?":
4 - Identifies both rifampicin and streptomycin as first-line antibiotics for leprosy treatment. May also mention dapsone as an alternative for resistant cases. Shows understanding that rifampicin is the primary antibiotic.
3 - Identifies both rifampicin and streptomycin but does not provide context about them being first-line. May be missing detail about dapsone. Answer is largely correct but lacks some context.
2 - Identifies one of the main antibiotics (rifampicin or streptomycin) but is missing the other. May provide an incorrect or irrelevant