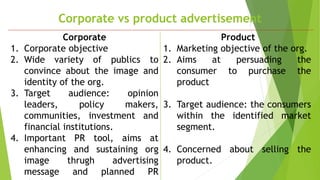
The document discusses advertising, including definitions from various organizations. It describes the key characteristics of advertising as non-personal communication that is paid for and controlled by the advertiser. It also outlines the 6 M's of advertising: mission, money, message, monitoring, media, and measurement. The objectives and types of advertising are explained. The differences between corporate and product advertising are highlighted. Finally, the document analyzes newspapers, radio, and television as advertising media.