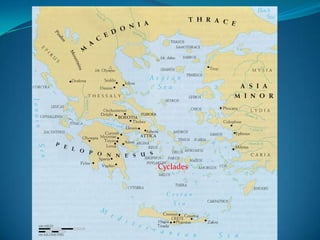
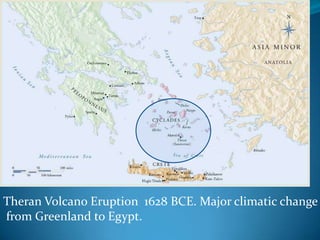
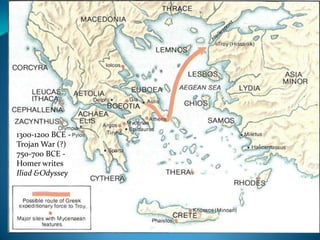
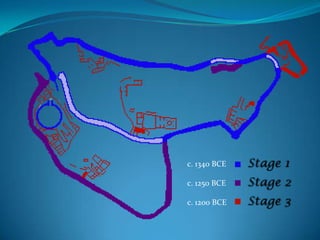
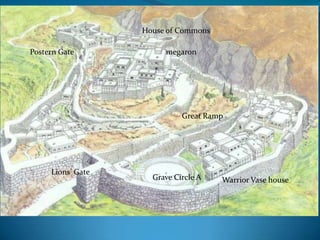
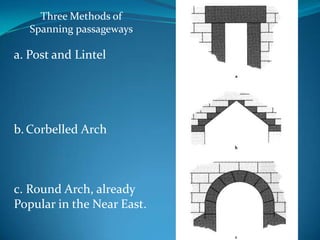
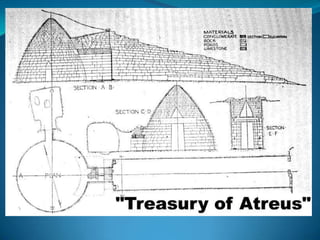
The document summarizes the major civilizations in the Aegean region from around 3000 BCE to 1100 BCE. It describes the Cycladic civilization in the Cyclades islands, notable for female and male marble figurines from around 2700-2300 BCE. It also details the Minoan civilization on Crete from around 3000-1100 BCE, including reconstructions of the Palace of Knossos and artifacts like the Minoan goddess and Toreador fresco. Finally, it outlines the Mycenaean civilization on the Greek mainland from around 3000-1100 BCE, mentioning sites like Mycenae with its cyclopean walls, Lion Gate, and Treasury of Atreus tomb entrance.