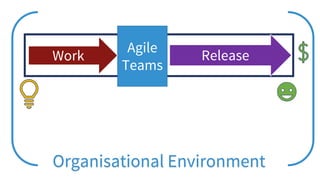
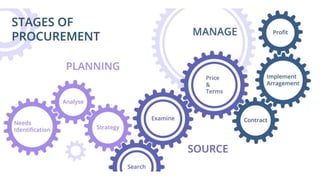
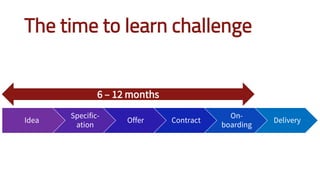
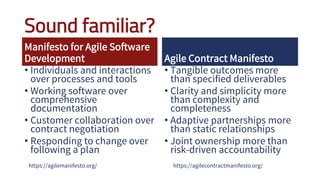
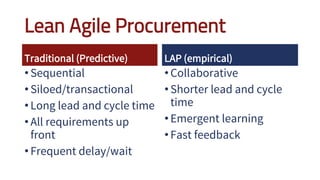
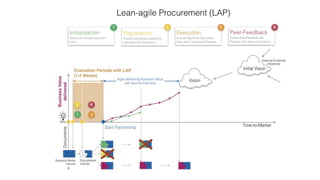
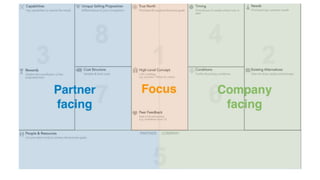
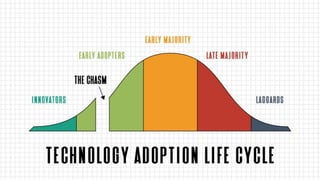
The document discusses adopting agile principles and practices for procurement processes. It proposes that procurement is similar to where software development was around 2000, wanting more effectiveness while managing significant risk. Traditional procurement is sequential and siloed with long lead times, while an agile or "Lean Agile Procurement" approach advocates being collaborative, emergent learning with shorter cycles. The document outlines challenges like misunderstandings, delays and disconnects that a LAP approach aims to address through cultural fit, collaboration, exploration and adaptive partnerships between procurement and suppliers.