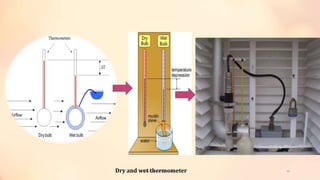
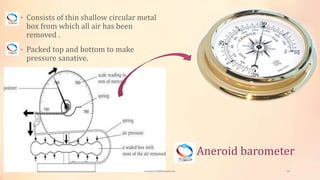
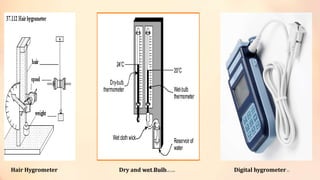
Vivek Yadav's presentation discusses agrometeorological instruments used for protected crop cultivation. It introduces meteorology and explains how measuring weather parameters like temperature, humidity, solar radiation, and rainfall can help farmers plan cropping patterns, reduce losses, and manage pests and diseases. The presentation describes common instruments for measuring these parameters, including sunshine recorders, quantum sensors, pyranometers, thermometers, barometers, hygrometers, and rain gauges. It provides photos and explanations of how each instrument works.