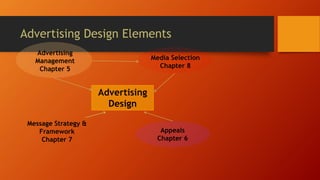
The document discusses advertising management and its essential components, including the selection of advertising agencies, campaign management, and the role of advertising in integrated marketing communications (IMC). It outlines the objectives of advertising, such as trial, continuity, brand switch, and switching back, as well as the process of creating effective advertising campaigns. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding the target audience and conducting research to inform advertising strategies.