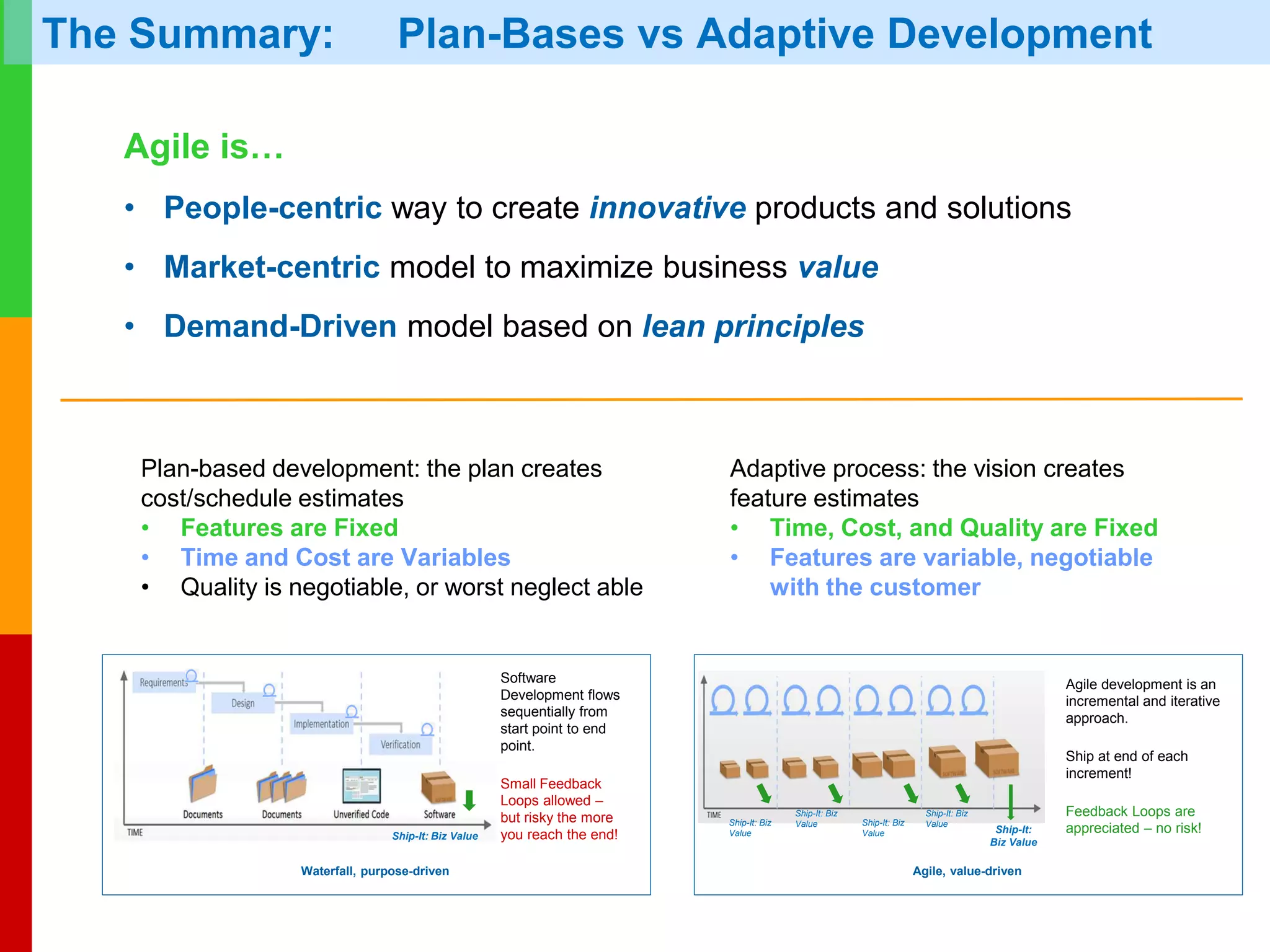
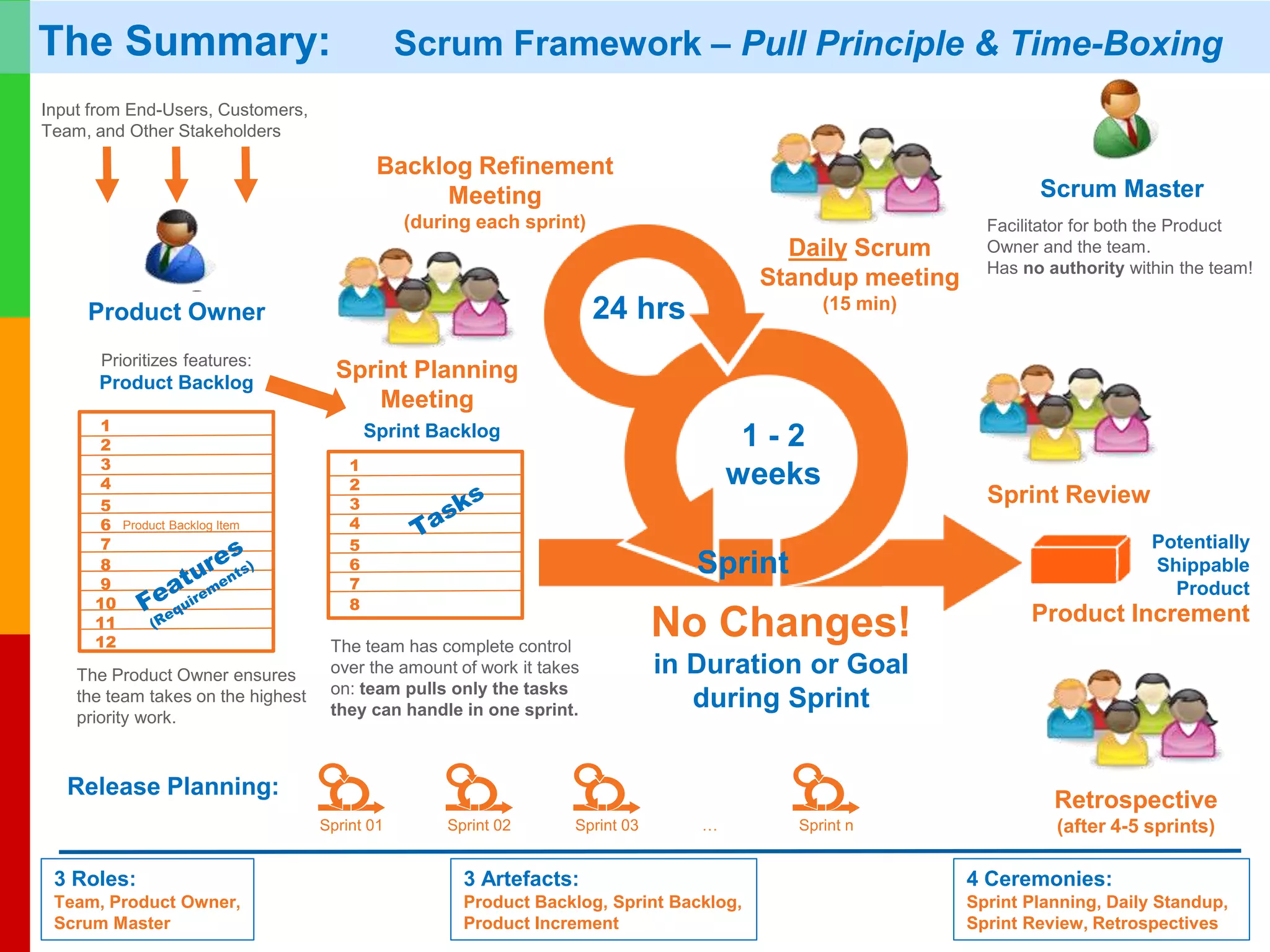
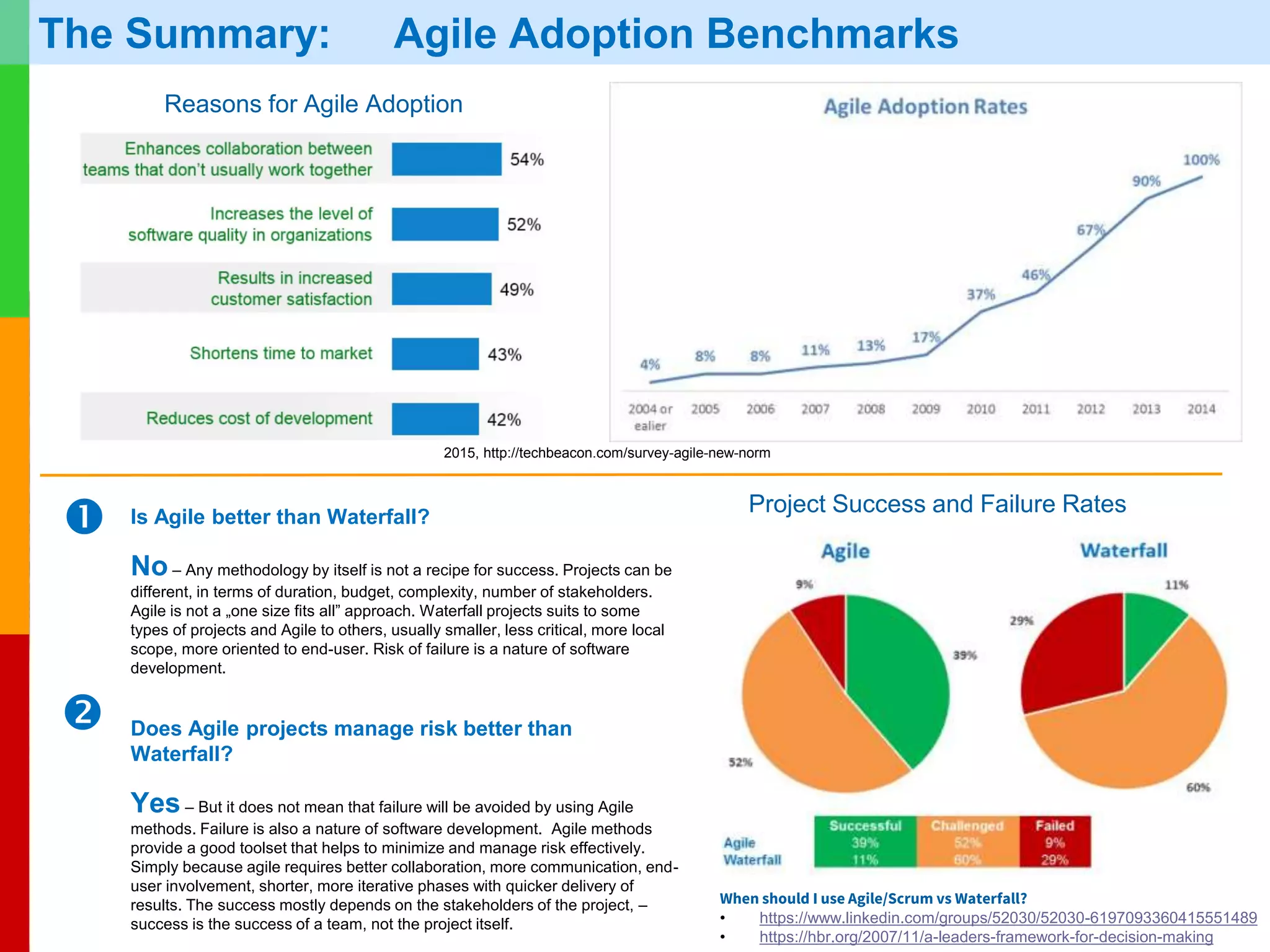
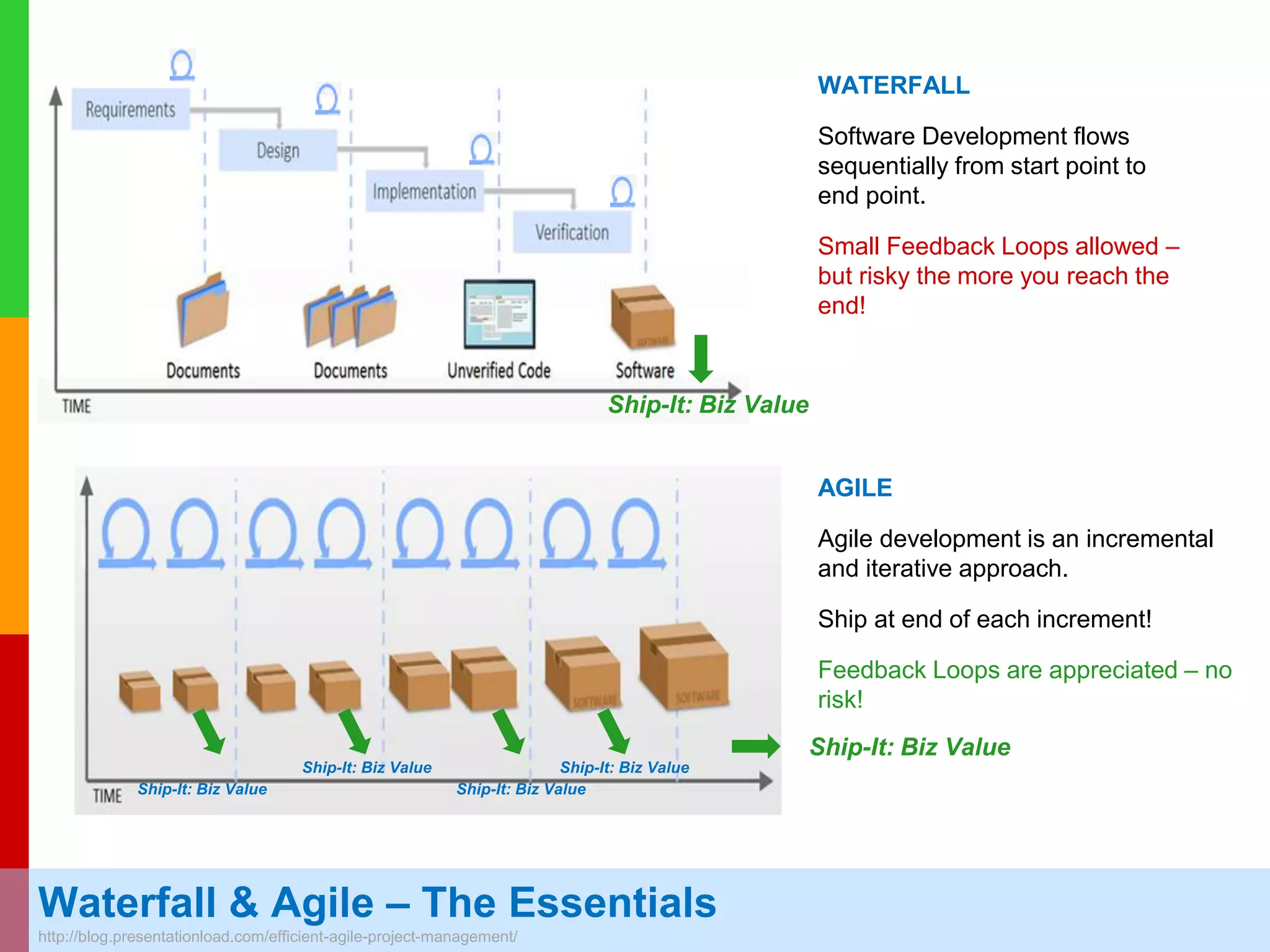
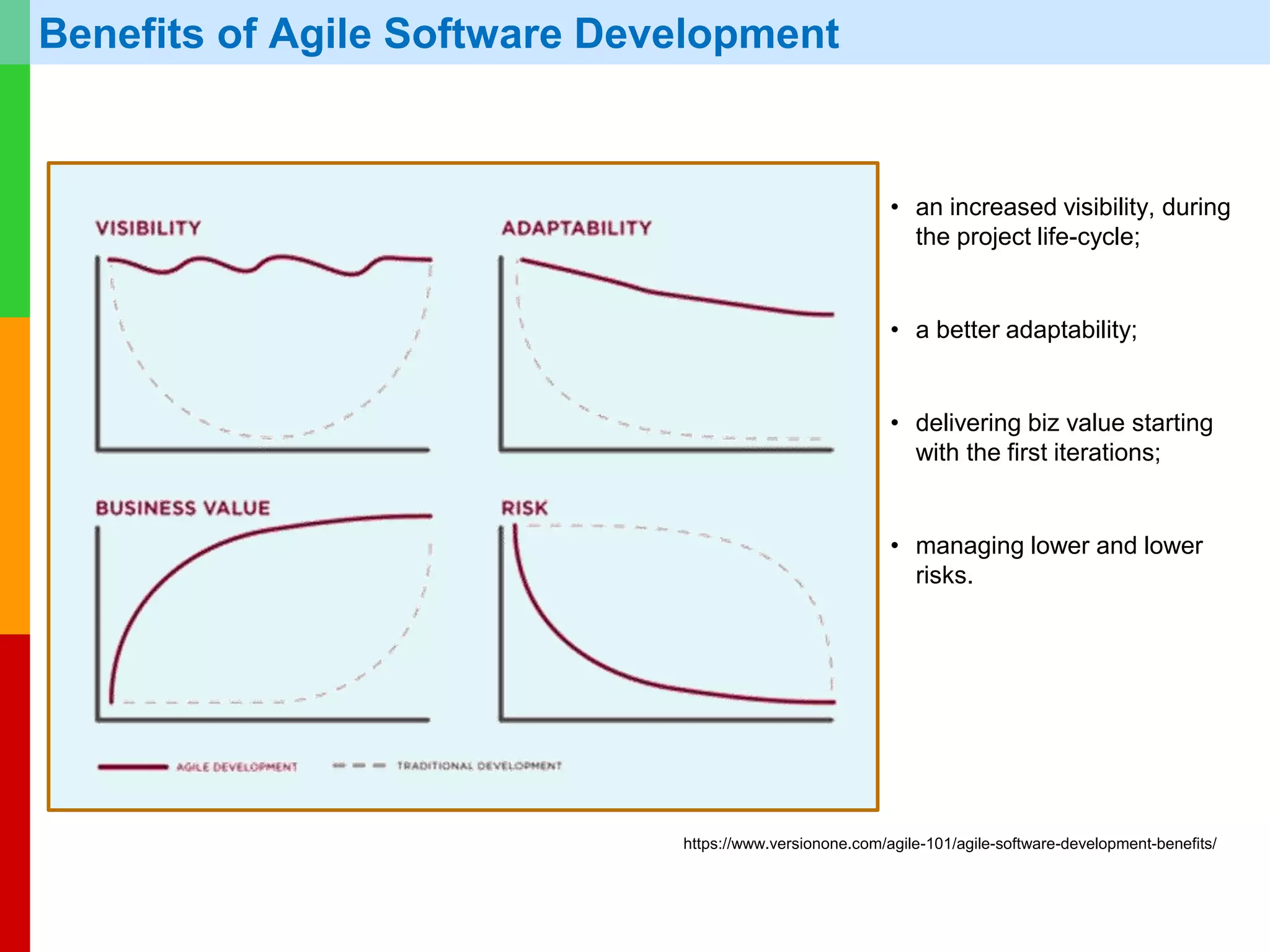
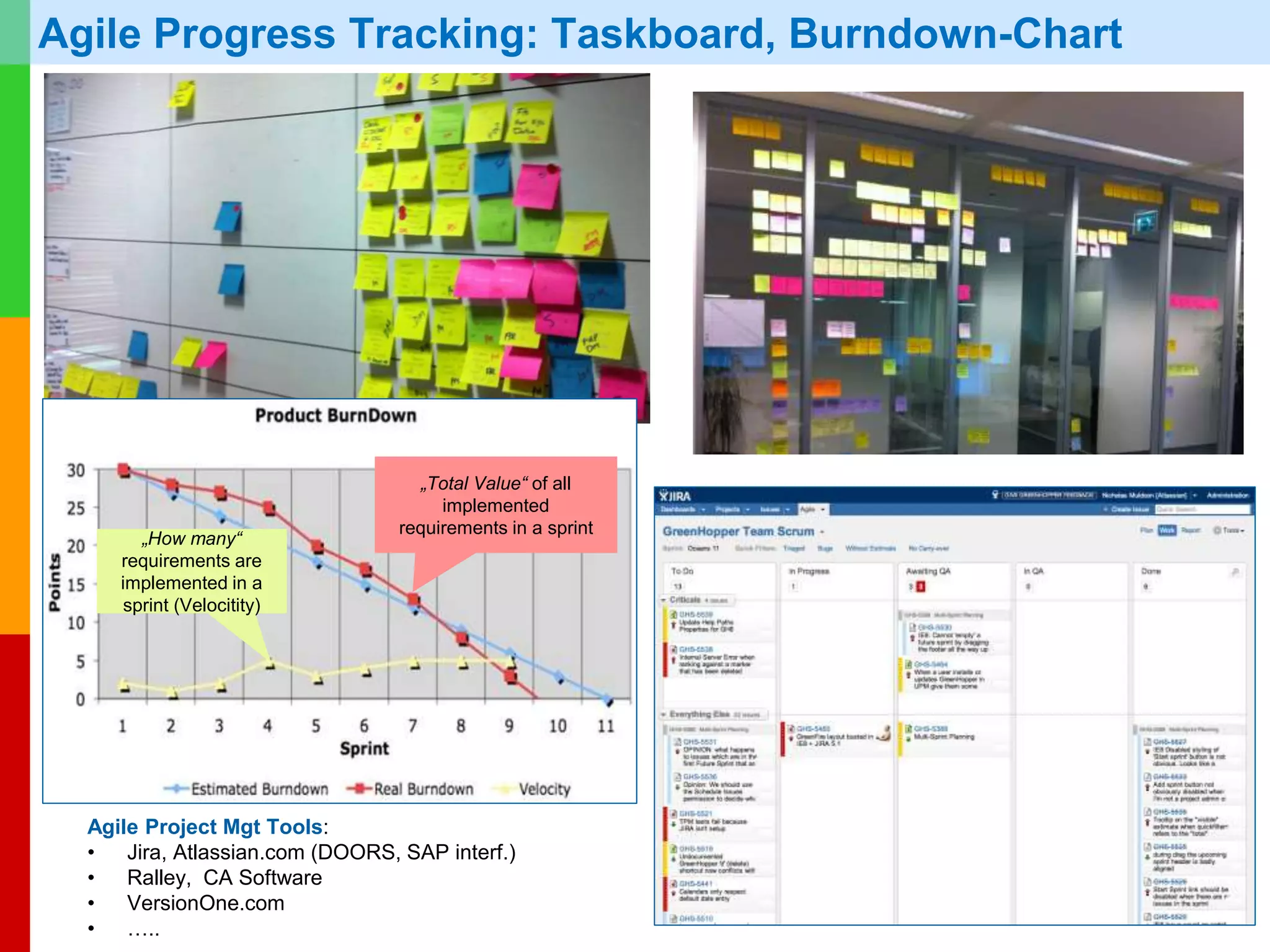
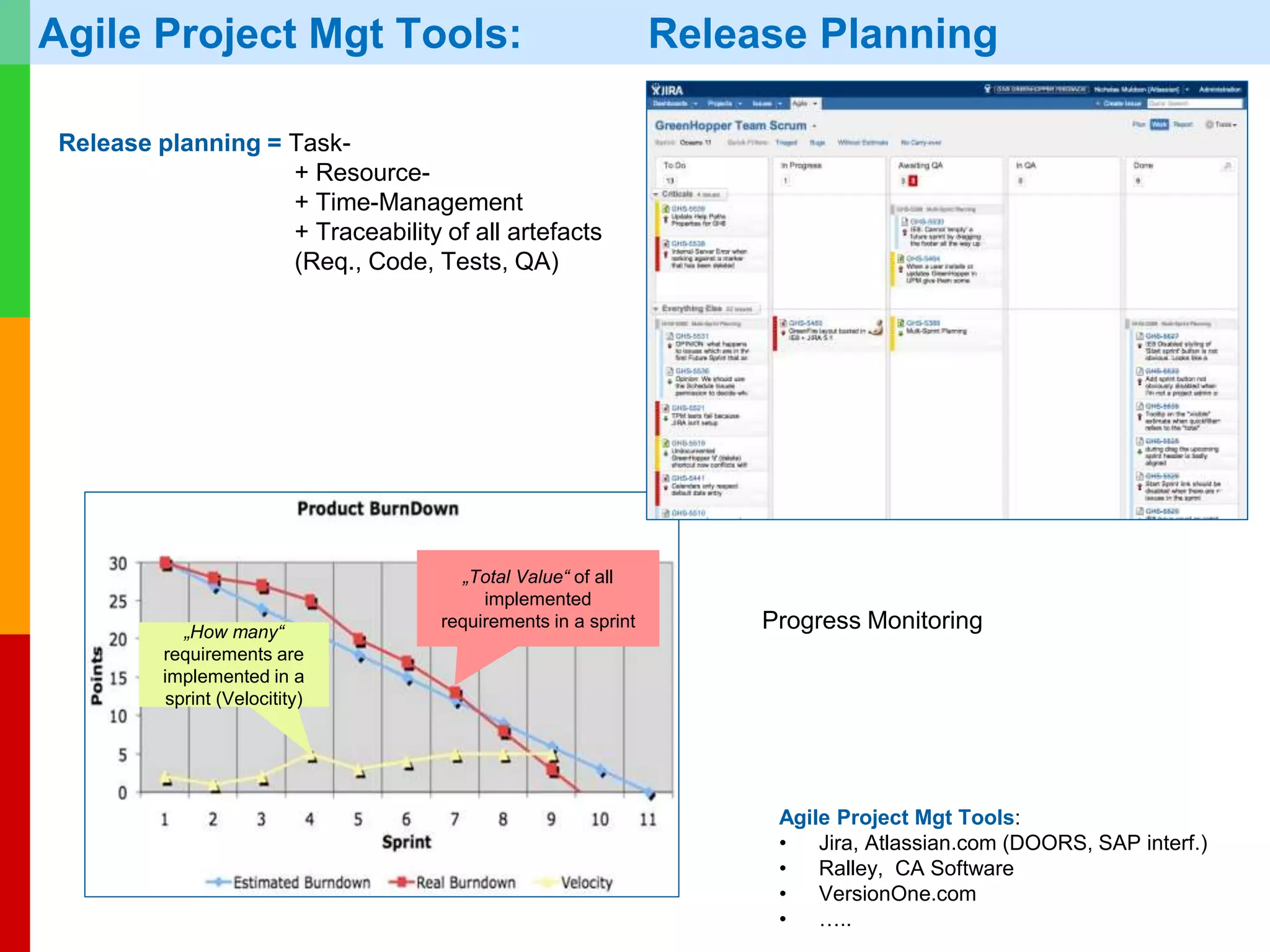
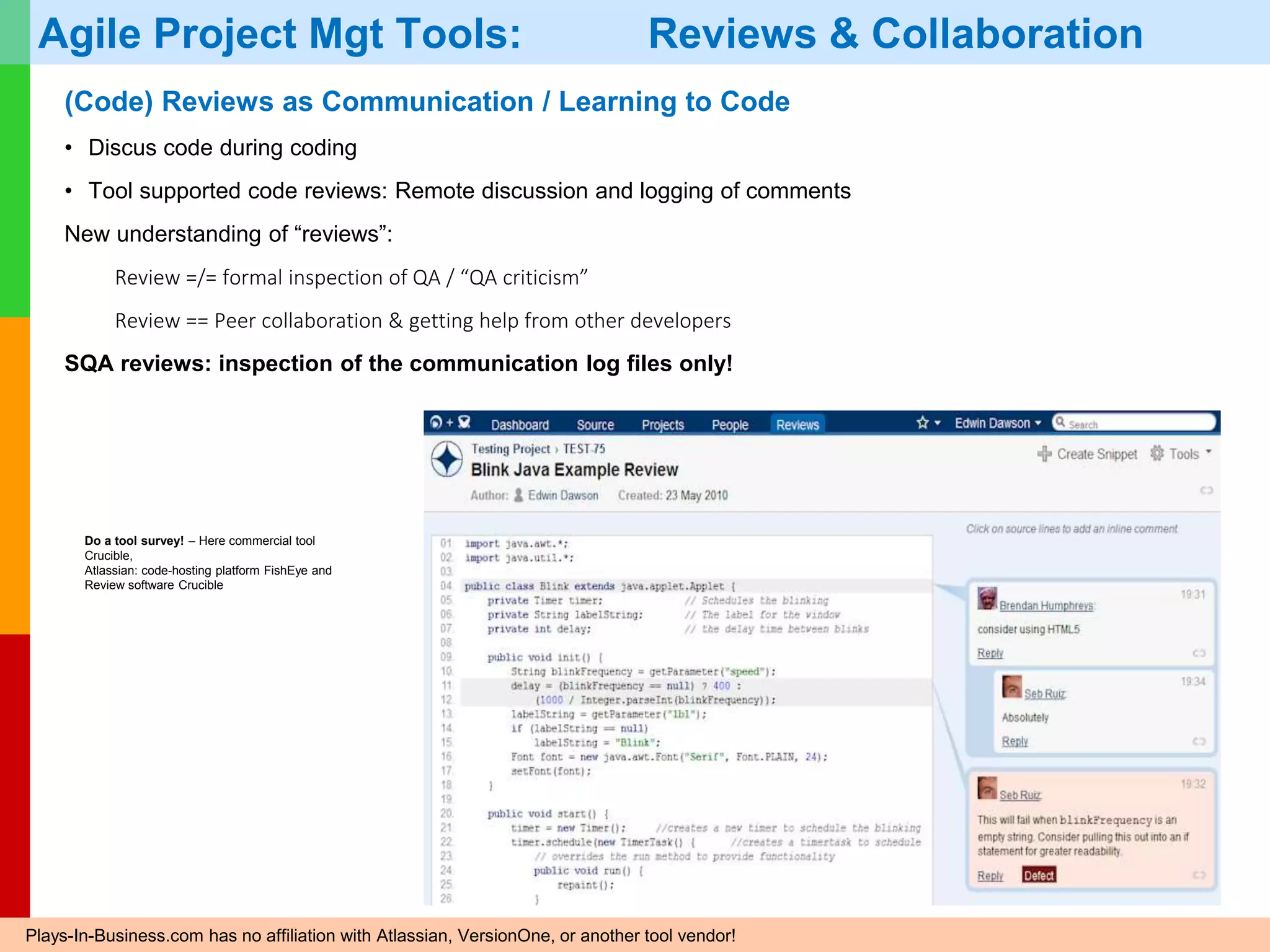
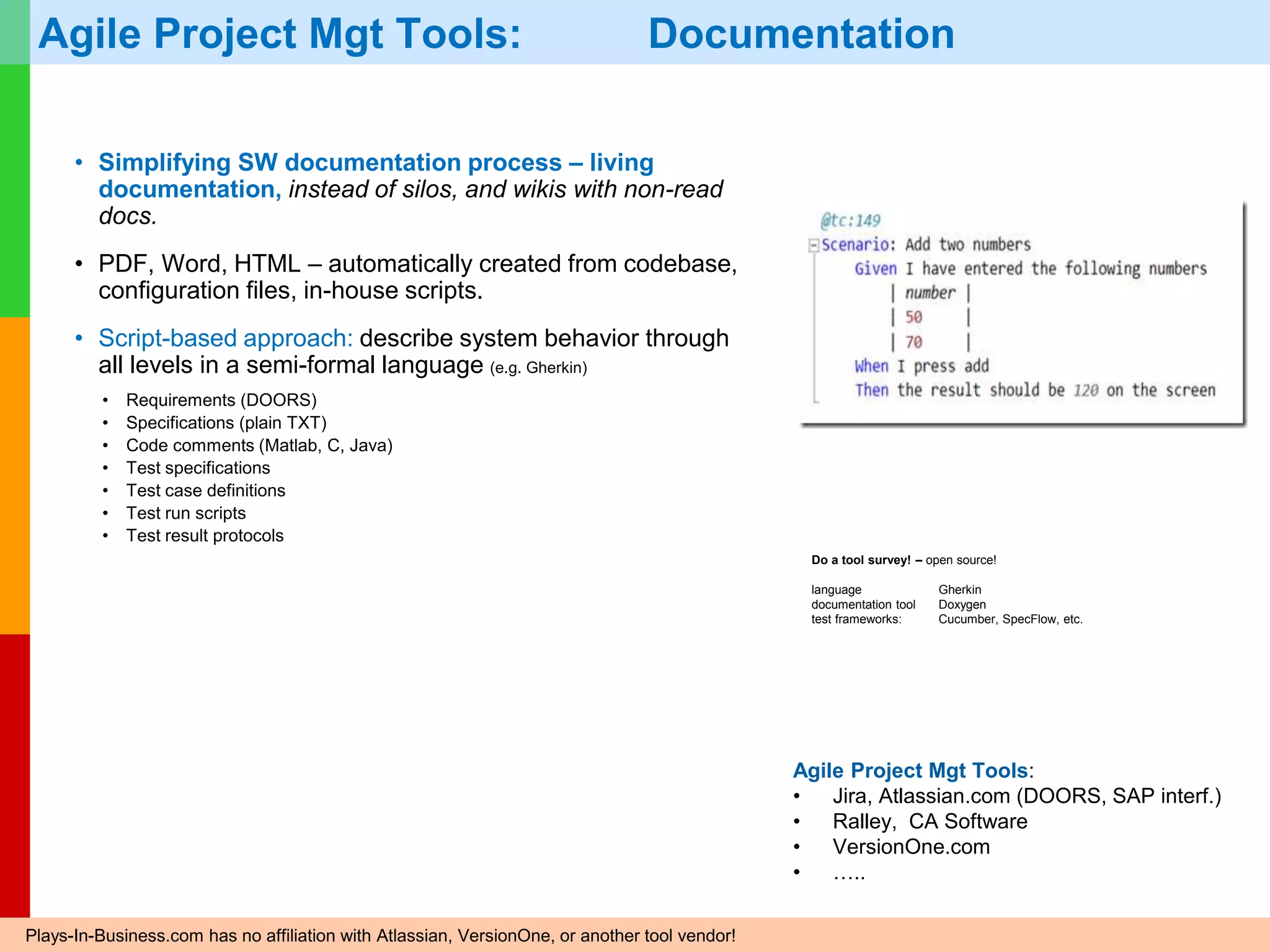
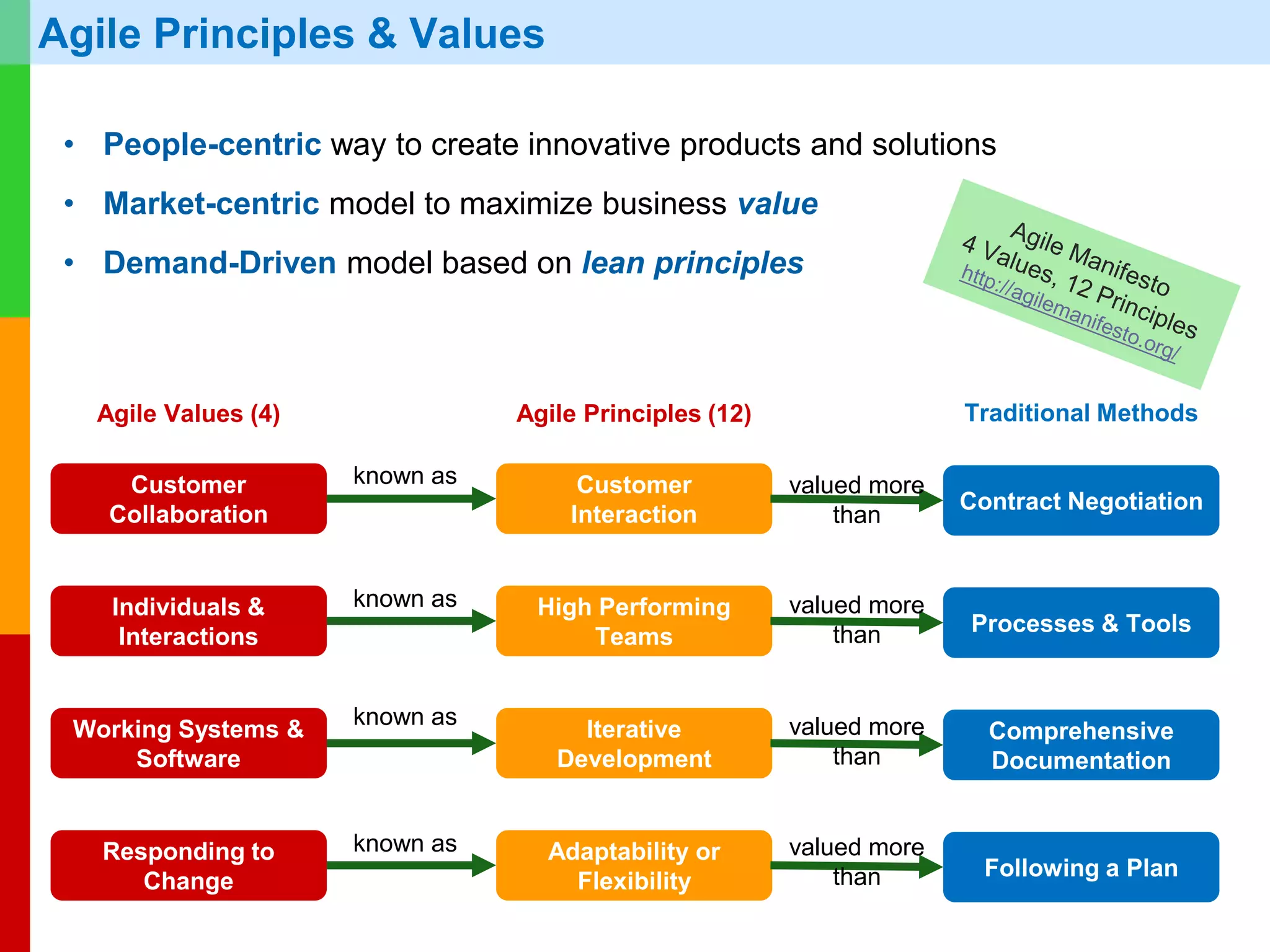
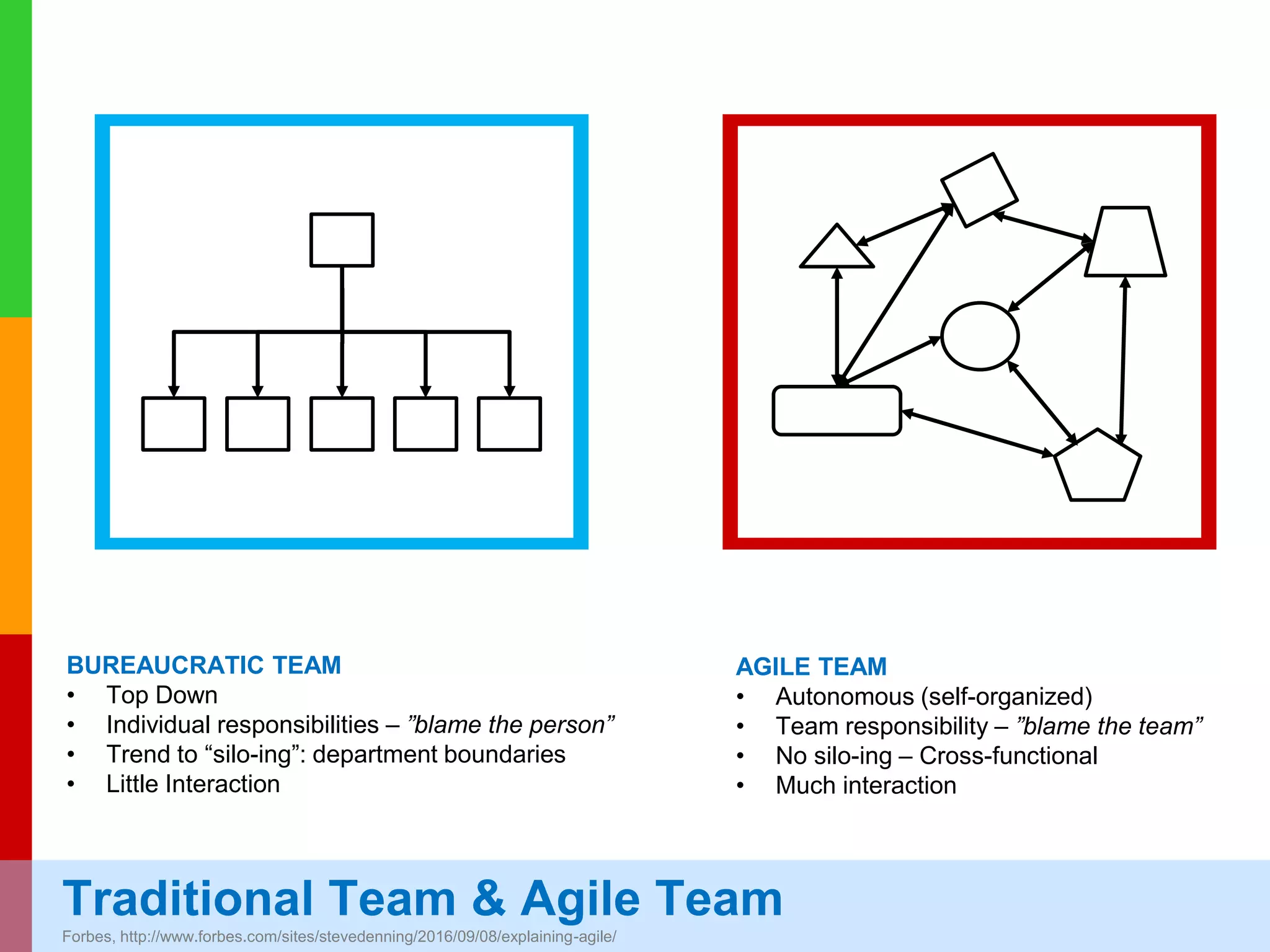
The document discusses Agile project management, emphasizing its value-driven, adaptive approach that prioritizes collaboration and delivery of business value over traditional plan-based methodologies. It outlines key frameworks such as Scrum, highlighting self-organizing teams, roles, ceremonies, and artifacts that facilitate Agile processes. Finally, it addresses common misconceptions about Agile practices, asserting that while Agile may better manage risks, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution and does not guarantee project success.