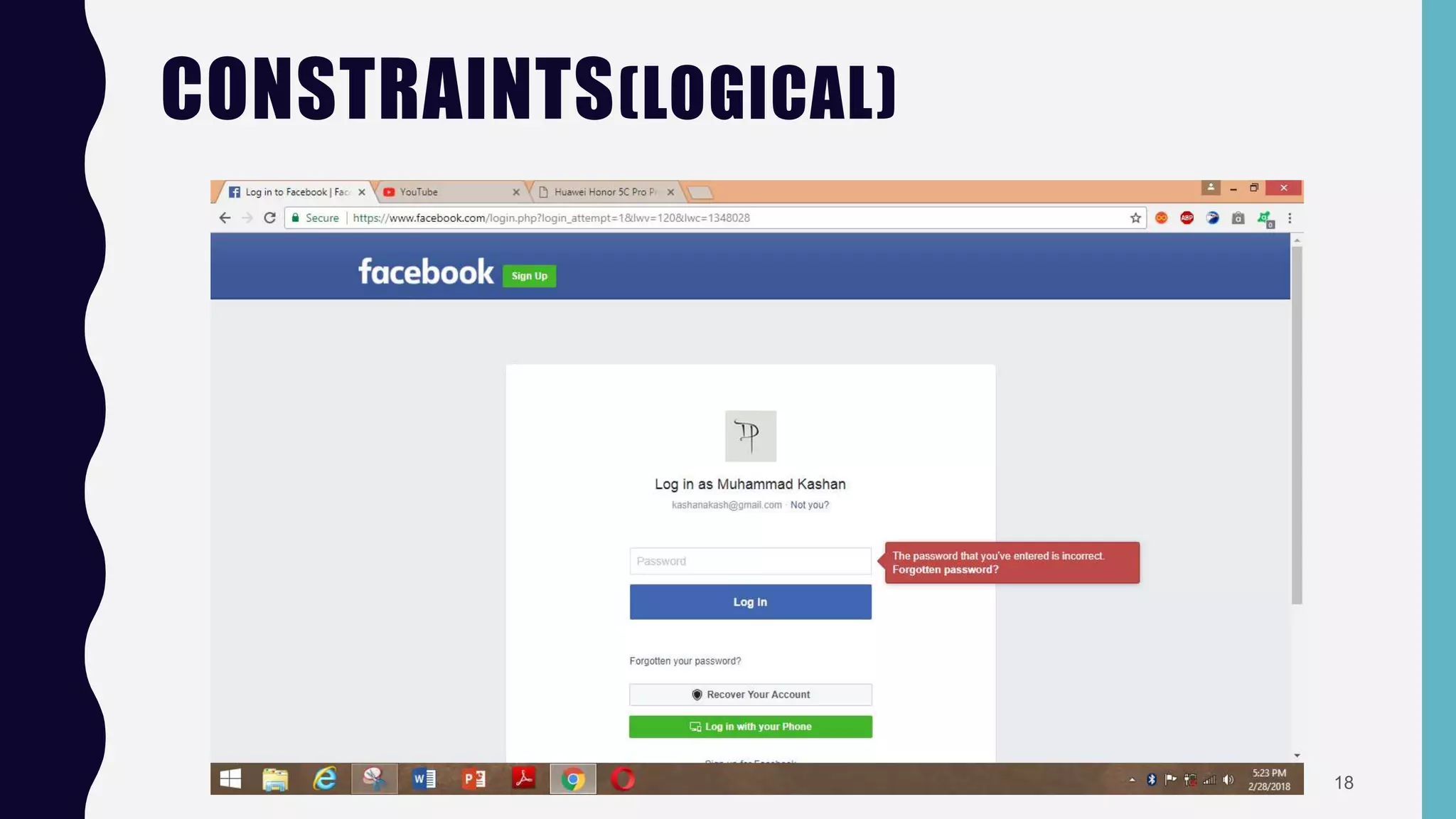
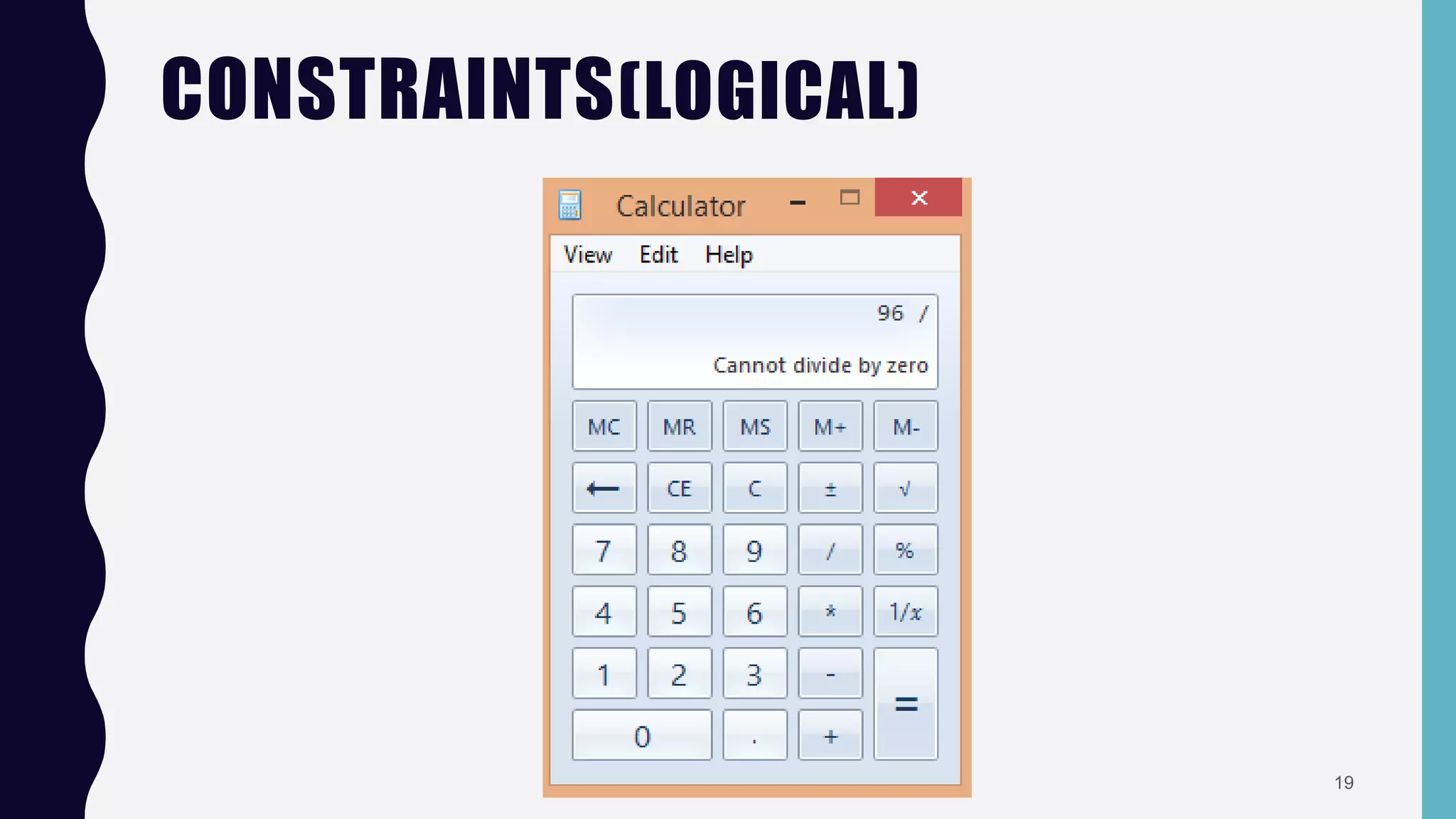
The document discusses key concepts in human-computer interaction (HCI), including affordances, mapping, causality, constraints, and conventions. It explains the difference between perceived and real affordance, emphasizes the importance of mapping controls to their functions, and highlights various types of constraints necessary for effective application design. The conclusion reiterates that all steps in these processes are essential for successful application development.