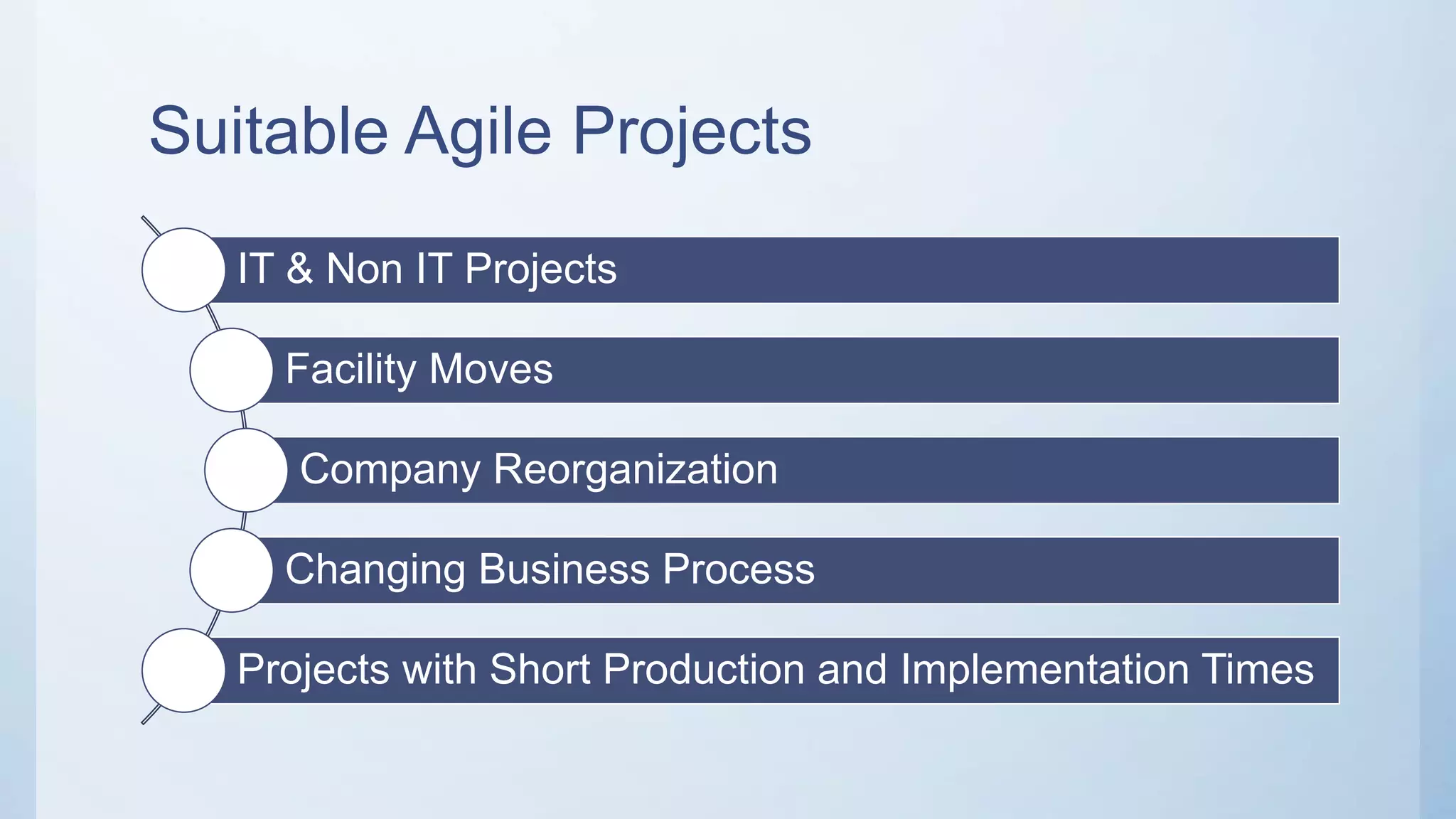
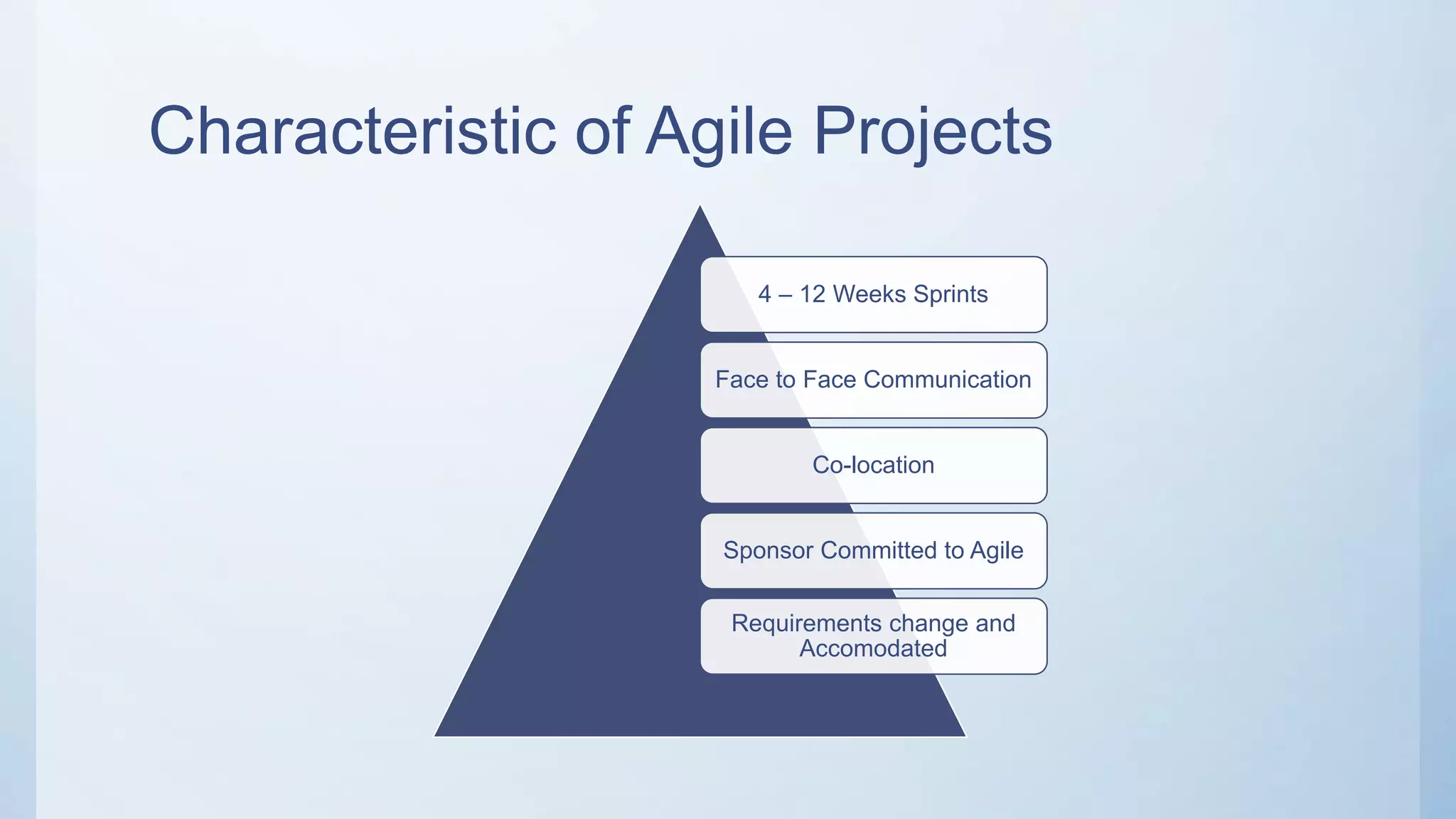
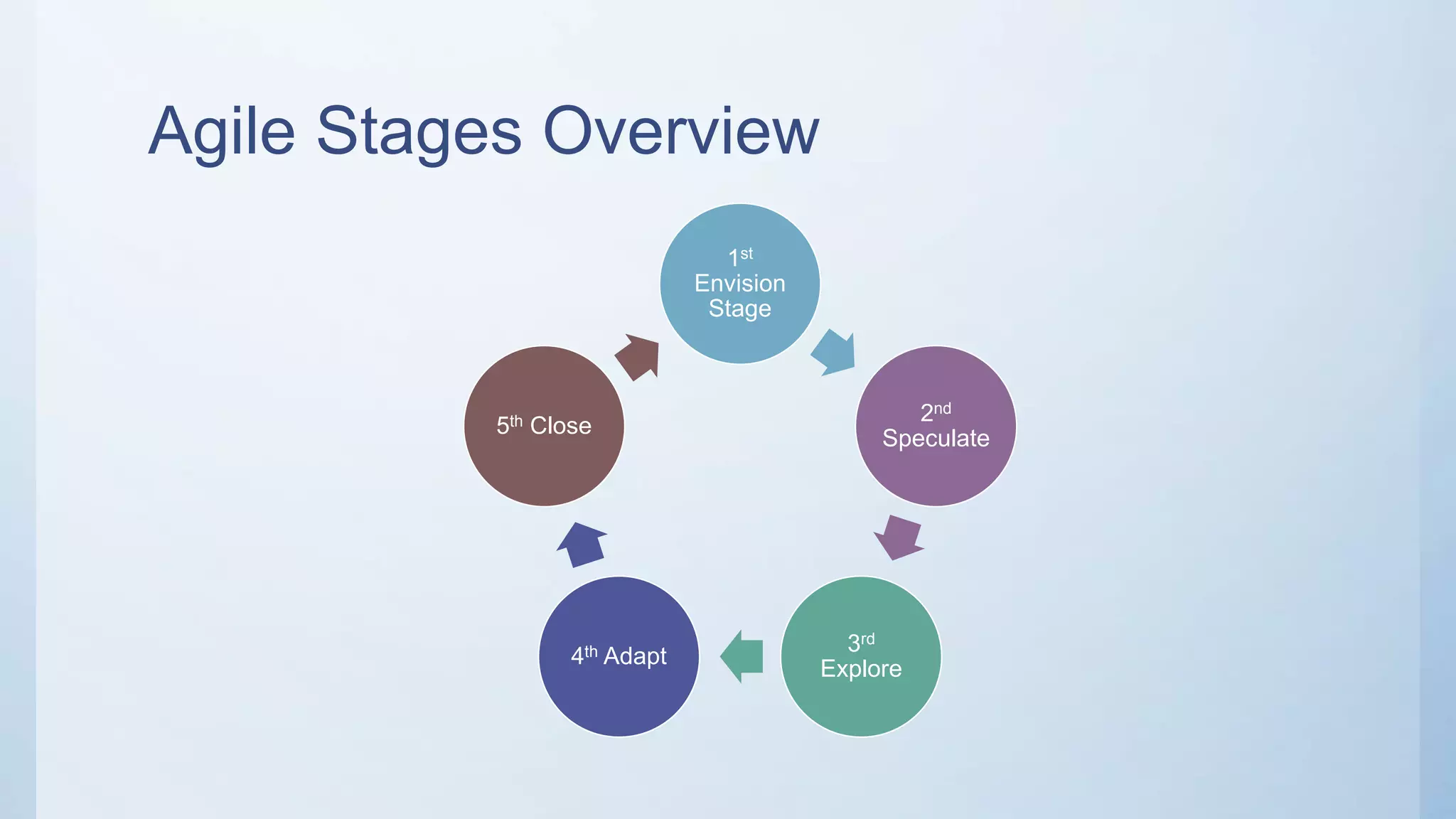
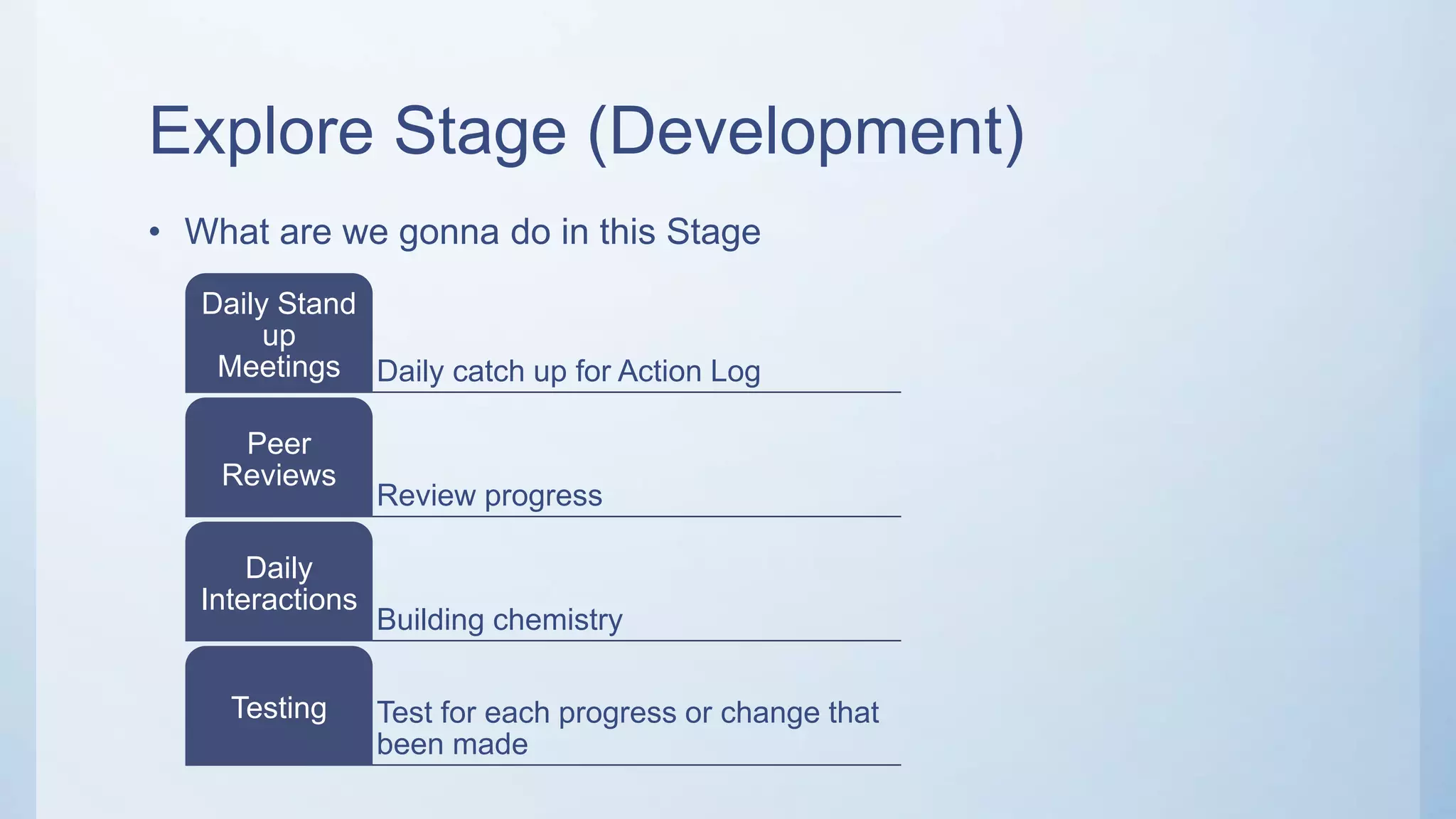
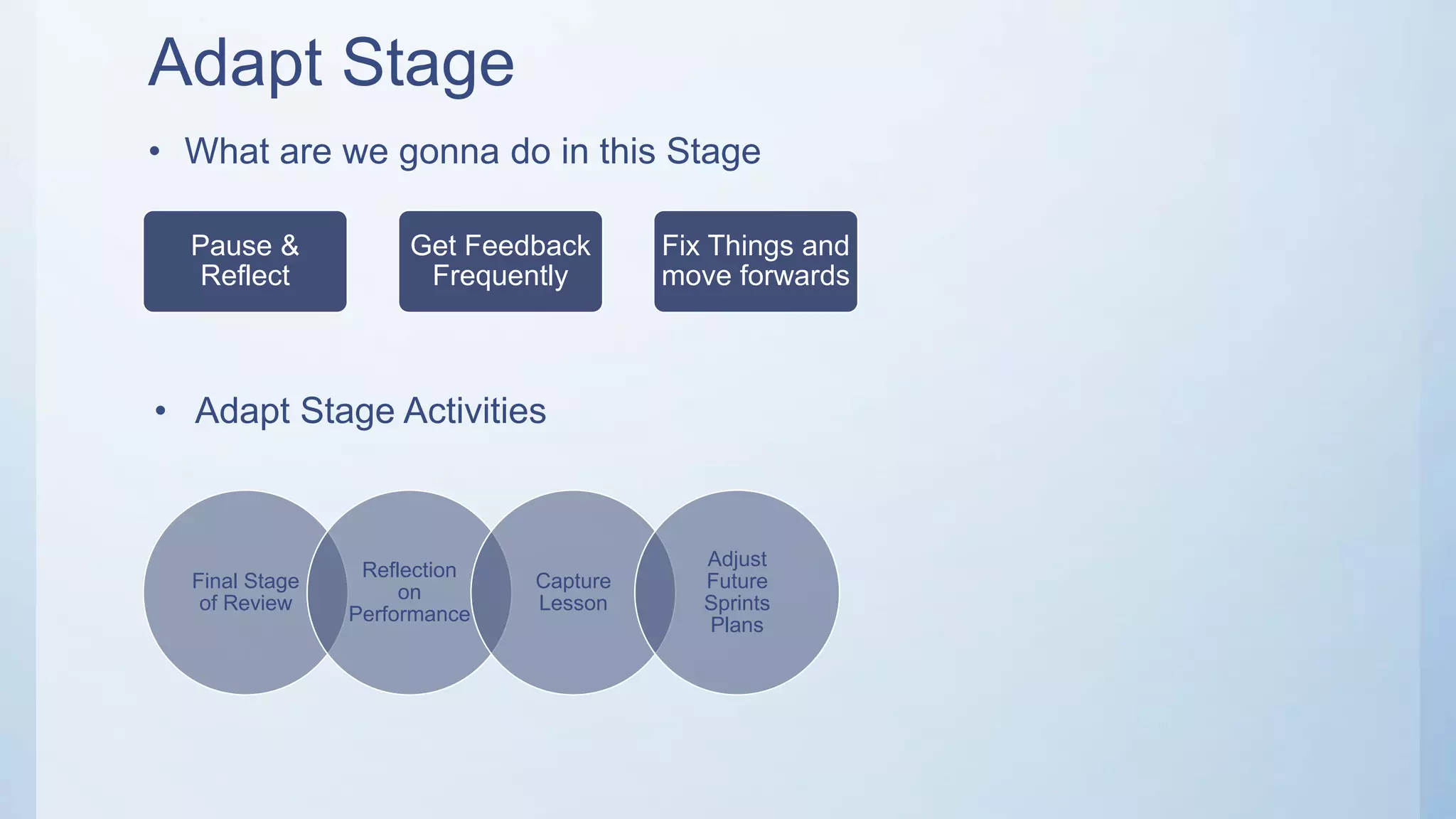
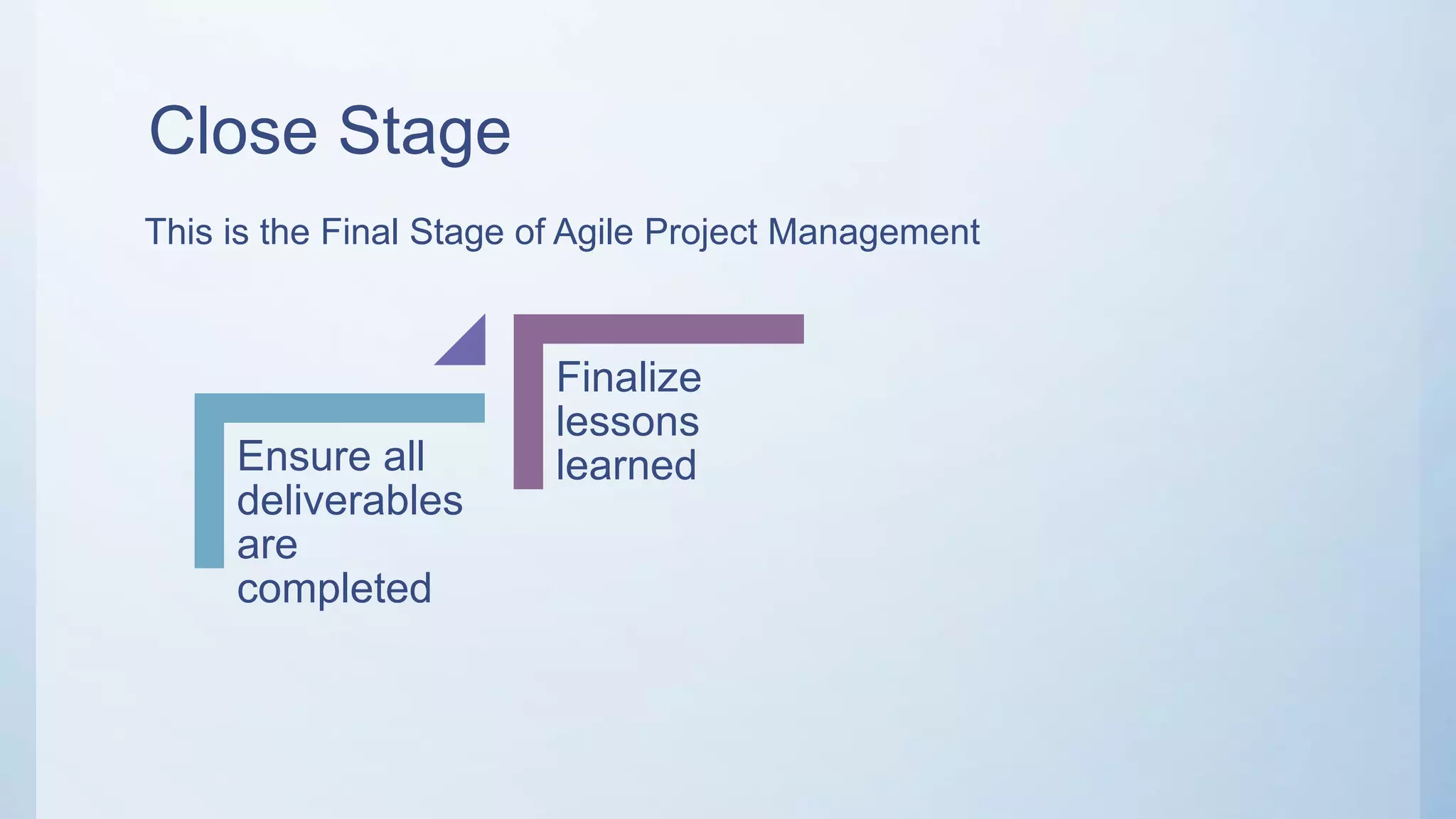
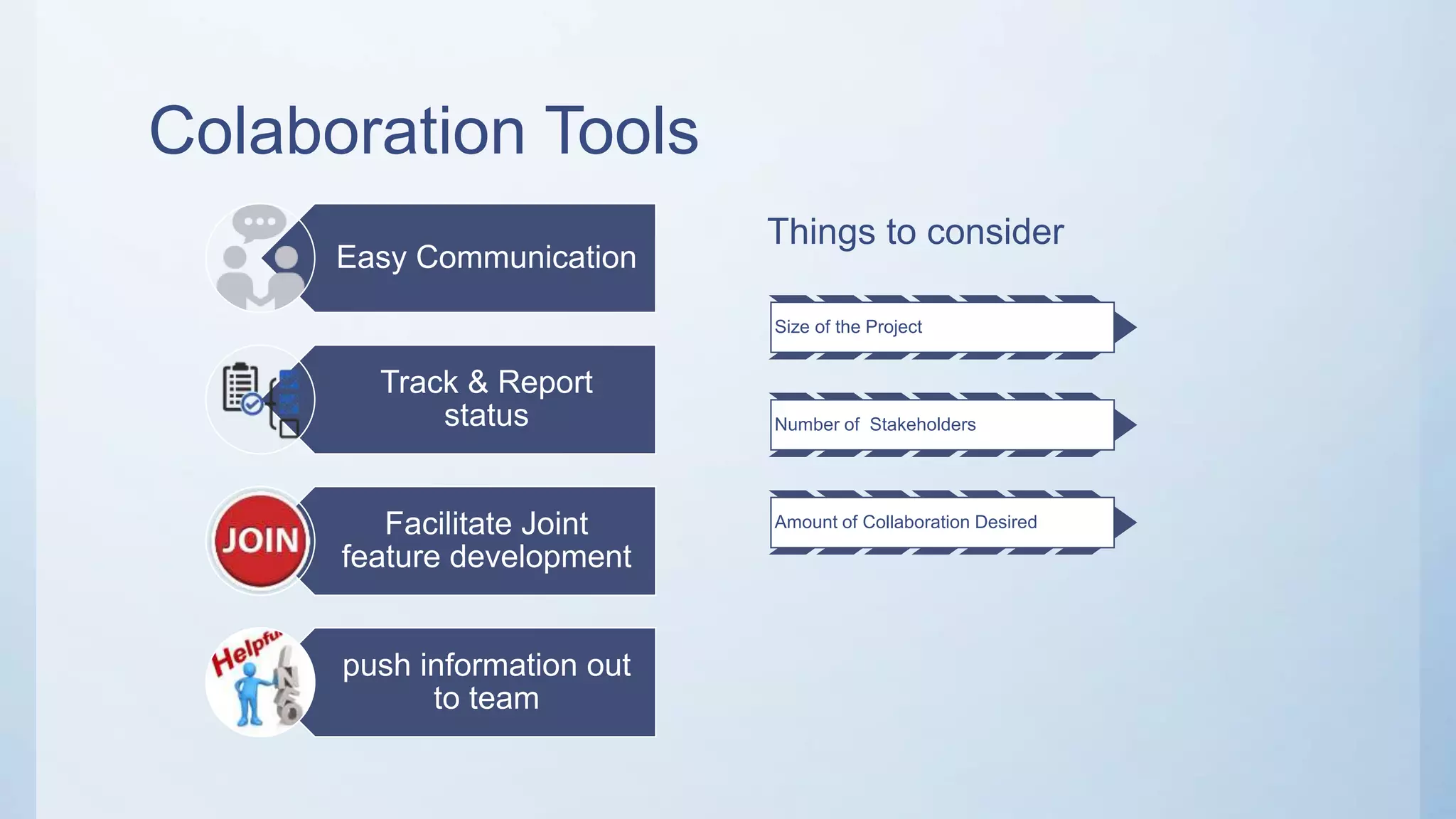
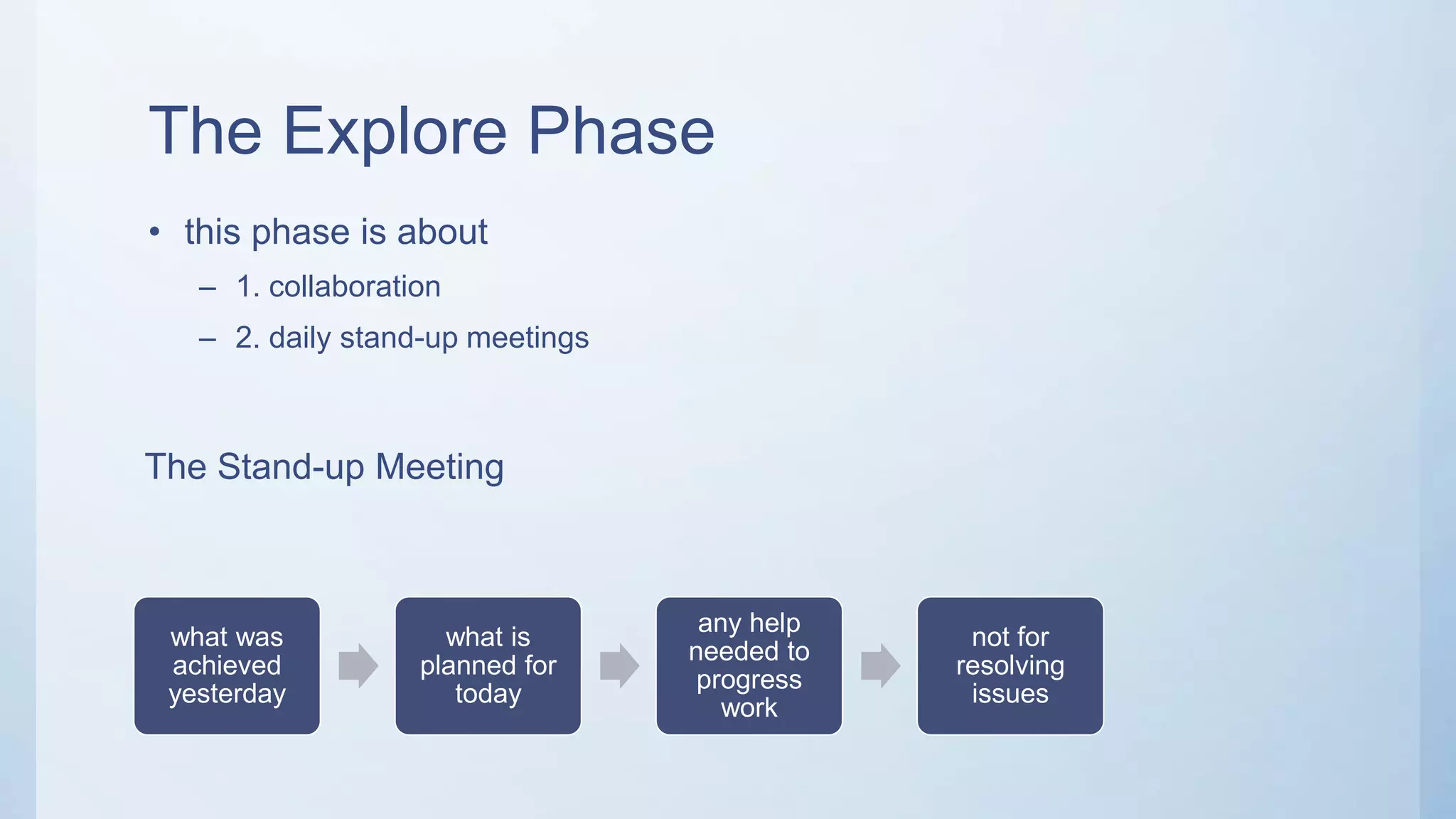
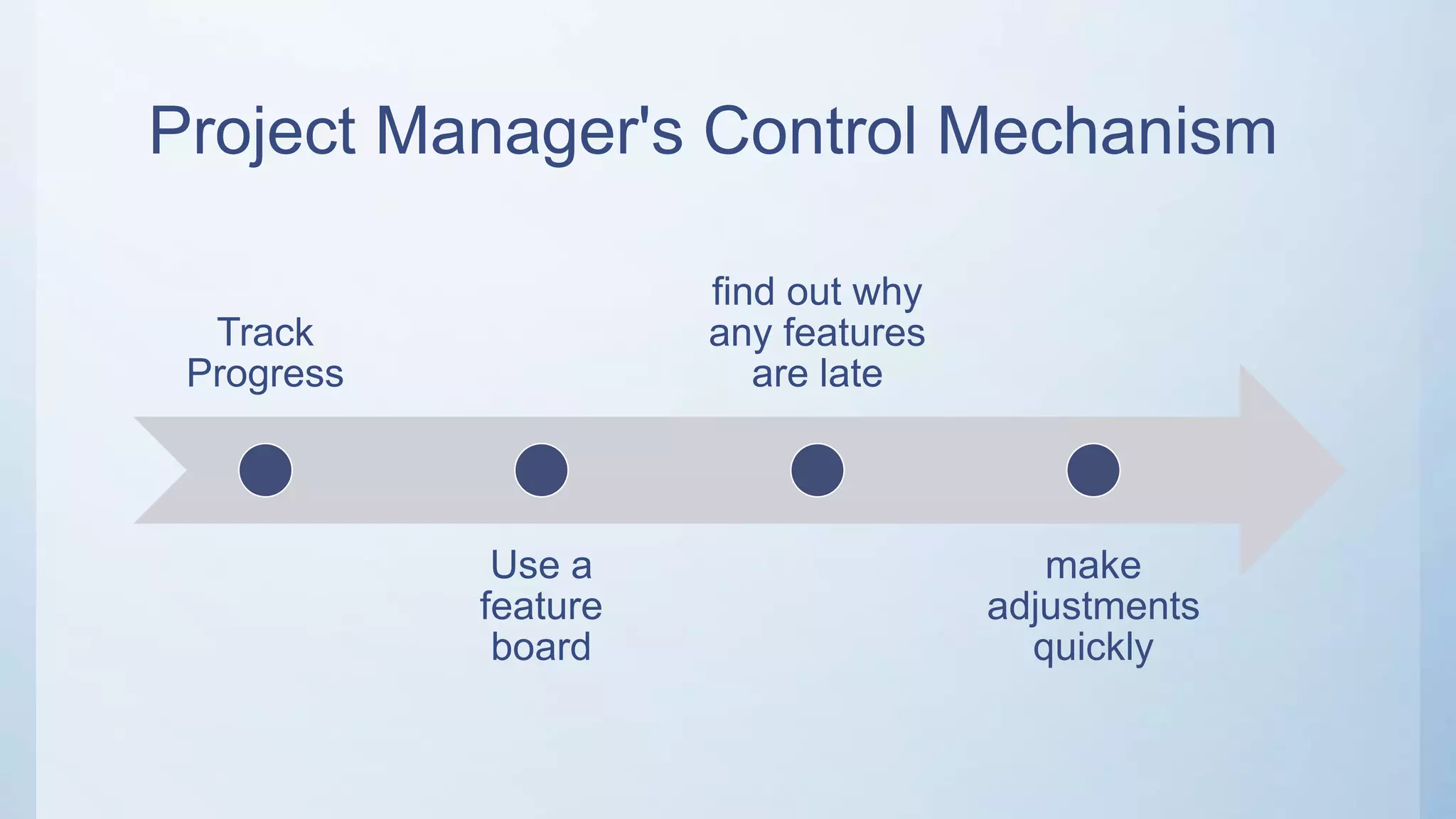
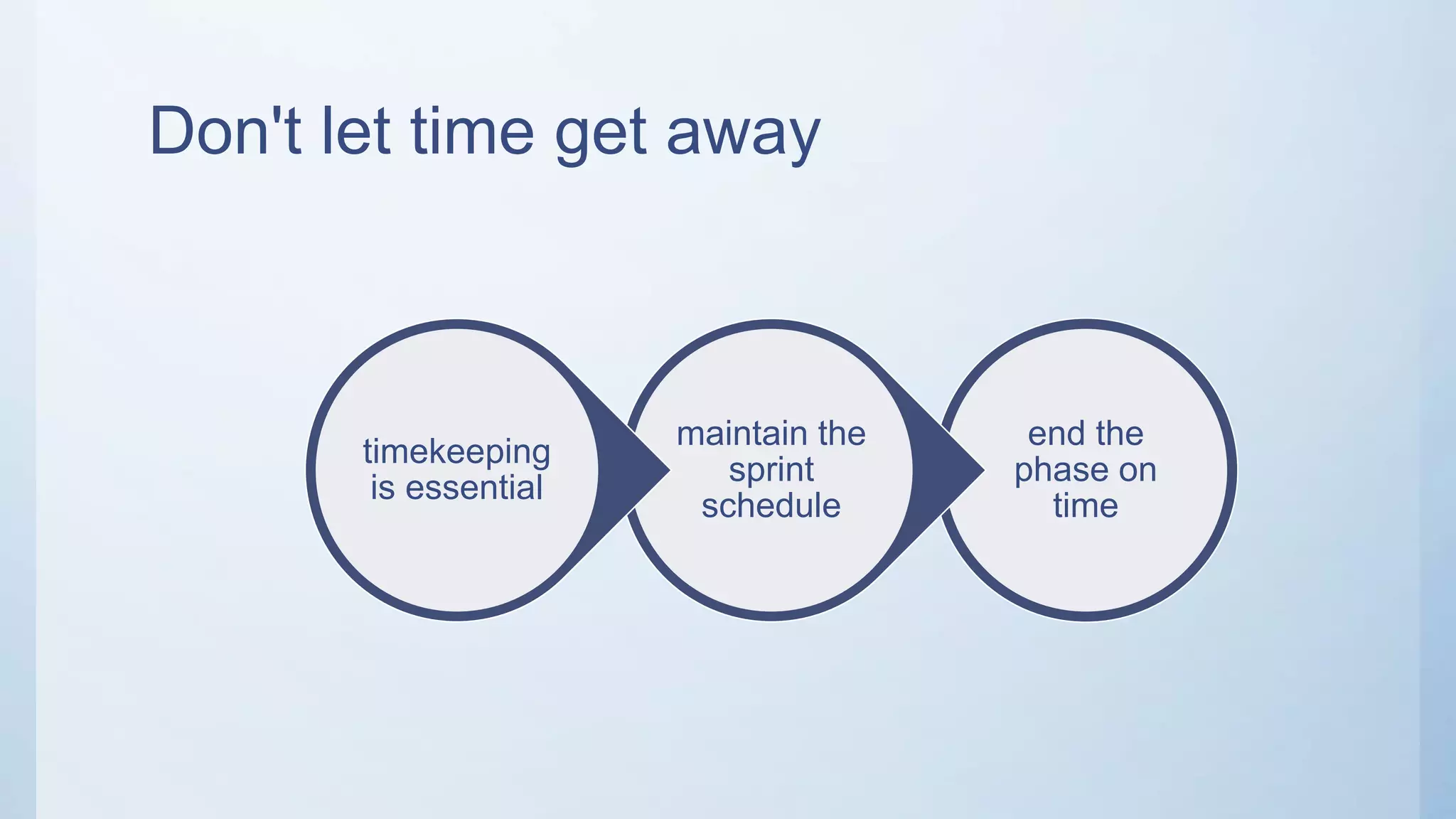
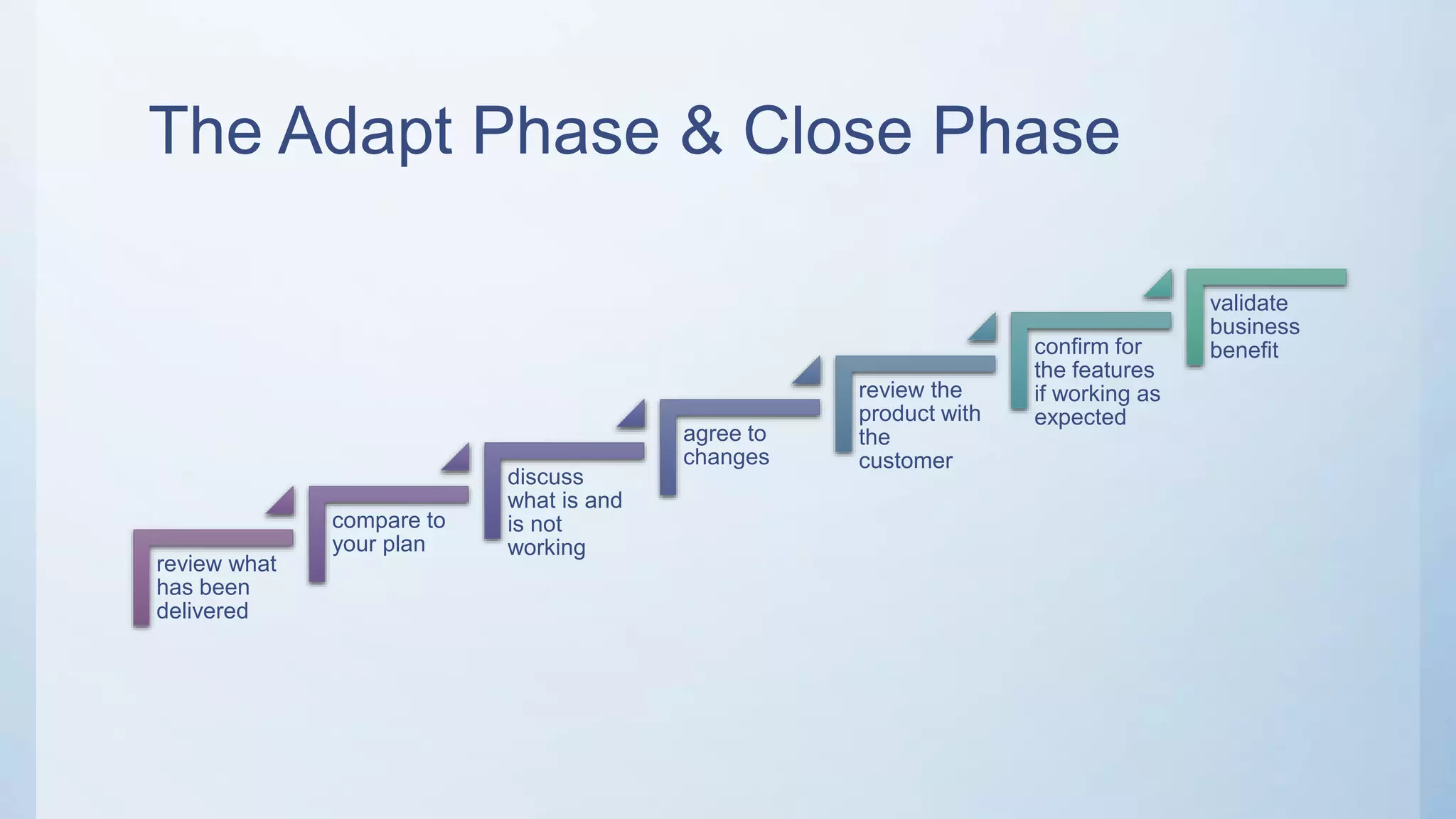
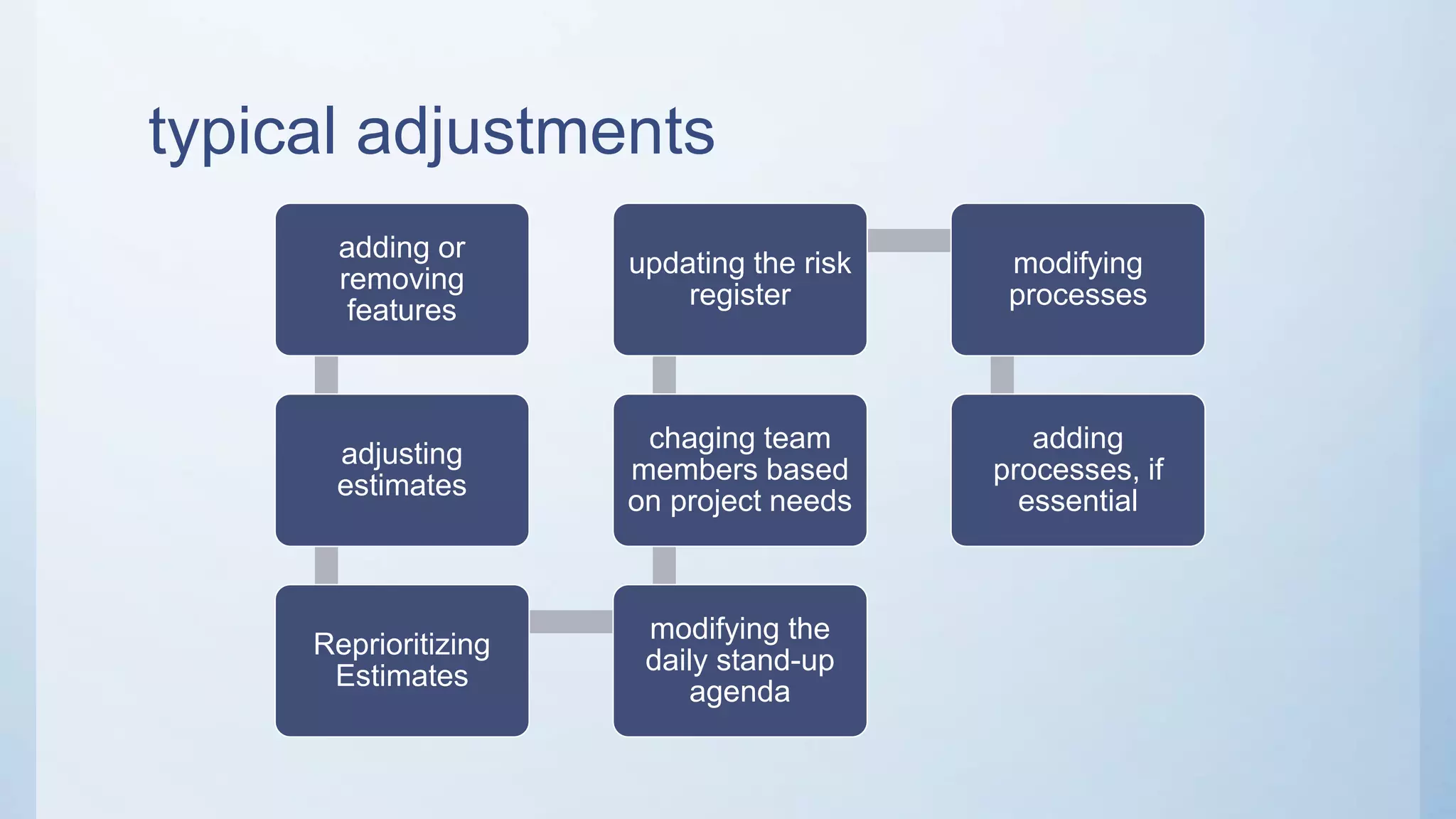
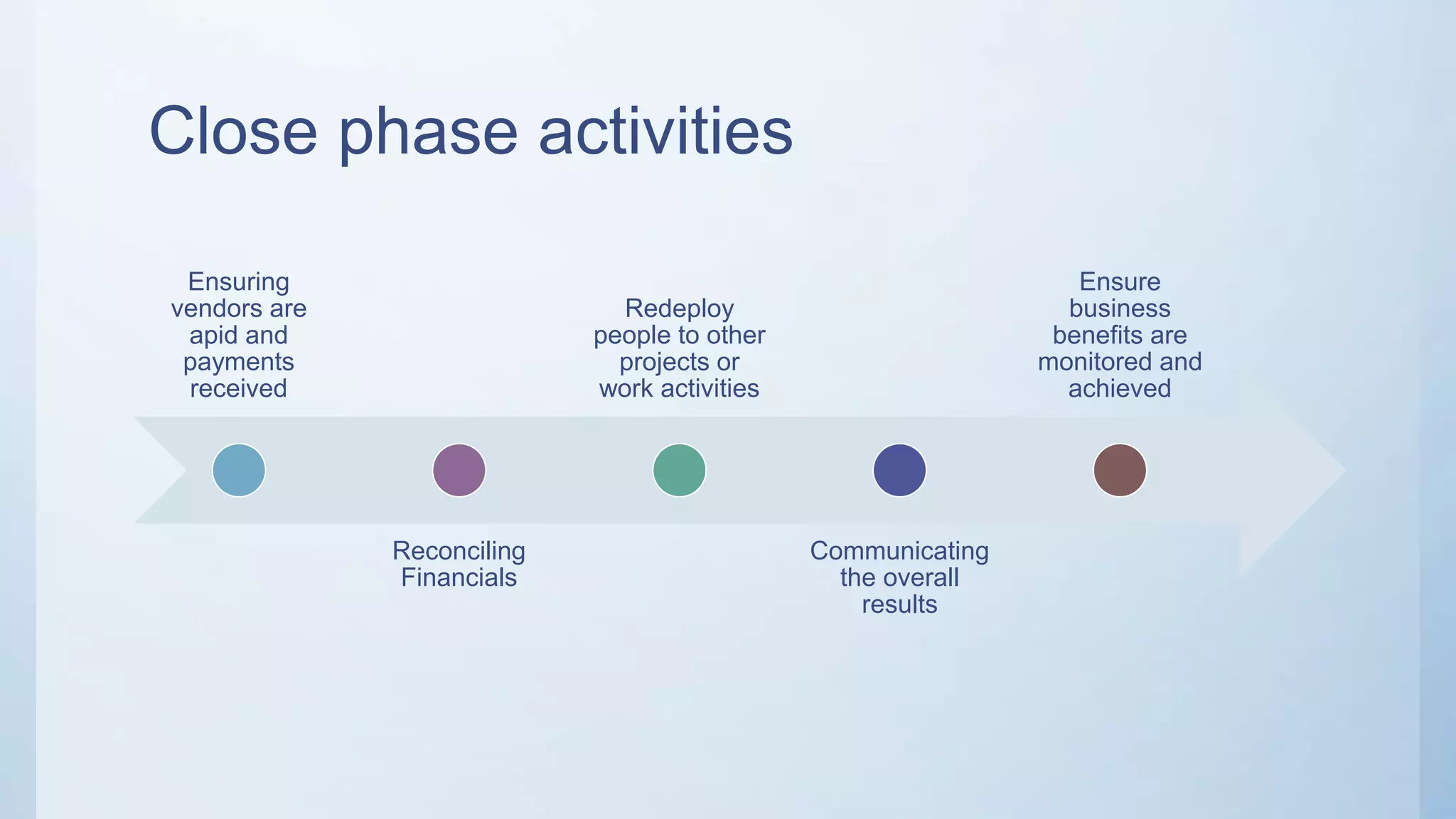
This document outlines the stages of an agile project management process: Envision, Speculate, Explore, Adapt, and Close. The Envision stage involves determining the project scope and establishing team values. The Speculate stage focuses on identifying features and estimating work. In the Explore stage, daily stand-up meetings are held for collaboration. The Adapt stage is for reviewing and making adjustments. Finally, the Close stage ensures all deliverables are complete and lessons learned are captured.