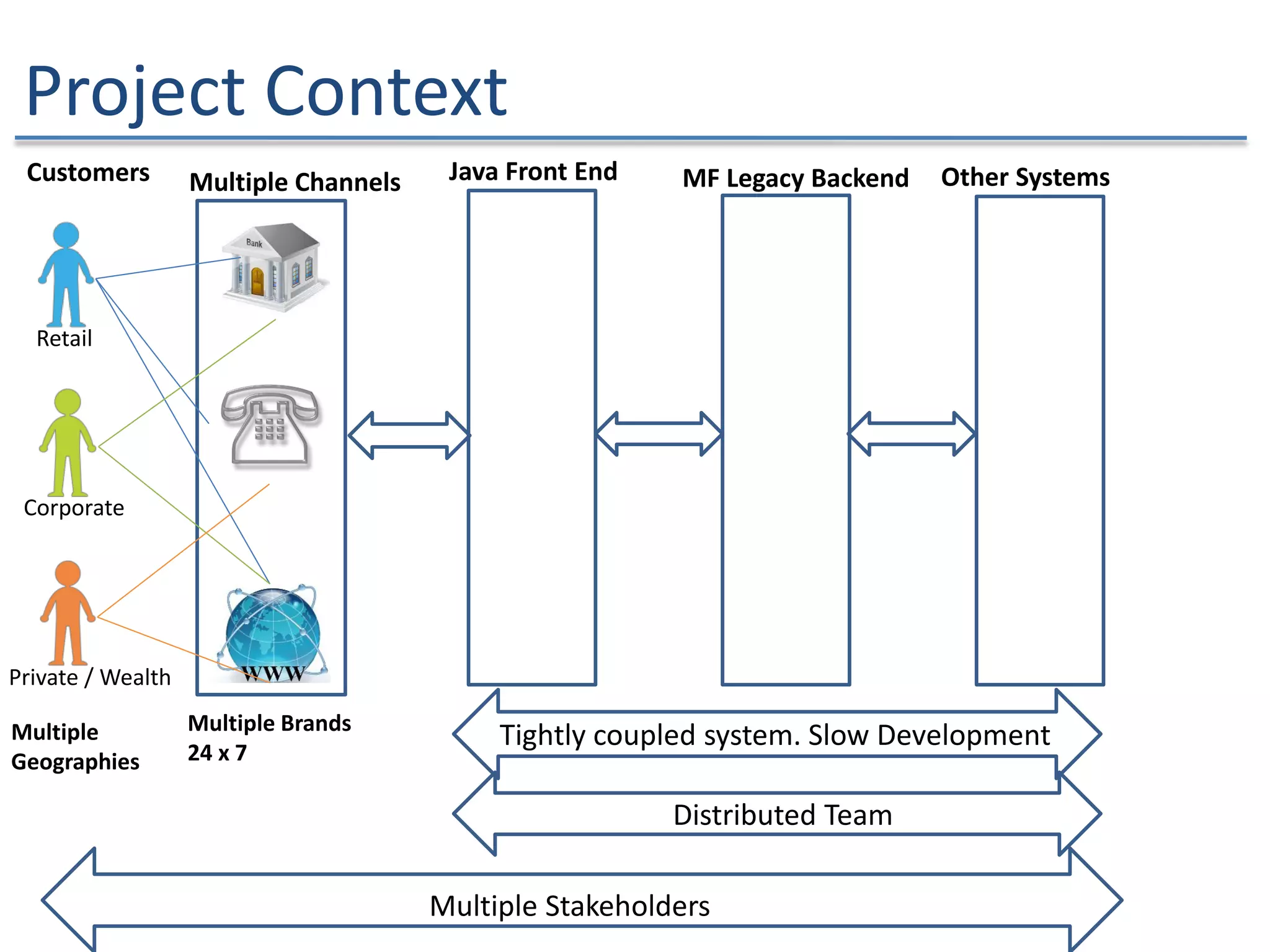
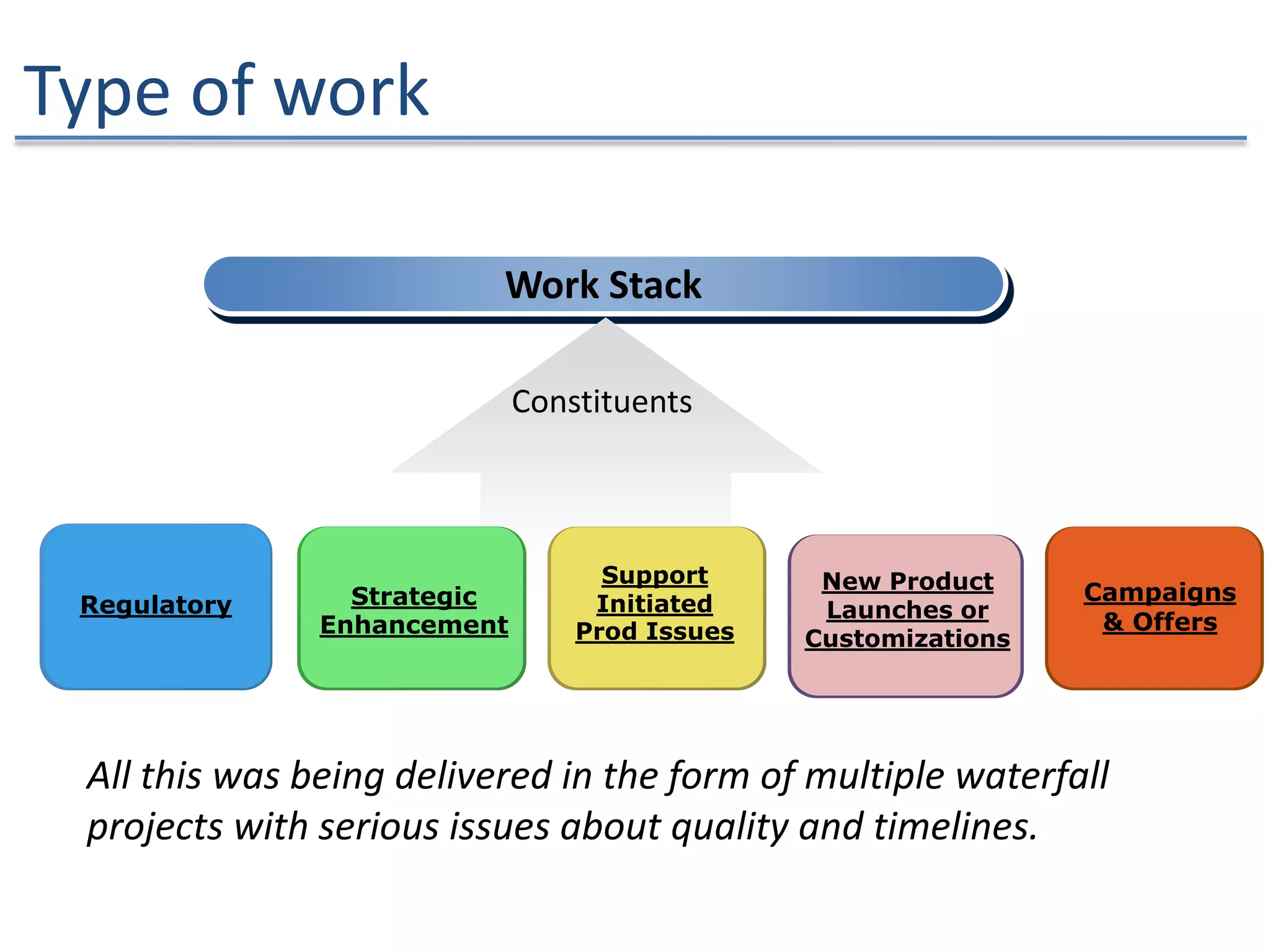
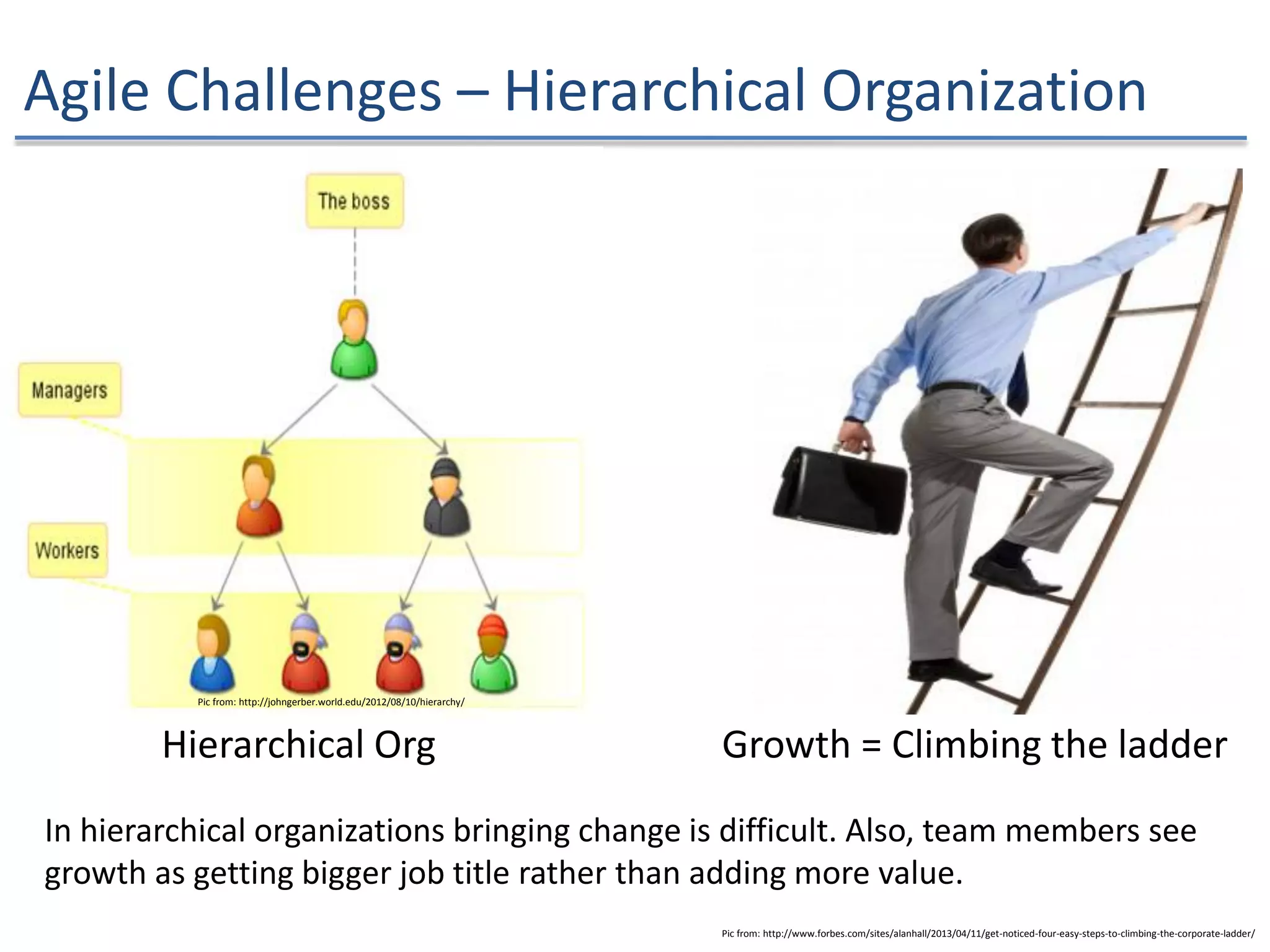
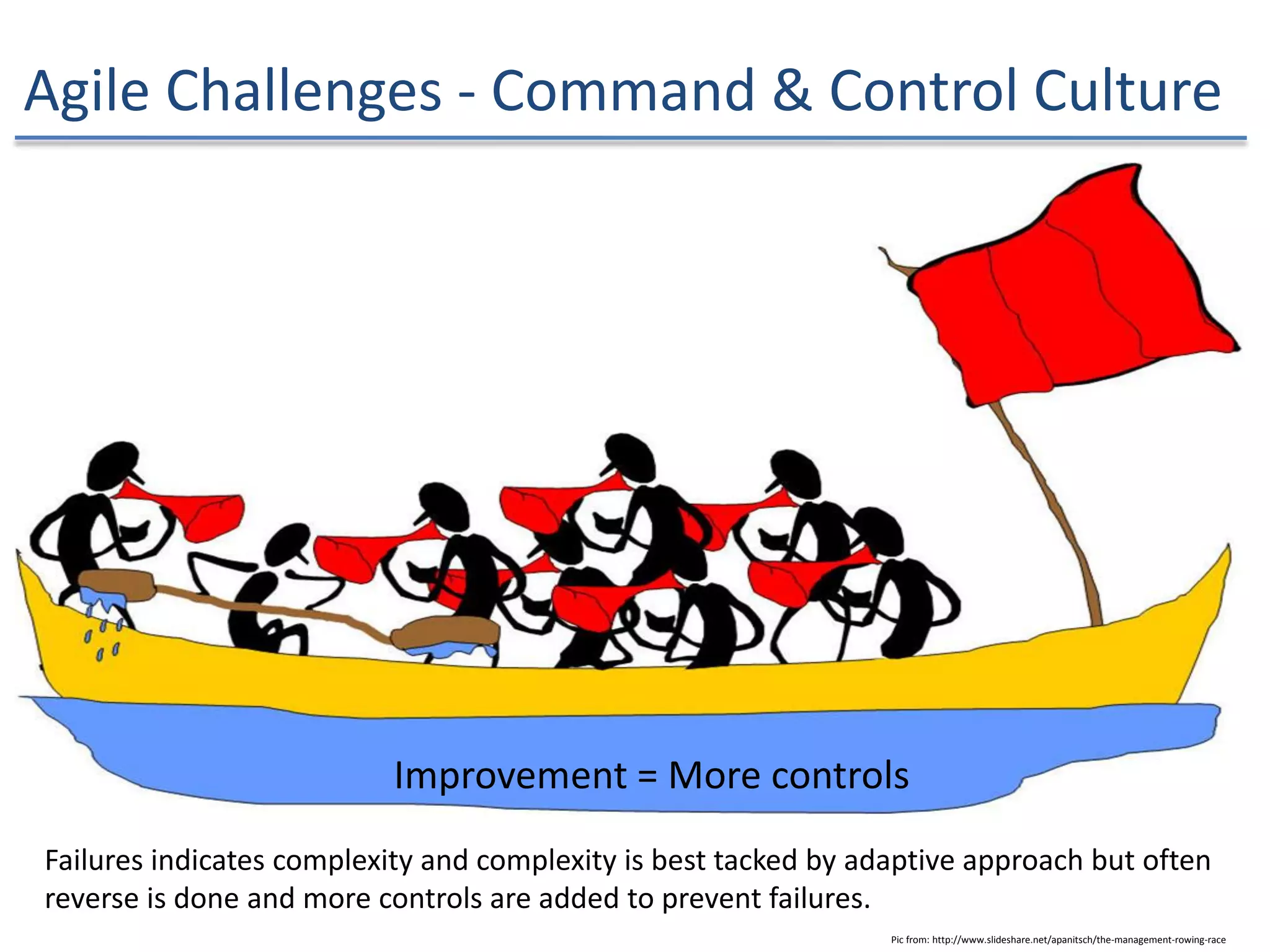
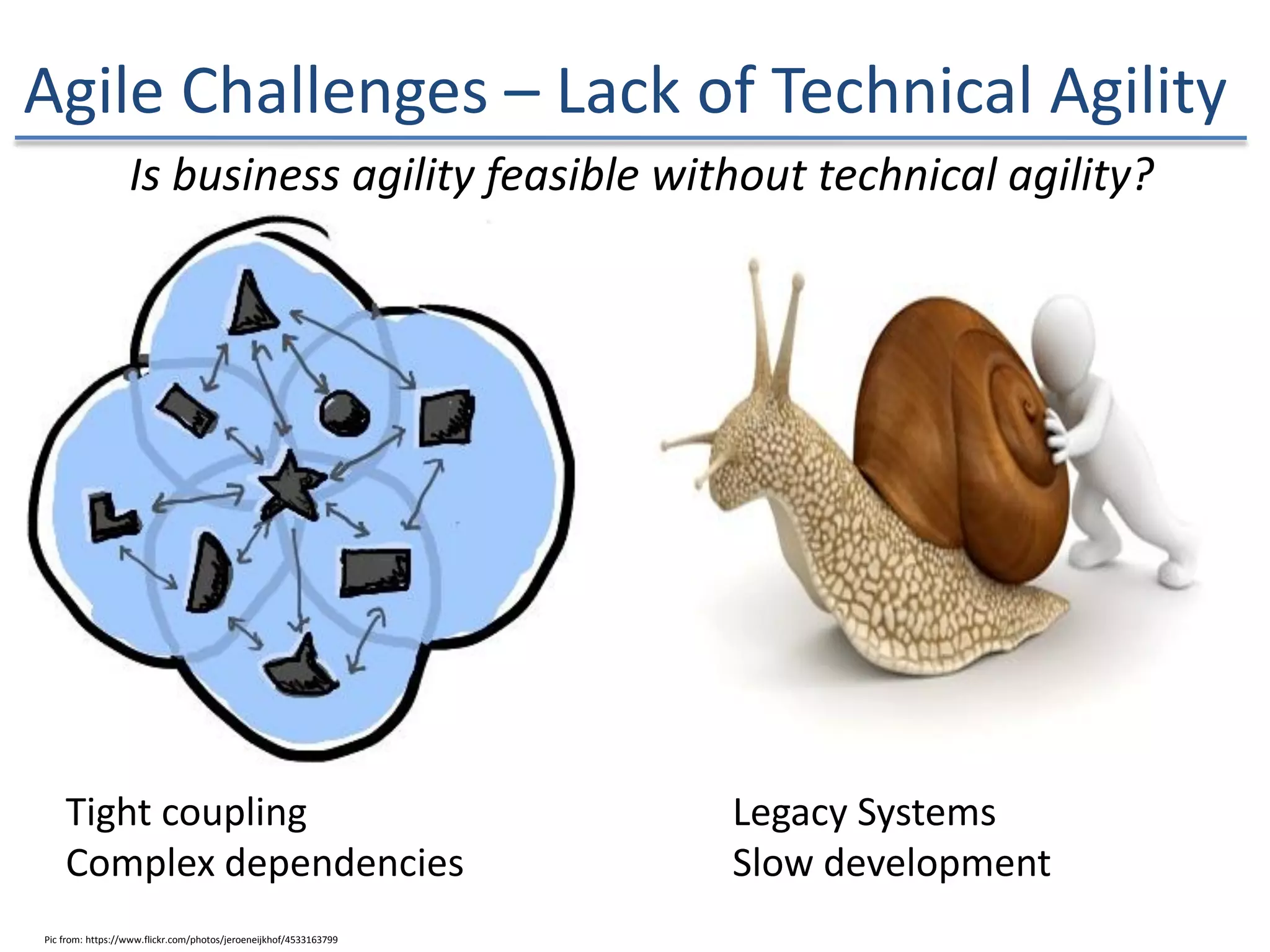
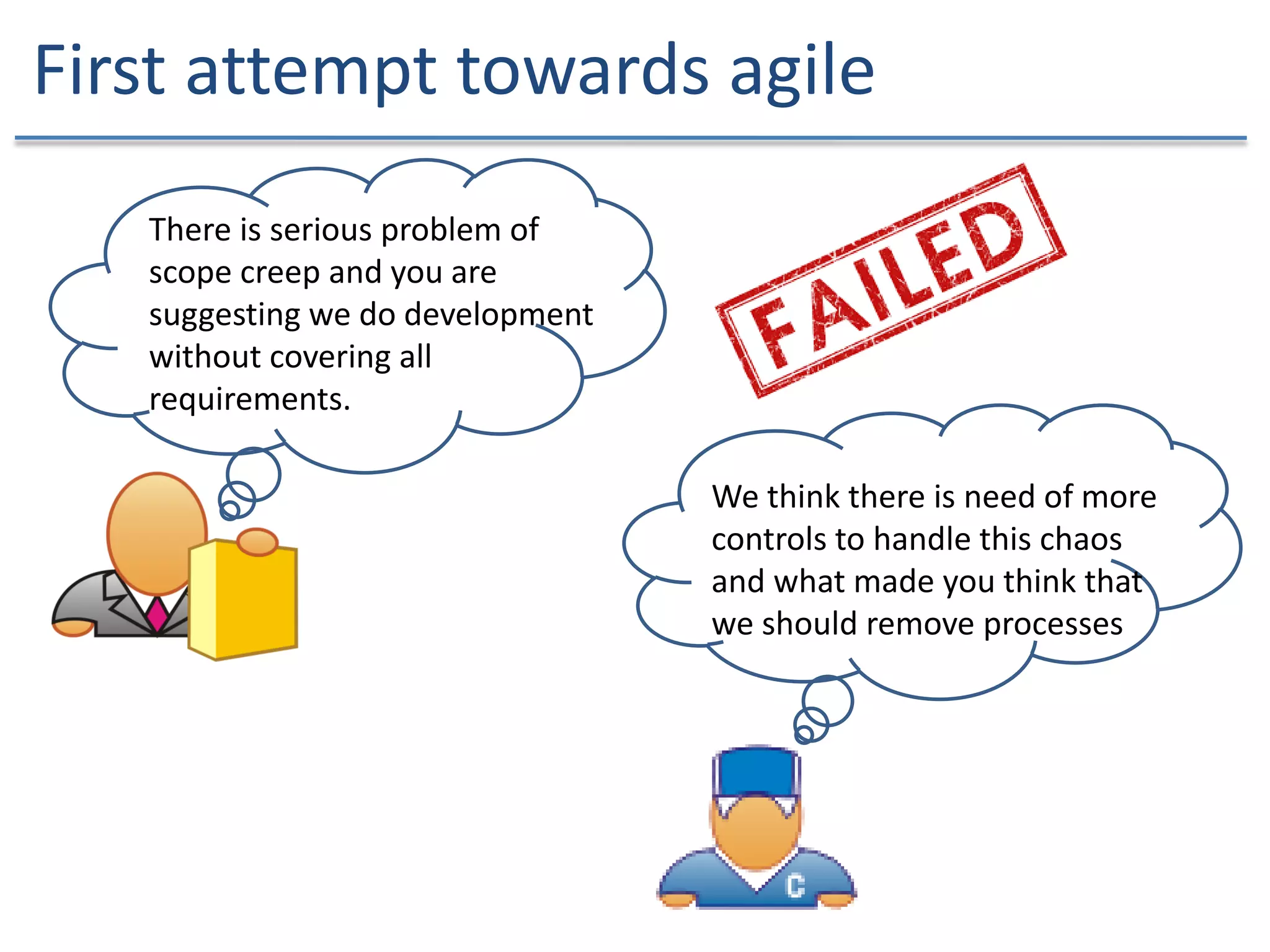
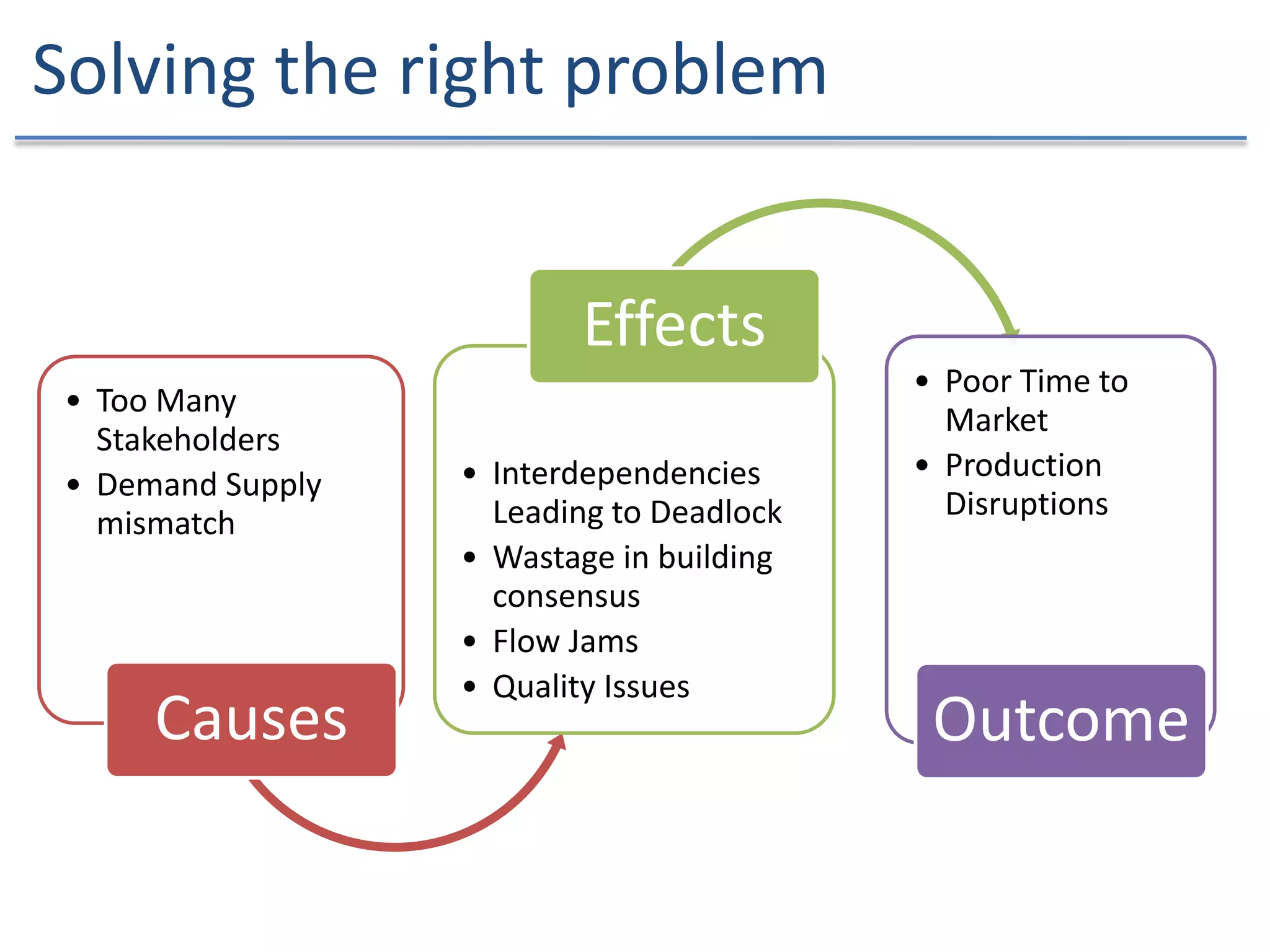
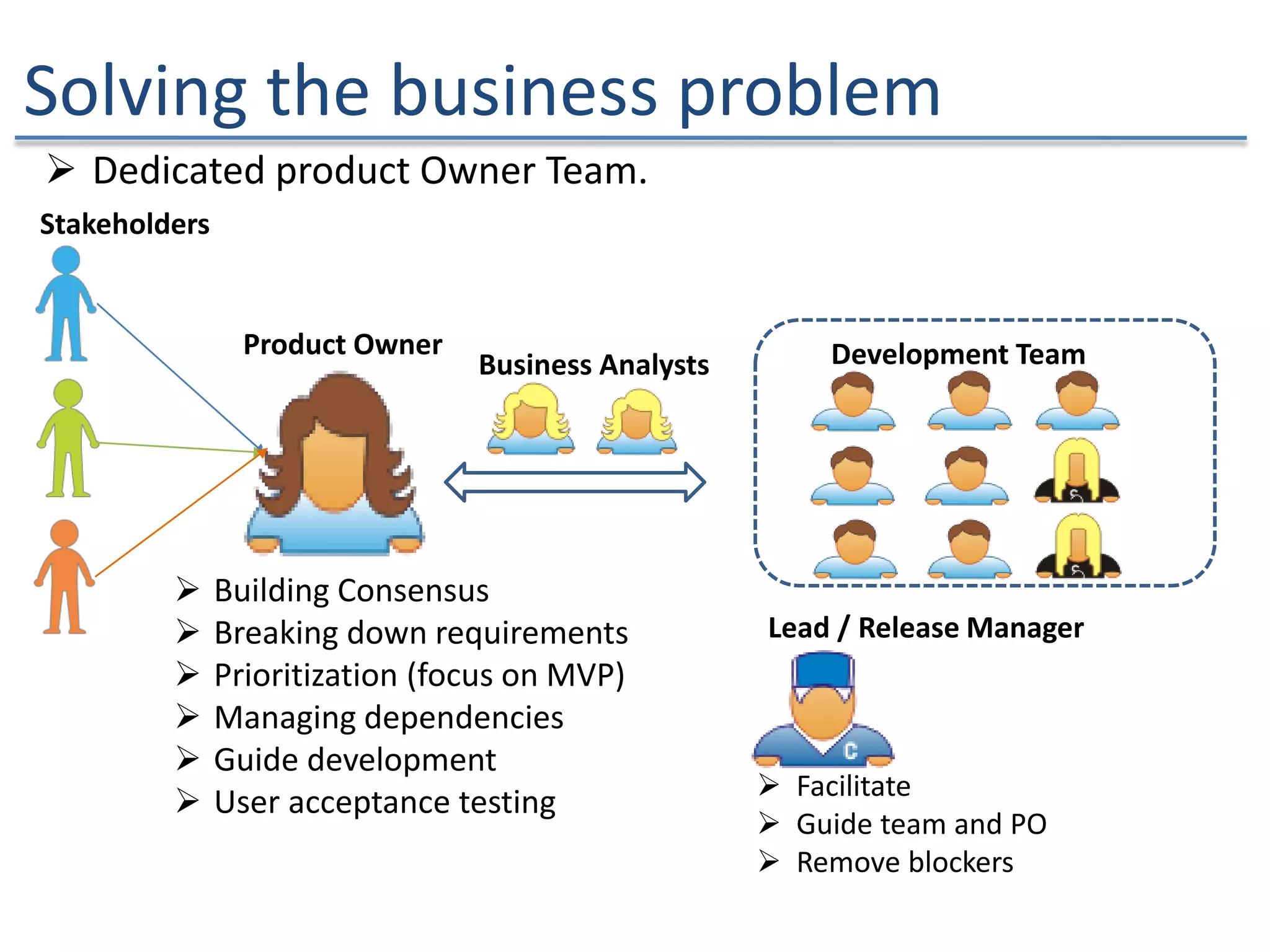
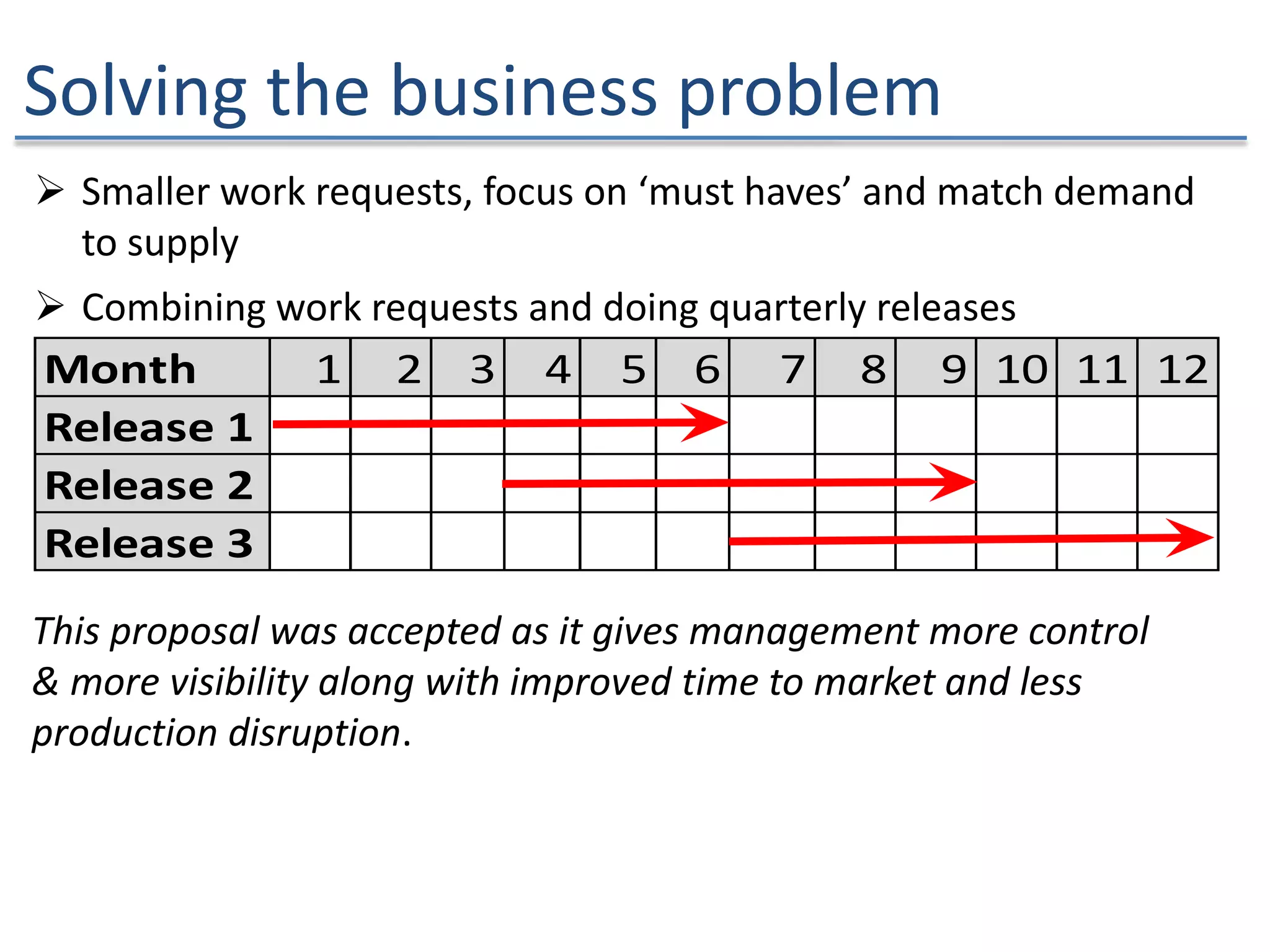
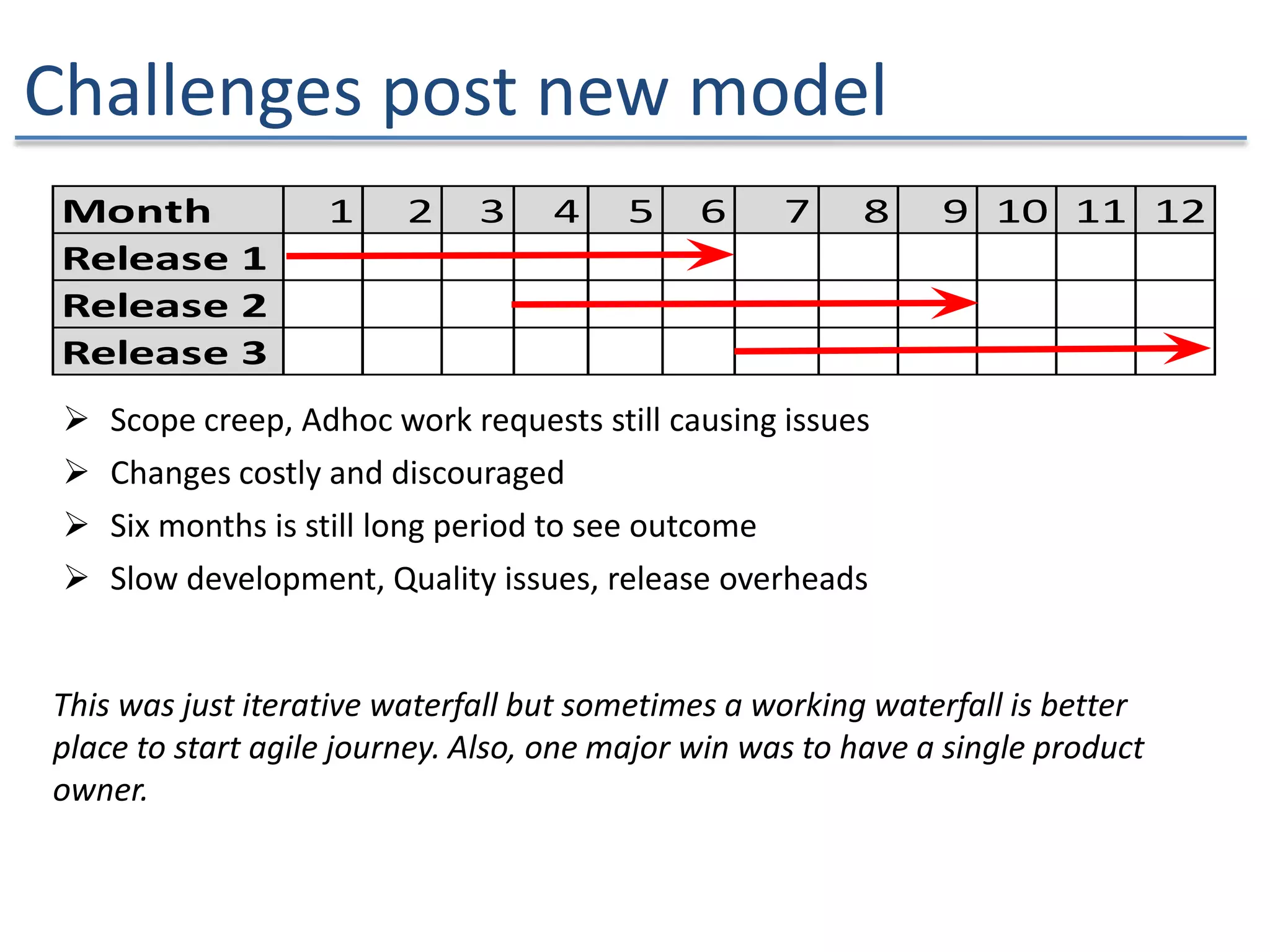
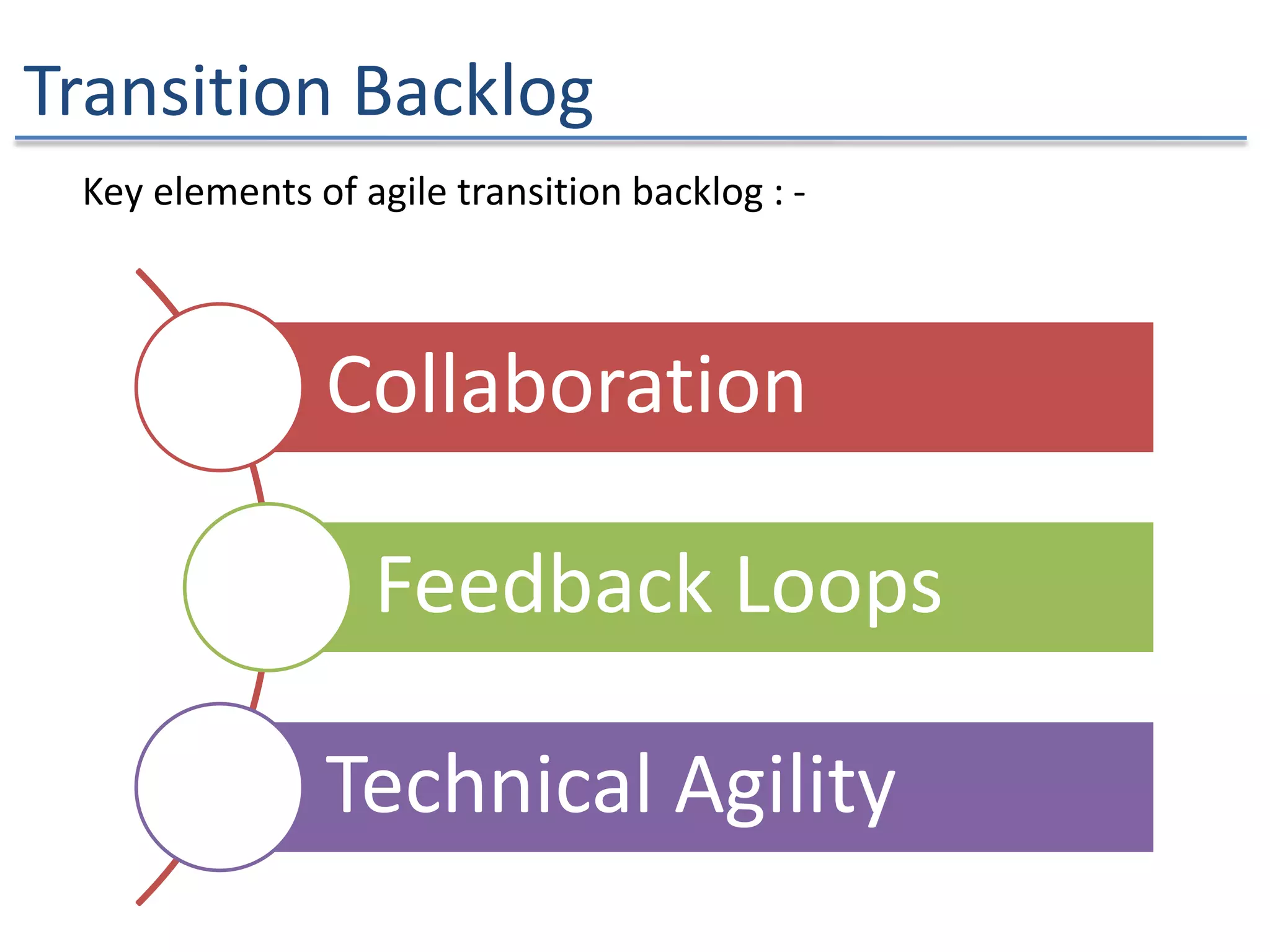
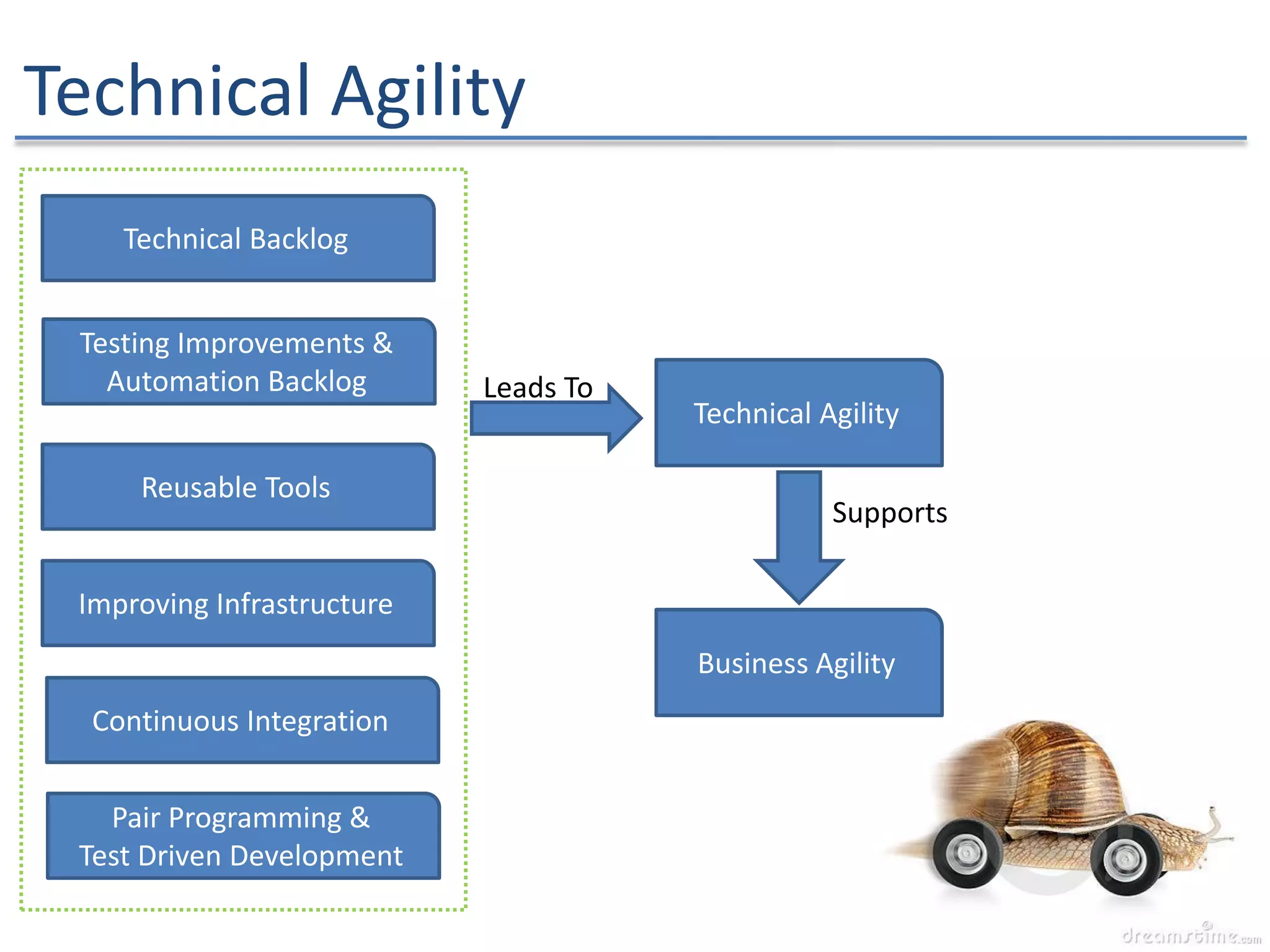
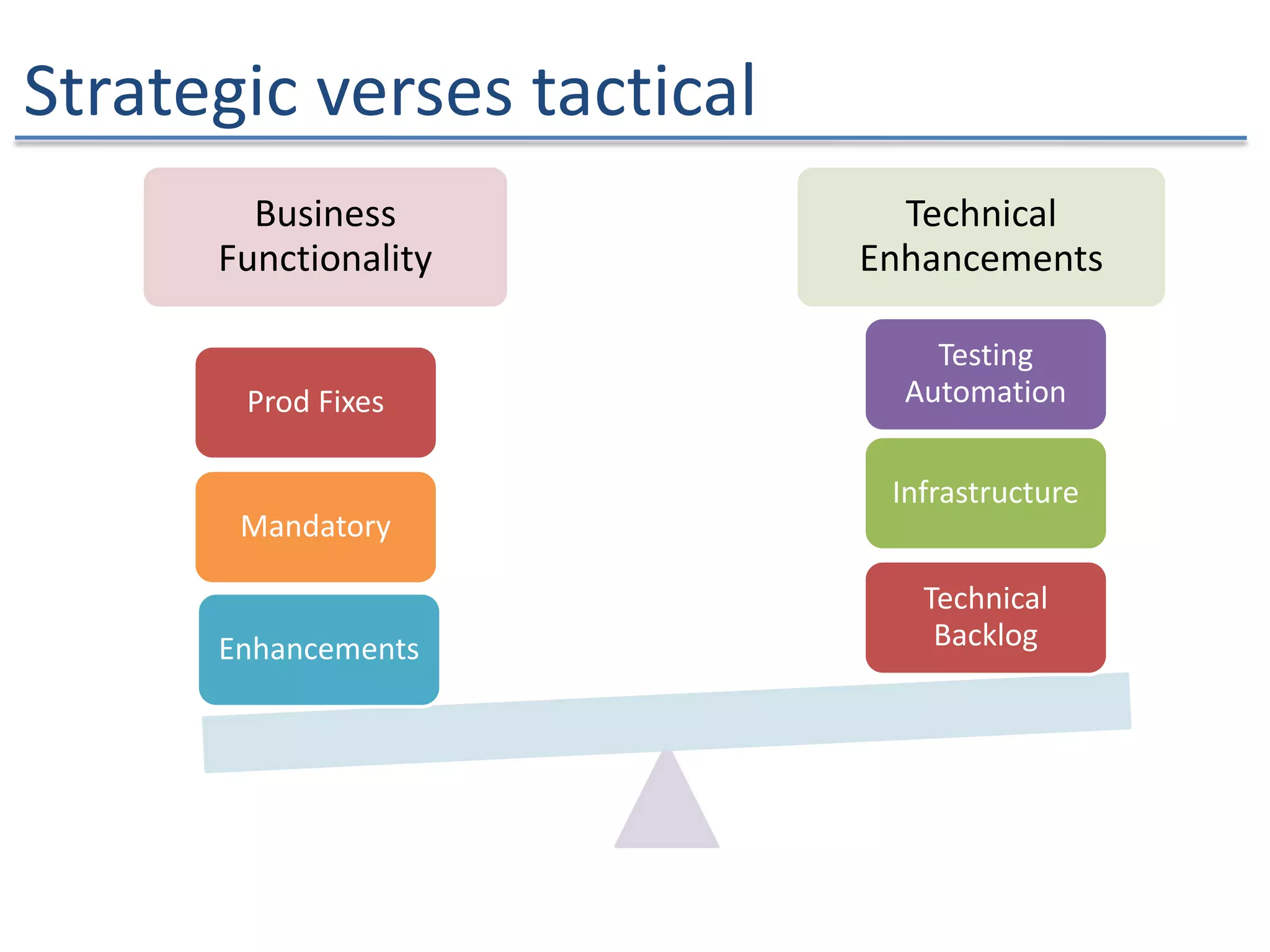
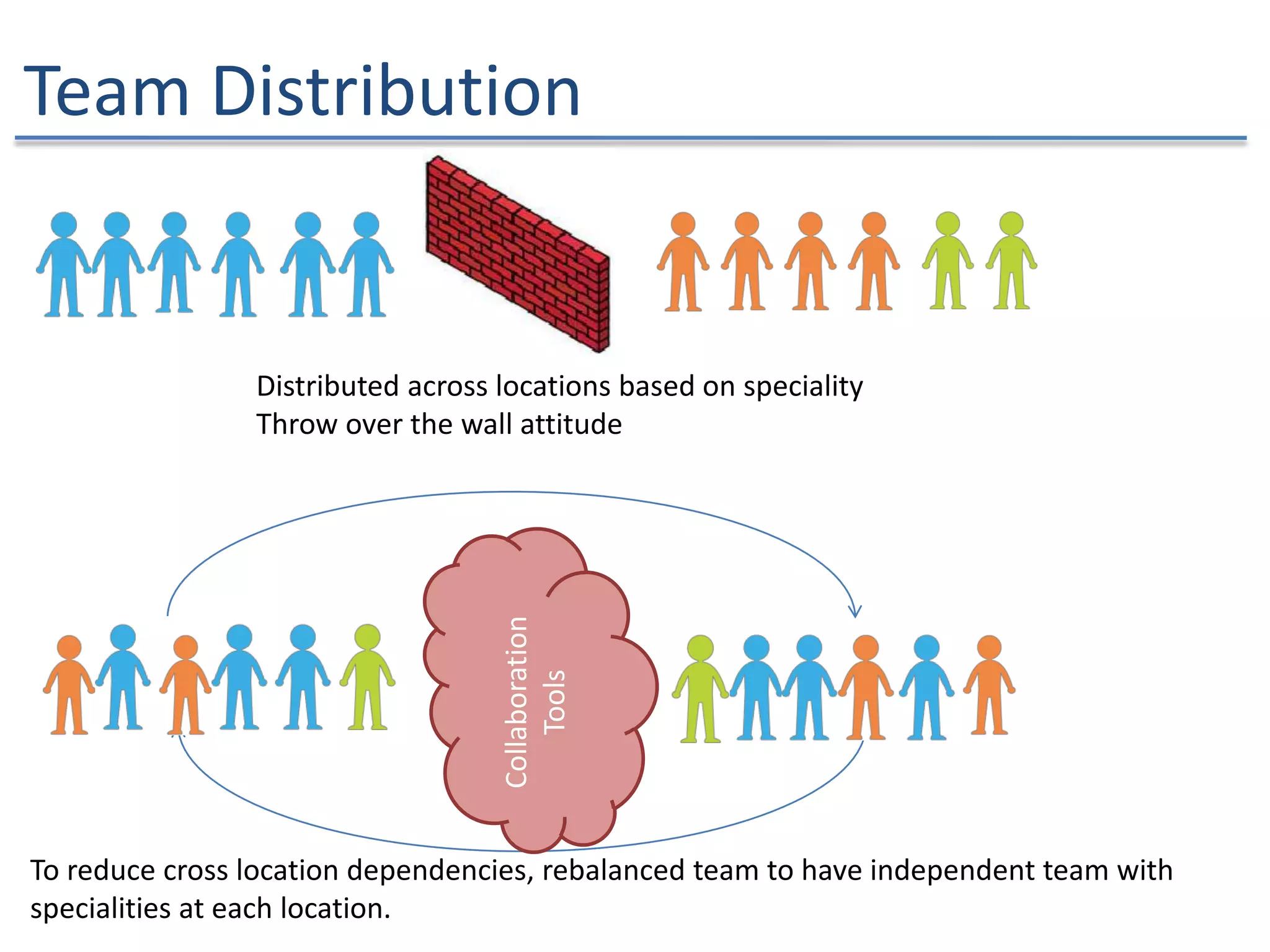
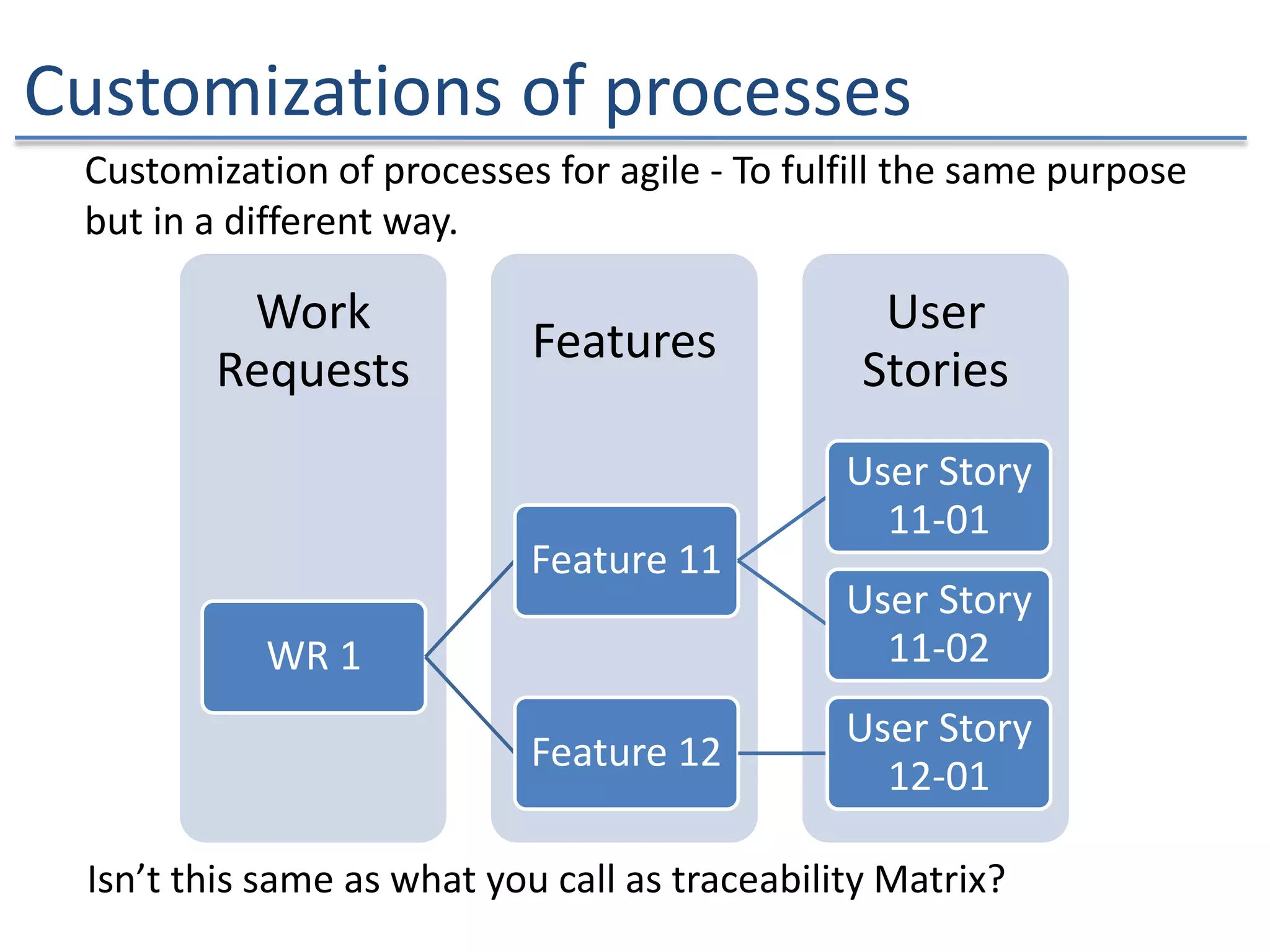
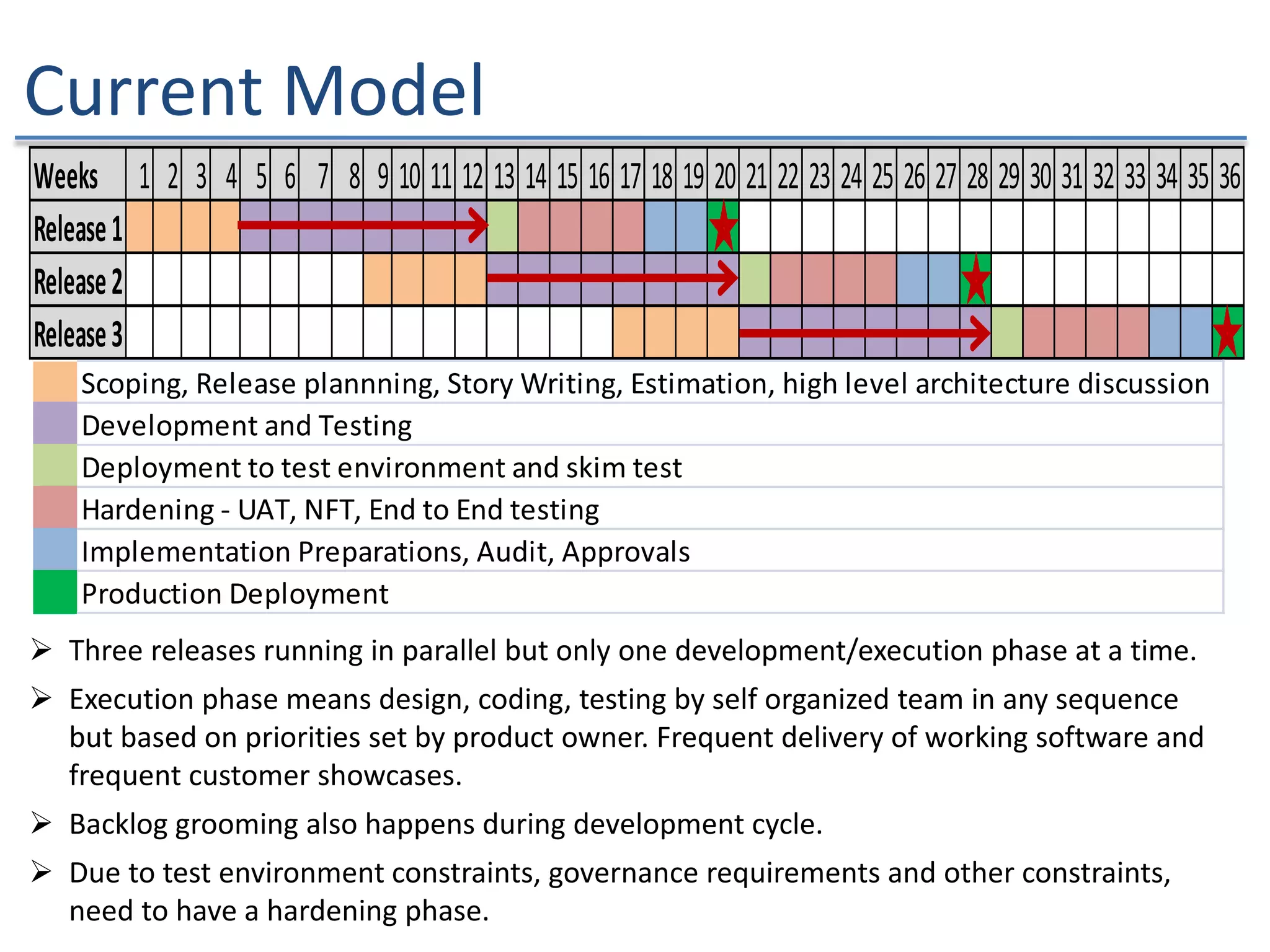
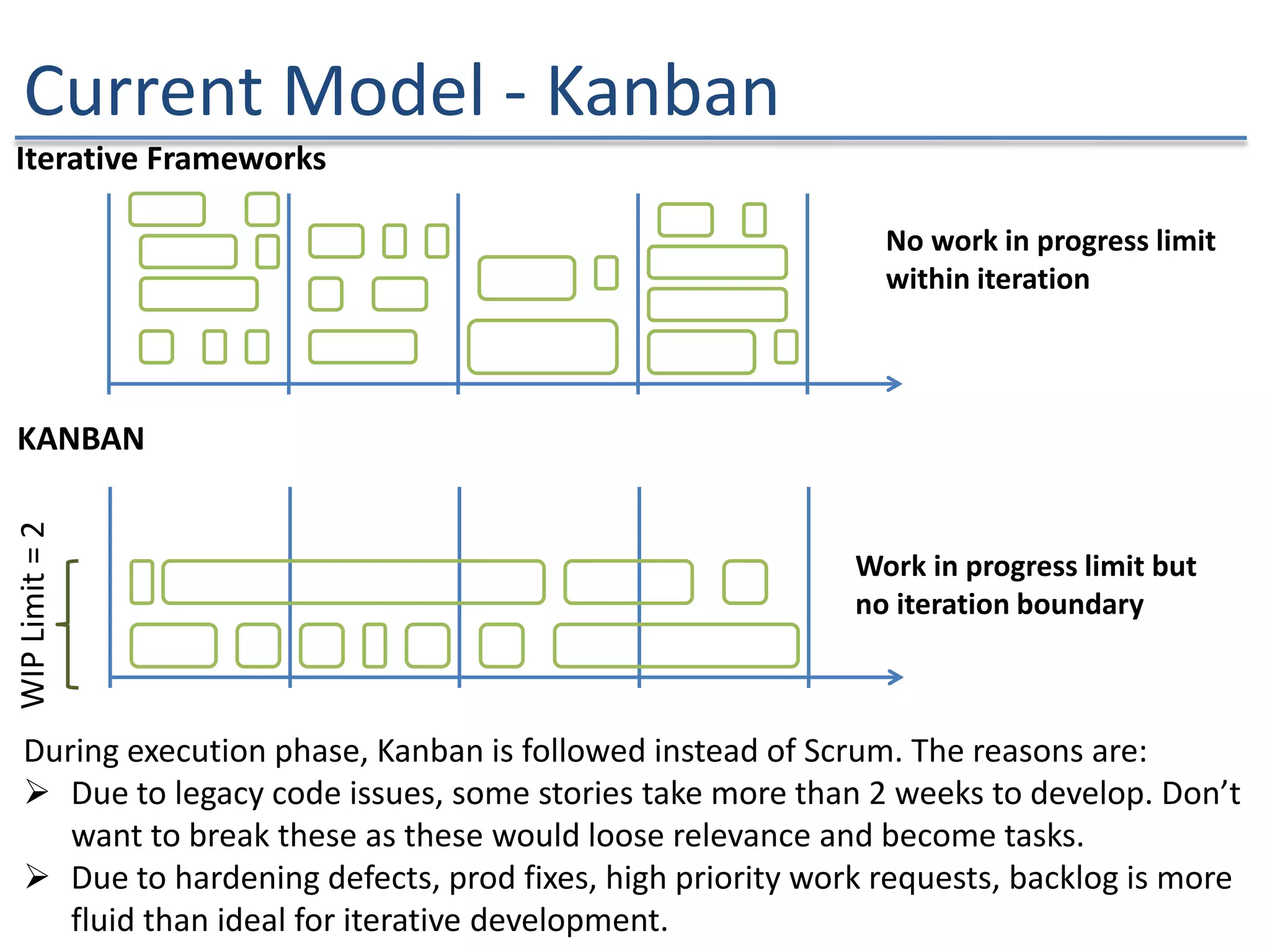
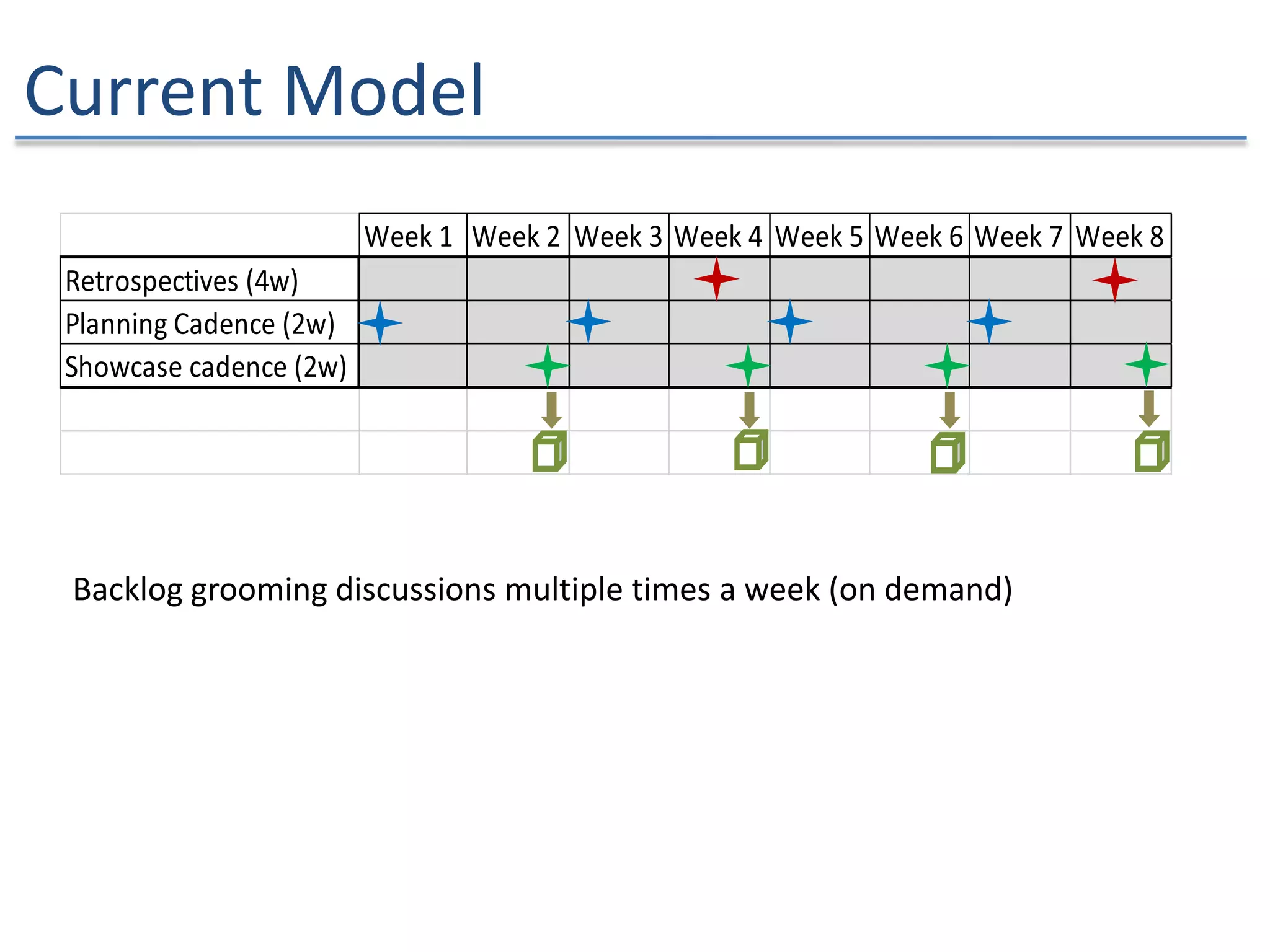
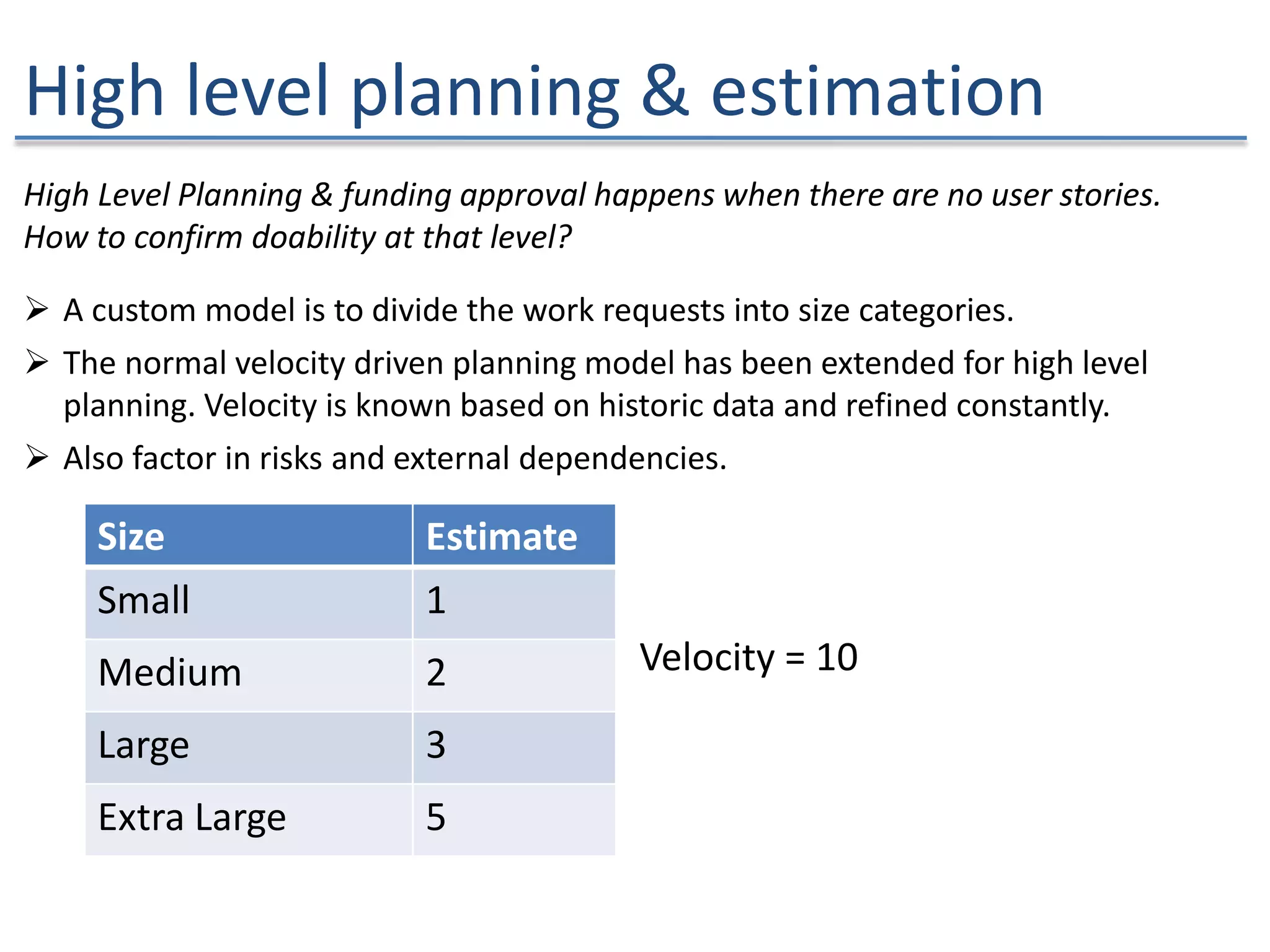
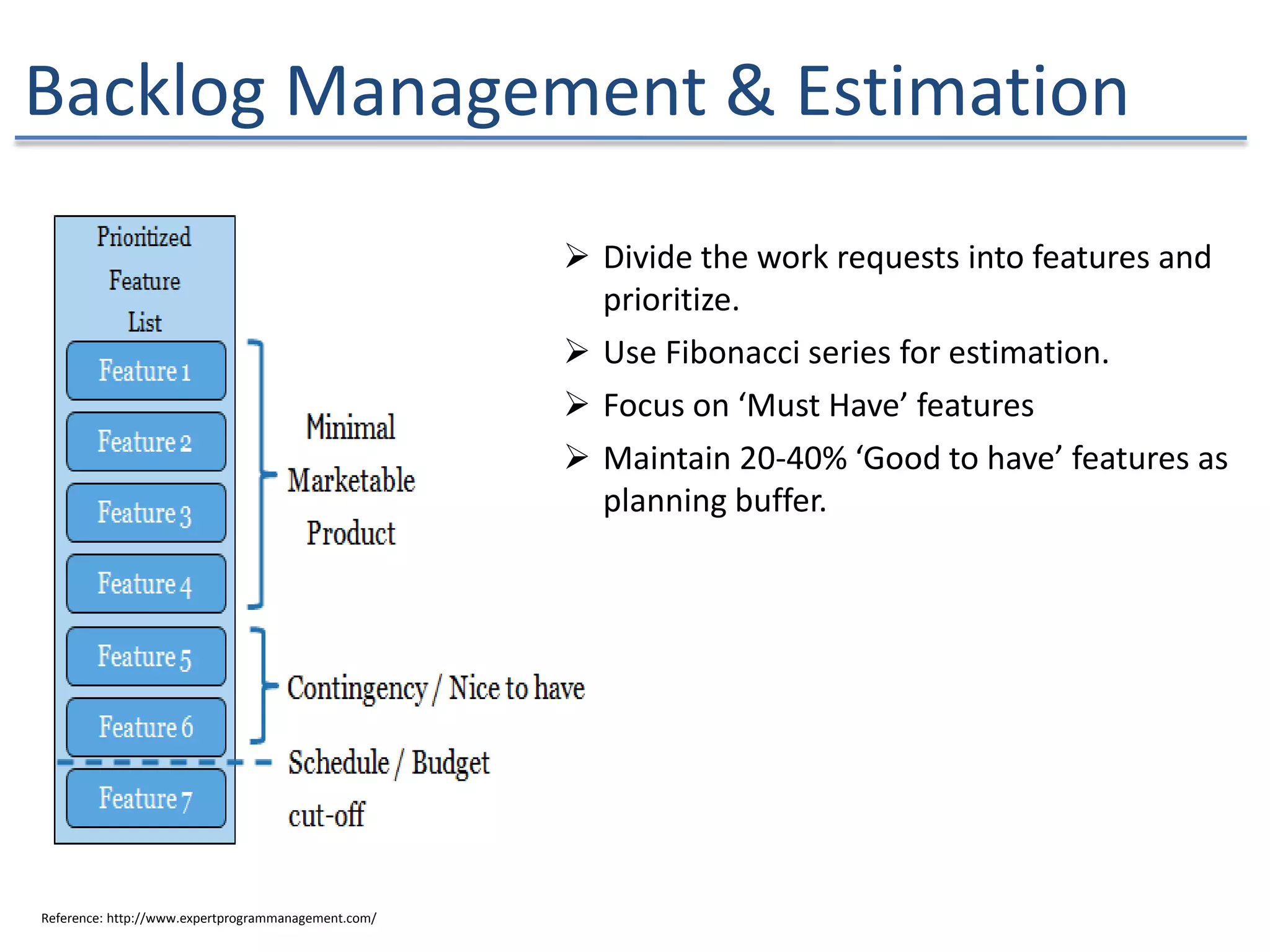
The document discusses the challenges and strategies of implementing Agile methodologies in a non-Agile environment during the Discuss Agile Conference in Delhi, 2015. Key issues include misalignment in hierarchical organizations, lack of technical agility, and ineffective governance processes, which hinder Agile adoption. The presentation emphasizes the importance of focusing on business problems, enhancing collaboration, and continuously improving technical processes for successful Agile transformation.